الفرق بين مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد 1
الفرق بين مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد: دليل سهل الفهم
هناك فرق كبير بين مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد على الرغم من أن الأسماء قد تبدو متشابهة بالنسبة لك. يوفر هذان النوعان من المولدات نتائج مختلفة تمامًا. كلاهما يوفر تيارات ، لكن التيارات النهائية مختلفة من حيث الطريقة التي تتحرك بها ، وآليتها ، وتصميمها ، واستخدامها. هنا ، سيشرح جهزلي الفرق بين مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد ويجيب على جميع الأسئلة التي قد تخطر ببالك أثناء القراءة عن الاثنين. دعونا أولاً نقدم بإيجاز مولدات التيار المتردد ومولدات التيار المستمر.
ينتج مولد التيار المتردد تيارًا متناوبًا يعكس الاتجاه بانتظام. من ناحية أخرى ، يحتوي مولد التيار المستمر على تيار مباشر أحادي الاتجاه. عادةً ما يكون الملف الذي ينتقل من خلاله التيار في مولد التيار المتردد ثابتًا ، بينما يتحرك المغناطيس. مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد هي منتجات مهمة للأنظمة الكهربائية. يتم توفير مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد من قبل العديد من الموردين والشركات ومصنعين مختلفين والكثير من الموزعين وهناك الكثير من مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد للبيع في غزلي.
توجد قائمة كاملة بخدمات مولدات التيار المتردد والتيار المستمر على موقع جهزلي الإلكتروني والتي تغطي جميع المتطلبات الكهربائية. يمكن لبائعي جهزلي مساعدتك في ذلك. يرجى الاتصال بخبراء مولدات التيار المتردد والتيار المتردد في جهزلي لمعرفة المزيد حول كيفية الاتصال بمجموعة متنوعة من مزودي الخدمة الذين يقدمون باستمرار عناصر عالية الجودة.
ما هو مولد التيار المتردد؟
يعتبر مولد التيار المتردد مولدًا كهربائيًا لتحويل الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى طاقة كهربائية. هذه الطاقة في شكل تيار متردد أو بديل EMF. إنهم يعملون وفقًا لمبادئ الحث الكهرومغناطيسي التي تنص على أن القوة الدافعة الكهربائية (EMF) تتولد في موصل يحمل تيارًا يقطع مجالًا مغناطيسيًا موحدًا. يمكن تحقيق ذلك إما عن طريق تدوير ملف موصل في مجال مغناطيسي ثابت ، أو عن طريق تدوير المجال المغناطيسي الذي يحتوي على الموصل الثابت. الترتيب المفضل هو إبقاء الملف ثابتًا لأنه من الأسهل سحب التيار المتردد المستحث من ملف المحرك الثابت بدلاً من الملف الدوار.
ما هو مولد التيار المستمر؟
تقوم مولدات التيار المستمر بتحويل الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى كهرباء تيار مستمر وهي اختصار للتيار المباشر. تعمل مولدات التيار المستمر وفقًا لمبادئ القوة الدافعة الكهربائية المستحثة بنشاط.
الآن ، دعنا نتعمق في الفرق بين مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد ونتعرف على كيفية استخدامها. بعد ذلك ، ستتمكن من تحديد أيهما يناسب احتياجاتك:
 مولد التيار المتردد مقابل مولد التيار المستمر
مولد التيار المتردد مقابل مولد التيار المستمر
- التصميم والآلية
- الاستخدام والصيانة
- الاتصال
AC مقابل DC: التصميم والآلية
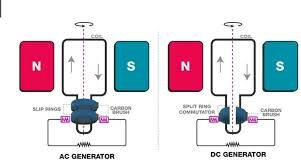
إن Diff BW AC و DC Generator من حيث التصميم هو أن تيار مولدات التيار المتردد يتحرك عبر الملف الثابت. يظل تدفق التيار في الاتجاه المعاكس بمساعدة مغناطيس متحرك. أثناء وجوده في مولدات التيار المستمر ، يتحرك الملف في مجال ثابت ويتدفق التيار بهذه الحركة ، لذلك لا توجد ملفات ثابتة لمولدات التيار المستمر.
أحد أوجه التشابه بين مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد هو أن كلاهما لهما حلقات انزلاقية (مصنوعة من المعدن) وأيضًا ملف حديد التسليح. يتصل المحرك بالدائرة الخارجية بمساعدة اتصال يؤثر بشكل مباشر على نوع التيار الناتج.
يحتوي مولد التيار المتردد على حلقتين معدنيتين تدوران مع ملف المحرك في وقت واحد. يتم توصيل طرفي المحرك بحلقة انزلاقية منفصلة بفرشاة كربون لتمكين هذه العملية. لكن مولدات التيار المتردد تحتوي على فرشاة ثابتة. الفرش هي العناصر التي تستقبل التيار المتدفق عبر حلقات الانزلاق. ومع ذلك ، فإن كلا من نهاية الدائرة الخارجية ونهاية المحرك متصلان بفرشاة واحدة.
هناك اختلاف آخر بين مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد في هذا الصدد وهو أنه بينما تحتوي مولدات التيار المتردد على حلقتين انزلاقيتين ، فإن مولدات التيار المستمر لها حلقة واحدة فقط. الحلقتان المعدنيتان شبه الدائرتان في المبدل معزولان عن بعضهما البعض. نهايات المحرك في مولد التيار المستمر متصلة بنصف المبدل. ثم ينتج عن كل دوران نصف دورة اتجاه عكسي للتيار في المحرك.
