Solar inverters specifications 1
What is an inverter?
 Inverters (inverter) is a device whose function is to convert the continuous DC electricity coming from the panels or batteries into an alternating current of 110/220/380 AC to operate home appliances or pumps or connect the solar energy system to the national electricity grid. Basic Technical Characteristics of Solar Inverters:
Inverters (inverter) is a device whose function is to convert the continuous DC electricity coming from the panels or batteries into an alternating current of 110/220/380 AC to operate home appliances or pumps or connect the solar energy system to the national electricity grid. Basic Technical Characteristics of Solar Inverters:
-
Characteristics of AC Output waves
The household current operates on a pure sine wave called the Pure Sine Wave, and there is another wave called the Modified Sine Wave.
 As the picture shows, the red color shows the normal current, and the other colors show other forms of waves. This will make a difference with you in operating some devices that only work on the real sine wave. So when buying an inverter, we will find that some devices are described as producing a pure or modified sine wave or pure sine wave. Modified Sine Wave, and this will have a difference in the price and also in the quality of the devices that can be operated. It used to operate it sometimes, but a change occurred in the behavior of the device, for example the fan worked, but a change was noticed in its sound and the motor cycle, and this is a negative point that is compensated by the low price. Modified sine wave inverters are not suitable for operating all devices that have AC motors, such as:
As the picture shows, the red color shows the normal current, and the other colors show other forms of waves. This will make a difference with you in operating some devices that only work on the real sine wave. So when buying an inverter, we will find that some devices are described as producing a pure or modified sine wave or pure sine wave. Modified Sine Wave, and this will have a difference in the price and also in the quality of the devices that can be operated. It used to operate it sometimes, but a change occurred in the behavior of the device, for example the fan worked, but a change was noticed in its sound and the motor cycle, and this is a negative point that is compensated by the low price. Modified sine wave inverters are not suitable for operating all devices that have AC motors, such as: -
Inverter capacity – Rated Power
It is noted that the devices often express their consumption in watts, and some inverters express their capacity in volt-ampere VA, and this calls for attention when calculating the capacity and converting volt-ampere into Watt requires multiplication in the electrical power factor. The devices that can be loaded on it have a total of 600 watts.For the motors that are loaded on the inverter, the actual current must be calculated when starting the motor by making the necessary correction for the electrical power factor, and here you will calculate the loads that are expected to be loaded. Set a margin of increase in order to avoid overloading. The user must be careful and aware of the nature of the device, not to overload it, and respond to the warnings issued by the device when increasing the load by reducing loads, turning off some devices, or turning off the device altogether if it cannot bear it, especially