الدوران 180 درجة بين الأقطاب المغناطيسية بواسطة المحرك يأخذ التيار من أعلى نقطة له إلى الصفر. لا تحتوي الحلقات الموجودة في مولد التيار المتردد على مفاتيح تبديل بينما تحتوي مولدات التيار المستمر على مبدلات حلقة منفصلة. بالإضافة إلى ذلك ، فإن السطح الأملس وغير المنقطع لحلقات الانزلاق AC ذو كفاءة عالية ولا يتآكل بسرعة في حين أن كلا الفرشاة لمولد التيار المستمر أقل كفاءة من مولد التيار المتردد لأنها تبلى بسرعة. تقلل كفاءة الفرش في مولد التيار المتردد من إمكانية حدوث ماس كهربائي ولكن الاحتمال مرتفع في مولدات التيار المستمر.
على الرغم من أن كل من مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد لها نهج مختلف تجاه جمع ونقل القوى الدافعة الكهربائية المستحثة في الدائرة الخارجية ، إلا أنهما يستخدمان المبادئ الكهرومغناطيسية للوصول إلى النتيجة المرجوة. لذلك هناك فرق آخر بين مولد التيار المتردد ومولد التيار المستمر. يرجع هذا الاختلاف إلى الاتصال بين المحرك والدائرة الخارجية في هذين النوعين من المولدات.
كيف يتم توليد التيار المتردد والتيار المستمر؟
يمكن إنتاج التيار المستمر بعدة طرق: يمكن توليد التيار المباشر بواسطة مولد التيار المتردد بجهاز يعرف باسم “المبدل”. استخدام “المعدل” ، وهو جهاز يحول التيار المتردد إلى التيار المستمر. تنتج البطاريات التيار المستمر نتيجة لعملية كيميائية داخل البطارية.
الفرق بين مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد: الاستخدام والصيانة
يُطلق على جهد الخرج الناتج عن مولدات التيار المتردد اسم المولدات. التردد العادي للمولدات هو 60 هرتز لأمريكا وأوروبا واليابان. يختلف جهد الخرج هذا في الوقت والسعة. تنتج مولدات التيار المستمر جهد خرج ثابت ، ومناسب لتشغيل المحركات الكبيرة. بينما تستخدم مولدات التيار المستمر بشكل أساسي لتزويد الطاقة للمحركات الكبيرة ، يتم استخدام مولدات التيار المتردد للمولدات الأصغر. يمكنك تشغيل أجهزتك الكهربائية في المنزل بمساعدة مكيفات الهواء مثل خلاطات الطعام والتركيبات الكهربائية وما إلى ذلك.
إن Diff BW AC و DC Generator من حيث الصيانة ضخمان. تتطلب مولدات التيار المستمر صيانة مستمرة وهي أقل موثوقية بينما تحتاج مولدات التيار المتردد إلى القليل من الصيانة وتكون أكثر موثوقية.
مولد التيار المتردد مقابل التيار المستمر: التوصيل
الفرق الآخر بين مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد هو الاتصال بينهما. تتميز مولدات التيار المستمر بتصميم يوفر اتصالاً سلسًا مع تدفق طاقة فعال. هذا في الغالب لأنهم لا يحتاجون إلى أي مفتاح تحويل. ومع ذلك ، في حالة مولدات التيار المتردد ، فإنها تتطلب جهدًا أكبر بكثير لنقل الكهرباء إلى أقسام بعيدة من الشبكة ، مما يجعلها أقل كفاءة عندما يتعلق الأمر بالاتصال.
أنواع مختلفة من مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد
مولدات التيار المتردد
- مولد أحادي الطور
- مولد متزامن
- مولد ثلاث مراحل
- مولد التعريفي
مولدات التيار المستمر
- مولد التيار المستمر ذاتي الإثارة ، مولد
الجرح ، مولد
تحويلة الجرح ، مولد
الجرح المركب
- مولد DC متحمس بشكل منفصل
مولدات التيار المستمر والتيار المتردد لها أنواع مختلفة لاستخدامات واحتياجات مختلفة. بعض منها على النحو التالي:
مولدات التيار المتردد لها أنواع مختلفة مثل المولدات أحادية الطور ، والمولدات المتزامنة ، والمولدات ثلاثية الطور ، والمولد التعريفي ، وما إلى ذلك.
- المولدات أحادية الطور : المولد أحادي الطور (المعروف أيضًا باسم المولد أحادي الطور) هو مولد كهربائي بتيار متناوب ينتج جهدًا واحدًا متناوبًا بشكل مستمر. يمكن استخدام المولدات أحادية الطور لتوليد الطاقة في أنظمة الطاقة الكهربائية أحادية الطور.
- المولدات المتزامنة : المولد المتزامن أو المولد هو آلة كهربائية تحول الطاقة الميكانيكية من المحرك الرئيسي إلى طاقة كهربائية متناوبة بجهد وتردد معينين. يعمل المحرك المتزامن دائمًا بسرعة ثابتة تسمى السرعة المتزامنة.
- المولدات ثلاثية الطور : تعمل المولدات ثلاثية الطور من خلال إنتاج ثلاث موجات منفصلة من طاقة التيار المتردد تعمل في تسلسل ، مما يضمن وجود تدفق مستمر للطاقة وأن مستوى الطاقة لا ينخفض أبدًا كما هو الحال مع المولدات أحادية الطور.
- مولدات الحث : يُعرف المولد التعريفي أيضًا باسم المولد غير المتزامن الذي له مبدأ عمل مشابه لمولد التيار المتردد. الفرق الوحيد بين مولد التيار المتردد العادي والمولد التعريفي هو أن المولد التعريفي هو جهاز دوار. يُعرف باسم غير متزامن لأن سرعة المولد التعريفي أقل من سرعة المولد المتزامن. وجدوا تطبيقات في الخلاطات والمطاحن.
تحتوي مولدات التيار المستمر بشكل أساسي على نوعين: مولد تيار مستمر ذاتي الإثارة ومولد تيار مستمر متحمس بشكل منفصل. اتصال المحرك الخاص بهم هو نفسه ولهذا السبب تم تصنيفهم على أنهم مولدات التيار المستمر.
- الإثارة الذاتية : في نوع الإثارة الذاتية ، يتم تنشيط ملفات المجال من التيار المتولد داخل المولد. يمكن تصنيف هذه الأنواع من المولدات أيضًا إلى مولدات الجرح المتسلسلة ، ومولدات الجروح التحويلية ، ومولدات الجروح
المركبة
. من سلسلة ولف التحويلة - متحمس بشكل منفصل: في مولد نوع متحمس منفصل ، يتم تنشيط ملفات المجال من مصدر خارجي مستقل للتيار المستمر.
أيهما أفضل: مولد التيار المتردد أم مولد التيار المستمر؟
يعتمد العثور على أفضل واحد بين مولد التيار المتردد ومولد التيار المستمر إلى حد كبير على الطريقة التي تريد استخدامها والنتيجة المرجوة. لكل منها العديد من المزايا التي تمكنك من تحقيق أقصى استفادة منها ، مثل:
مزايا مولدات التيار المستمر
- الجهد السلس
- ملاءمة المحركات الكبيرة
- تصميم بسيط
مزايا مولدات التيار المتردد
- ملاءمة الأجهزة الكهربائية والمحركات الصغيرة
- احتياجات صيانة منخفضة
- سهولة توزيع المخرجات باستخدام المحول
- كفاءة
- الخسائر أقل نسبيًا من مولدات التيار المستمر
- قد يكون حجم ارتباط الإرسال أرق بسبب ميزة التصعيد
- يمكن تصعيد مولدات التيار المتردد وتنحيها بسهولة من خلال المحولات.
- حجم مولدات التيار المتردد أصغر نسبيًا من مولدات التيار المستمر.
من الجيد أيضًا معرفة أن مولدات التيار المستمر تكون ميسورة التكلفة مقارنة بمولدات التيار المتردد. تكلف مولدات التيار المتردد أكثر قليلاً.
لذا ، الآن أنت تعرف كل ما تحتاج لمعرفته حول الفرق بين هذين! هل تعتقد أن الفرق بين مولد التيار المتردد والتيار المستمر يؤثر على جوانب أخرى من حياتك أو الصناعة بخلاف ما ذكرناه أعلاه؟ شاركنا أفكارك في قسم التعليقات. ولا تتردد في التسجيل على موقعنا على الإنترنت إذا كنت تريد من خبرائنا الإجابة على أسئلتك الأكثر تعقيدًا فيما يتعلق بهذا المجال.
ما هو مبدأ العمل لمولد التيار المستمر؟
المولدات هي آلات كهربائية تبدأ عملها عندما تنقطع الطاقة الكهربائية من الشبكة المحلية. هنا حيث تبدأ المولدات بالعمل لتوفير الكهرباء. تعمل هذه الآلات الكهربائية كمصدر لتزويد الطاقة الكهربائية للعديد من المنشآت التجارية والمباني الصناعية وحتى المنازل عند انقطاع التيار الكهربائي. يتم تصنيف المولدات إلى نوعين من مولدات التيار المتردد والتيار المستمر. نحن هنا لشرح السؤال “ما هو مبدأ عمل مولد التيار المستمر؟” ومناقشة البلدان النامية بالتفصيل. لقد جمع جهزلي معظم المعلومات الدقيقة والأكثر دقة حول هذا الموضوع لتقرأها.
قبل أن نناقش الموضوع الرئيسي لهذه المقالة ، يجب أن نعرف الهيكل والوظائف الرئيسية لمراكز البيانات DC. دعونا نلقي نظرة سريعة على إنشاءات مولدات التيار المستمر ووظائفها وأجزائها ومكوناتها.
على منصة جهزلي ، ستجد جميع المعلومات التي تحتاجها فيما يتعلق بمعدات وأجهزة مولد التيار المستمر. خبراء جهزلي متاحون للمساعدة في أي أسئلة قد تكون لديكم حول DC Generators. توقف لحظة لقراءة ” ما هو مولد التيار المباشر؟ “.
ما هو مولد التيار المستمر؟
كما ذكرنا سابقًا ، هناك نوعان من المولدات بناءً على المخرجات: مولدات التيار المتردد والتيار المستمر. تتمثل الوظيفة الرئيسية لمولدات التيار المباشر في تحويل الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى كهرباء. هناك الكثير من المصادر التي توفر الطاقة الميكانيكية لمولدات التيار المستمر مثل المحركات ذات الاحتراق الداخلي ، وتوربينات الماء والغاز والبخار ، وحتى الأذرع اليدوية. هناك وظيفة عكسية محددة لمولدات التيار المستمر: يمكن إنجاز هذه الوظيفة العكسية باستخدام محرك كهربائي.
يقوم محرك DC بتغيير الطاقة الكهربائية إلى طاقة ميكانيكية. تنتج مولدات التيار المستمر طاقة كهربائية على أساس مبدأ قانون فاراداي للحث الكهرومغناطيسي. بناءً على هذا القانون ، عندما يتحرك موصل في مجال مغناطيسي ، يتم قطع خطوط القوة المغناطيسية. هذا يؤدي إلى تحريض القوة الكهرومغناطيسية في الموصل.
للحصول على إجابة أوضح على السؤال “ما هو مبدأ عمل مولد التيار المستمر؟” ، دعونا نلقي شرحًا موجزًا عن أجزائه ومكوناته أيضًا. في القسم التالي ، سنخبرك بإيجاز شديد عن الأجزاء الرئيسية لمولد التيار المستمر وكيف تعمل. تابع القراءة.
بناء مولد التيار المستمر
في القسم السابق ، نشرح ما هو مولد التيار المستمر باختصار شديد. الآن نريدك أن تكون أكثر دراية ببنائها. هناك العديد من المكونات في مولد التيار المستمر الفردي والتي تساعد الجهاز بأكمله على العمل بالطريقة التي ينبغي أن يعمل بها. في مقالات مختلفة ، تم ذكر أكثر من عشرة أجزاء لمولدات التيار المستمر.
لن نتوسع في كل هذه المكونات لأن شرح وظيفة هذه الأجزاء خارج نطاق هذه المقالة وسيأخذنا بعيدًا عن الموضوع الرئيسي لمناقشتنا. في الأقسام التالية ، سوف تقرأ عن أربعة من أهم مكونات مولد التيار المستمر التي تساعدك في الحصول على إجابة للسؤال “ما هو مبدأ عمل مولد التيار المستمر؟”
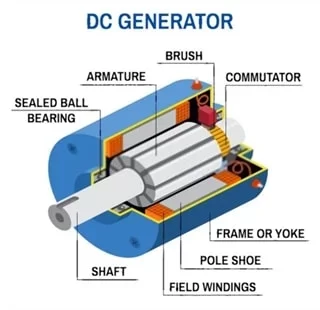
 الجزء الثابت
الجزء الثابت
أحد الأجزاء الأساسية لمولد التيار المستمر هو الجزء الثابت الذي تتمثل مهمته في توفير المجالات المغناطيسية التي تدور حولها الملفات. يتكون الجزء الثابت من مغناطيسين مستقرين مع أقطاب متقابلة تواجه بعضها البعض. يتم وضع هذه المغناطيسات لتناسب منطقة الدوار.
الدوار
يعتبر الدوار أو قلب المحرك جزءًا مهمًا آخر من مولد التيار المستمر. توجد صفائح حديدية مشقوقة في العضو الدوار مع فتحات مكدسة لتشكيل قلب المحرك الأسطواني. بشكل عام ، يتم تقليل الفاقد بسبب تيار الدوامة في هذه التصفيح.
العاكس
إن تشغيل المبدل هو بمثابة مقوم لتحويل جهد التيار المتردد إلى جهد تيار مستمر في تقوية ملف المحرك. يحتوي على قطعة نحاسية وكل قطعة نحاسية بمساعدة صفائح الميكا محمية من بعضها البعض. إنه يجلس على عمود الآلة.
الفرش
بمساعدة الفرش ، يمكن ضمان التوصيل الكهربائي بين المبدل ودائرة الحمل الخارجية.
الآن بعد أن أصبحت على دراية بالجوهر والمكونات الرئيسية لمولد التيار المستمر ، فإنه يشبه قطعة من الكعكة لفهم كيفية عمل مولد التيار المستمر. في القسم التالي ، سنناقش كيفية عمل مولد التيار المستمر بلغة مفهومة. ابقى معنا.
ما هو مبدأ العمل لمولد التيار المستمر؟
في الأقسام السابقة ، ناقشنا ما الذي يحدد مولد التيار المستمر وكيف يعمل. في هذا القسم ، نحن على وشك التحدث عن مبدأ عمل مولدات التيار المستمر.
كما ذكرنا من قبل ، مولد التيار المستمر هو محول طاقة يحول الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى طاقة كهربائية. يحدث هذا التغيير في شكل الطاقة بناءً على مبدأ الحث الكهرومغناطيسي والذي يعني أنه أينما يحدث تغيير في التدفق المغناطيسي المرتبط بموصل أو EMF أو قوة كهرومغناطيسية فيه. يتسبب هذا الحث في تدفق تيار في حالة إغلاق دائرة الموصل.
لذلك ، بناءً على ما قلناه حتى الآن ، فإن المتطلبات الرئيسية لمولد التيار المستمر هي المجال المغناطيسي والموصل. يتحرك الموصل لقطع التدفق المغناطيسي. لذلك ، يمكننا القول أن مولد التيار المستمر يعمل على مبدأ القوة الكهرومغناطيسية المستحثة ديناميكيًا. هذا هو ما يقوله قانون فاراداي للحث الكهرومغناطيسي: عندما يتم وضع موصل يحمل تيارًا داخل مجال مغناطيسي متغير ، يتم إحداث EMF في الموصل. من ناحية أخرى ، واستنادًا إلى قاعدة اليد اليمنى لـ Fleming ، أينما يتغير اتجاه حركة الموصل ، يتغير اتجاه التدفق المستحث أيضًا.
تخيل عضوًا يدور في اتجاه عقارب الساعة وموصلًا على اليسار يتحرك لأعلى. الآن عندما ينجز المحرك نصف دوران ، فإن اتجاه حركة الموصل سينعكس لأسفل. لذلك ، فإن اتجاه التيار في كل عضو في المحرك سوف يتغير. ولكن مع مبدل الحلقة المنقسمة ، تنعكس اتصالات موصلات المحرك عند حدوث الانعكاس الحالي. لذلك ، نحصل على تيار أحادي الاتجاه في المحطات.
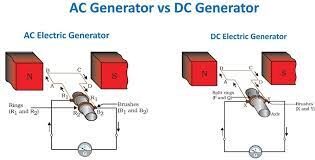
مثال سهل الفهم لمبدأ عمل مولد التيار المستمر
دعنا نجعل وظيفة مولد التيار المستمر ومبدأ العمل أبسط بالنسبة لك. يجب أن تلاحظ ما إذا كان المولد صغيرًا جدًا ، على سبيل المثال يتم استخدامه لمتجر أو ورشة صغيرة أو سينما أو منزل ، أو المحرك الرئيسي أو مورد الطاقة الميكانيكية هو محرك ديزل. إذا كان المولد كبيرًا جدًا كما هو الحال في محطات الطاقة ، فسيكون المحرك الرئيسي عبارة عن توربين مائي أو بخاري أو غازي.
نظرًا لأن الطاقة الميكانيكية التي يوفرها المحرك الرئيسي تُعطى للمولد ، يبدأ عضو الإنتاج في الدوران. عادةً ما تكون الأقطاب الموجودة على النير مصنوعة من مغناطيس دائم. وهذا يعني أنه وفقًا لقوانين فاراداي للحث الكهرومغناطيسي ، تقوم موصلات المحرك بقطع المجال المغناطيسي الضعيف الذي تم إنشاؤه بواسطة مغناطيس دائم ويتم تحفيز كمية صغيرة من EMF في ملف المحرك. تقوم هذه القوة الكهرومغناطيسية المستحثة بتدوير كمية صغيرة من التيار عبر لف المجال وتقوي التدفق المغناطيسي المزود وبالتالي EMF المستحث. وبالتالي ، نظرًا لتقوية التدفق و EMF ، يوفر المولد الجهد المقنن.
ما هي تطبيقات مولدات التيار المستمر؟
تُستخدم مولدات التيار المستمر المحمولة عند الحاجة إلى مصدر طاقة منخفض. إلى جانب استخدامها كدينامو للدراجات النارية ، يمكن أيضًا العثور عليها في الألعاب ، مثل سيارات التحكم عن بعد ، والأجهزة المنزلية ، مثل ماكينات الحلاقة الكهربائية. بالنسبة للحام القوسي ، الذي يتطلب قطرات جهد هائلة وتيارًا ثابتًا ، يتم استخدام مولدات من هذا النوع.
ما هي أنواع مولدات التيار المستمر؟
فيما يلي الأنواع الثلاثة الرئيسية لمولدات التيار المستمر القائمة على طرق الإثارة:
- مولدات DC ذات المغناطيس الدائم حيث يتم إثارة ملفات المجال بواسطة المغناطيس الدائم.
- مولدات التيار المستمر المتحمسة بشكل منفصل والتي تحتوي على ملفات ميدانية يتم تحفيزها بواسطة مصدر خارجي.
ما هي مزايا مولدات التيار المستمر؟
تتميز معظم مولدات التيار المستمر بأنها موثوقة للغاية ، حيث يتم تصنيفها بكفاءة بنسبة 85-95٪. فهي مدمجة وخفيفة الوزن. تنتج مولدات التيار المستمر ناتجًا ثابتًا ومتسقًا. يمكن أيضًا تعديلها لتوفير مخرجات مختلفة.
استنتاج
ما هو مبدأ عمل مولد التيار المباشر كان الموضوع الرئيسي لهذه المقالة التي حاولنا الإجابة عليها. للإجابة على هذا السؤال ، أولاً ، قررنا الحصول على شرح قصير جدًا ولكنه مفيد لما هو مولد التيار المستمر . كانت الخطوة التالية هي التعرف على المكونات الرئيسية لمحول الطاقة هذا. لذلك ، قمنا بالتفصيل في 4 من أهم أجزاء مولد التيار المستمر وكيفية عملها.
أخيرًا ، وصلنا إلى قسم ما هو مبدأ العمل لمولد التيار المستمر وحاولنا شرحه بمثال حي. إذا كان لديك أي أسئلة أخرى حول الموضوع ، فإن غزلي مستعد للإجابة عليها. كل ما تحتاجه هو التسجيل . علاوة على ذلك ، إذا كانت لديك أي خبرة في استخدام مولدات التيار المستمر ، فسيسعدنا مشاركتها معنا في التعليقات. أتمنى أن تكون قد استمتعت بهذا المقال.
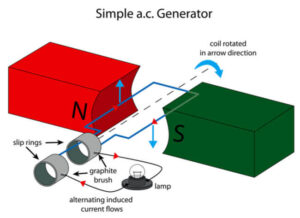
 مبدأ العمل لمولد التيار المتردد
مبدأ العمل لمولد التيار المتردد
مبدأ العمل لمولد التيار المتردد – مولد التيار المتردد (مولد التيار المتردد) هو جهاز يحول الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى طاقة كهربائية بديلة للاستخدام. تستخدم مولدات التيار المتردد حلقات الانزلاق لإنتاج تيار متناوب ، بينما تستخدم مولدات التيار المستمر تيارًا مباشرًا. تستخدم محطات الطاقة والمراكب الشراعية والدراجات البخارية الكهربائية والدراجات وغيرها من التطبيقات مولدات التيار المتردد. يتم توفير الطاقة الميكانيكية عادةً لمولدات التيار المتردد عن طريق التوربينات البخارية والغازية ، فضلاً عن محركات الاحتراق الداخلي. تعد مولدات التيار المتردد مفيدة في توربينات الرياح ومحطات الطاقة الكهرومائية الصغيرة وتحويل تيارات الغاز عالية الضغط إلى تيارات غاز منخفضة الضغط.
توفر لك منصة جهزلي جميع المعلومات التي تحتاجها حول معدات مولدات التيار المتردد والأجهزة والمنتجات ذات الصلة المتوفرة في السوق اليوم. .
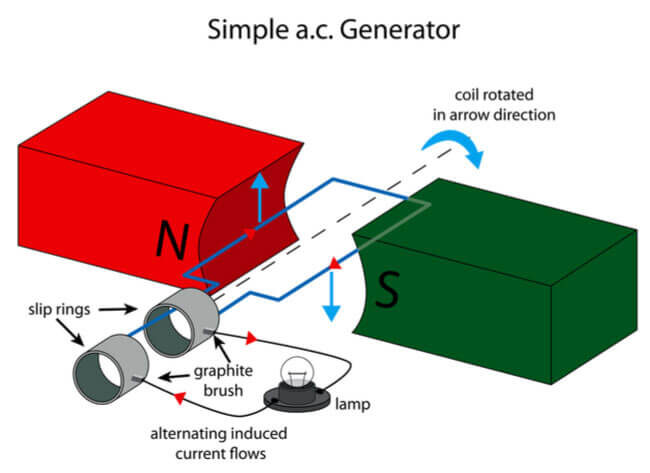 ما هو مولد التيار المتردد؟
ما هو مولد التيار المتردد؟
تُعرف الآلة التي تحول الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى طاقة كهربائية في شكل EMF البديل باسم مولد التيار المتردد. يحكم قانون فاراداي للحث الكهرومغناطيسي تشغيل مولد التيار المتردد البسيط. إنه مصنوع من ملف سلكي يدور في مجال مغناطيسي.
مبدأ العمل لمولد التيار المتردد
مبدأ العمل لمولدات التيار المتردد هو أنه يشار إليها كثيرًا باسم المولدات وتعمل وفقًا لمبدأ قانون فاراداي للحث الكهرومغناطيسي. يتغير التدفق المغناطيسي المرتبط بالملف عندما يتحرك موصل في مجال مغناطيسي موحد ، مما يتسبب في وجود EMF.
الكهرباء منتشرة على نطاق واسع ، من قلب المفتاح إلى تسخين وجبة خفيفة في الميكروويف. قد تتساءل كيف يتم توليد مصدر الطاقة الحيوي هذا وتسليمه إلى منزلك الآن بعد أن أعطيته بعض الاهتمام.
تستخدم التوربينات والمولدات لتوليد الكهرباء في محطات الطاقة. تقوم المولدات الكهربائية بتحويل الدوران إلى كهرباء ، بينما تقوم التوربينات بتحويل الطاقة المتاحة إلى دوران. تنقسم المولدات إلى مجموعتين بناءً على ناتجها الكهربائي: مولدات التيار المتردد ومولدات التيار المستمر. ستتم مناقشة مبدأ ومكونات مولد التيار المتردد بتعمق في هذا المنشور. إذا كنت ترغب في معرفة المزيد حول مبدأ العمل وخصائص مولد التيار المستمر ، فتفضل بزيارة مولد التيار المستمر.
تُعرف الآلة التي تحول الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى طاقة كهربائية باسم مولد التيار المتردد. يتم توفير الطاقة الميكانيكية لمولد التيار المتردد من خلال التوربينات البخارية والتوربينات الغازية ومحركات الاحتراق. الطاقة الكهربائية المتناوبة على شكل جهد متناوب والتيار هو الخرج.
ينص قانون فاراداي للحث الكهرومغناطيسي على أن القوة الدافعة الكهربائية (EMF أو الجهد الكهربي) تتولد في موصل يحمل تيارًا يقطع مجالًا مغناطيسيًا موحدًا. تعمل مولدات التيار المتردد على هذا الأساس. يمكن استخدام كل من تدوير ملف موصل في مجال مغناطيسي ثابت أو تدوير المجال المغناطيسي الذي يحيط بالموصل الثابت لتحقيق ذلك. نظرًا لأنه من الأسهل استخراج التيار المتردد المستحث من ملف المحرك الثابت مقارنة بالملف الدوار ، فهذا هو التكوين المفضل.
يعد الملف وحلقات الانزلاق والفرش والحقل المغناطيسي القوي المكونات الرئيسية لمولد التيار المتردد.
وظيفة مولد التيار المتردد بالتفصيل
لإنشاء مجال مغناطيسي قوي ، يتم تدوير الملف في المجال المغناطيسي. يتم إحداث EMF في اتجاه واحد حيث يرتفع الملف عبر المجال المغناطيسي على جانب واحد. يتم إحداث EMF في الاتجاه العكسي حيث يدور الملف ويتحرك هذا الجانب من الملف لأسفل ويتحرك جانب آخر من الملف لأعلى. يتم تحديد اتجاه EMF المستحث باستخدام قاعدة اليد اليمنى لـ Fleming . في كل دورة ، تتكرر هذه العملية ، وتكون المجالات الكهرومغناطيسية المولدة من النوع البديل.
يتم عرض رسم بياني يوضح إخراج مولد التيار المتردد أعلاه. وصف الحروف كالتالي:
- أ – عندما يكون الملف عند 0 درجة ، فإنه يتحرك بالتوازي مع اتجاه المجال المغناطيسي وبالتالي لا ينتج عنه EMF.
- ب – يتحرك الملف بزاوية 90 درجة إلى المجال المغناطيسي ، وبالتالي يستحث أكبر قدر من المجالات الكهرومغناطيسية عندما يكون عند 90 درجة.
- C – عندما يتم تدوير الملف 180 درجة ، فإنه يتحرك بشكل موازٍ للحقل المغناطيسي مرة أخرى ، مما يؤدي إلى عدم إنشاء EMF.
- D – عندما يكون الملف عند 270 درجة ، فإنه يعود إلى 90 درجة إلى المجال المغناطيسي ، مما يؤدي إلى الحد الأقصى من EMF. الكهرومغناطيسي المستحث في هذه الحالة هو عكس القطب ب.
- أ – أكمل الملف دورة واحدة عندما يصل إلى 360 درجة عندما يتحرك بالتوازي مع المجال المغناطيسي وينتج صفر EMF.
ضع في اعتبارك ملفًا مستطيلًا به دوران ‘N’ يدور في مجال مغناطيسي متجانس ‘B’ بسرعة زاوية تبلغ ”. في كل مرة ‘t’ ، يتم إعطاء الزاوية بين المجال المغناطيسي ‘B’ والعادي للملف بواسطة ، θ = ωt.
يكون التدفق المغناطيسي عموديًا على مستوى الملف في هذا الموقع ، ويتم إعطاؤه بواسطة B Cos ωt. التدفق المغناطيسي المرتبط بملف من المنعطفات N يساوي ɸ = B Cos ωt A ، حيث A هي منطقة الملف. تحدد قوانين فاراداي للحث الكهرومغناطيسي المجال الكهرومغناطيسي المستحث في الملف.
� = −���� = −� (��������) �� = �������� (��)
عندما يدور الملف بمقدار 90 درجة ، تقترب قيمة الجيب 1 ويصل EMF المستحث إلى الحد الأقصى ، مما يقلل من المعادلة السابقة إلى:
�0 = ����� =
أين
يتم الإشارة إلى كثافة التدفق القصوى في Wb / m 2 بواسطة Bm ،
يُشار إلى مساحة الملف في م 2 بالحرف “أ” ،
تشير الحرف “f” إلى تكرار دوران الملف في عدد الدورات في الثانية.
عن طريق استبدال المعادلة الثانية في الأولى ،
� = �0��� (��
يشير مصطلح “التيار المتردد المستحث” إلى التيار الذي يتم إنشاؤه عند تشغيل الجهاز.
� = �� = �0������
يختلف ارتباط التدفق في المحرك بشكل مستمر لأنه يدور بين أقطاب المغناطيس على محور عمودي على المجال المغناطيسي. نتيجة لذلك ، ينتقل تيار كهربائي عبر الجلفانومتر ، وحلقات انزلاقية وفرشاة. يغير الجلفانومتر قيمته من الموجب إلى السالب. هذا يعني أن الجلفانومتر يتلقى تيارًا متناوبًا. يمكن استخدام قاعدة فليمنج اليمنى لتحديد اتجاه التيار المستحث.
بناء مبدأ مولد التيار المتردد
الدوار والجزء الثابت هما المكونان الرئيسيان لمولد التيار المتردد البسيط. الجزء المتحرك هو مكون دوار ، في حين أن الجزء الثابت هو مكون ثابت للآلة.
الجزء الثابت
الجزء الثابت هو مكون ثابت يثبت ملف المحرك في مكانه. الهدف من ملف المحرك هو نقل التيار إلى الحمولة ، والتي قد تكون أي معدات خارجية تستخدم الكهرباء. وهي مقسمة إلى ثلاثة أقسام:
- إطار الجزء الثابت – إنه إطار خارجي يحمل كلاً من قلب الجزء الثابت ولفائف المحرك.
- الجزء الثابت – لتقليل خسائر تيار الدوامة ، يتم تصفيحه بالفولاذ أو الحديد . لعقد لفات المحرك ، يتم قطع الفتحات في الجزء الداخلي من النواة.
- لفات حديد التسليح – يتم لف ملفات المحرك في فتحات قلب المحرك.
الدوار
دوار مولد التيار المتردد هو مكون دوار. تشكل اللفات المجال المغناطيسي الهيكل. الأقطاب المغناطيسية ممغنطة باستخدام مصدر تيار مستمر. حلقات الانزلاق متصلة بكل طرف من لفات المجال المغناطيسي. يدور الدوار على عمود مشترك مقترن بهذه المجموعة. دوارات القطب البارزة ودوارات القطب الأسطوانية هما نوعان من الدوارات.
دوار القطب البارز
تم توضيح أهم نوع دوار للقطب في الرسم التخطيطي أدناه. يمكن رؤية عدد الأعمدة البارزة ، والمعروفة باسم الأقطاب البارزة ، مع قواعدها المثبتة على الدوار ، في هذا النوع من الدوار. يتم استخدامها في التطبيقات ذات السرعات المنخفضة والمتوسطة.
دوار القطب الأسطواني
تحتوي الدوارات الأسطوانية على أسطوانة غير مكدسة وقوية مع فتحات موضوعة على السطح الخارجي للأسطوانة. إنه مستخدم في التطبيقات التي تتطلب الكثير من السرعة. يظهر الجزء الدوار للقطب الأسطواني في الرسم البياني أدناه.
 أنواع مبدأ مولد التيار المتردد
أنواع مبدأ مولد التيار المتردد
يتم تصنيف مولدات التيار المتردد إلى نوعين بناءً على مبدأ العمل الخاص بهم.
المولدات غير المتزامنة
المولدات الحثية هي اسم آخر للمولدات غير المتزامنة. يساعد الانزلاق على دوران الدوار في هذا النوع من المولدات. يحاول الجزء المتحرك أن يطابق السرعة المتزامنة للجزء الثابت ولكنه يفشل. عندما يساوي الجزء المتحرك السرعة المتزامنة للجزء الثابت ، تكون السرعة النسبية صفرًا ، ولا يحتوي الجزء المتحرك على عزم دوران. يمكن استخدامها لتشغيل توربينات الرياح.
المولدات المتزامنة
المولد المتزامن هو مولد تيار متردد يدور بنفس السرعة طوال الوقت. إنه يعمل على أساس قانون فاراداي للحث الكهرومغناطيسي ، والذي ينص على أنه عندما يدور ملف في مجال مغناطيسي موحد ، يتم إحداث EMF. يتم استخدامها في الغالب لإنشاء جهد عالي في محطات توليد الطاقة.
التطبيقات
يستخدم مولد التيار المتردد لتوليد الكهرباء من طواحين الهواء والسدود الكهرومائية ومصادر أخرى.
مزايا مولدات التيار المتردد على مولدات التيار المستمر
تتمتع مولدات التيار المتردد بالمزايا التالية مقارنة بمولدات التيار المستمر:
- من خلال المحولات ، يمكن ببساطة تصعيد مولدات التيار المتردد لأعلى ولأسفل.
- بسبب ميزة التصعيد ، يكون حجم ارتباط الإرسال في مولدات التيار المتردد أقل.
- الخسائر في مولدات التيار المتردد أقل من تلك الموجودة في أجهزة التيار المستمر.
- مولد التيار المتردد أصغر في الحجم من مولد التيار المستمر.
يبدأ الغالبية منا دراستنا بالتيار المباشر ، لكن سرعان ما نكتشف أنه ليس النوع الوحيد من التيار الذي نواجهه. تنتج بعض مصادر الطاقة الفولتية والتيارات المتناوبة في الطبيعة. التيار المتردد ، أو AC ، هو اسم هذا النوع من الكهرباء. سيساعدك الفيديو في فهم مبدأ العمل لمولد التيار المتردد.
أسئلة وأجوبة حول مبدأ العمل لمولد التيار المتردد
1) ما هو الفرق بين مولد التيار المتردد ومولد التيار المستمر؟
إن التيار الكهربائي في مولد التيار المتردد يغير اتجاهه بانتظام ، مما ينتج عنه تيار متناوب. يتدفق التيار الكهربائي في مولد التيار المستمر في اتجاه واحد فقط.
2) هل مولدات السيارة بها تيار متردد أو تيار مستمر؟
يولد المحرك الدوار التيار المتردد ، والذي يتم تحويله إلى تيار مستمر باستخدام المبدل والفرش.
3) مولد التيار المتردد يعمل على أي مبدأ؟
تعمل وفقًا لقوانين فاراداي الخاصة بالحث الكهرومغناطيسي.
4) ما هي أنواع مولدات التيار المتردد؟
مولدات التيار المتردد المتزامن وغير المتزامن.
5) هل البطاريات AC أو DC؟
تُصنف البطاريات على أنها تيار مستمر لأنها تجري تيارًا في اتجاه واحد فقط.
6) كيف ينتج مولد التيار المتردد الكهرباء؟
يحكم قانون فاراداي للحث الكهرومغناطيسي تشغيل مولدات التيار المتردد. يختلف ارتباط التدفق في المحرك بشكل مستمر لأنه يدور بين أقطاب المغناطيس على محور عمودي على المجال المغناطيسي. يتم إنشاء EMF في المحرك نتيجة لذلك. نتيجة لذلك ، ينتقل تيار كهربائي عبر الجلفانومتر ، وحلقات انزلاقية وفرشاة.
7) ما هي العوامل التي تعتمد عليها المجالات الكهرومغناطيسية المولدة في مولد التيار المتردد؟
يتم تحديد مقدار EMF الذي تم إنشاؤه من خلال عدد لفات ملف المحرك ، وشدة المجال المغناطيسي ، وسرعة المجال الدوراني.
8) ما هي بعض مزايا مولدات التيار المتردد على مولدات التيار المستمر؟
من خلال المحولات ، يمكن ببساطة تصعيد مولدات التيار المتردد لأعلى ولأسفل. الخسائر في مولدات التيار المتردد أقل من تلك الموجودة في أجهزة التيار المستمر.
9) في أي جزء من مولد التيار المتردد يتم توليد الخرج؟
المحرك هو المكان الذي يتم فيه إنشاء الإخراج.
تم استكشاف مولد التيار المتردد وتشغيله في هذا المنشور.
فتيل كهربائي
يسعدنا زيارتك لصفحاتنا على مواقع التواصل الاجتماعي ،
حيث ننشر عروض حصرية على موقعنا.
صفحتنا على Facebook هنا .
حساب تويتر لدينا هنا .





























اترك تعليقاً
يجب أنت تكون مسجل الدخول لتضيف تعليقاً.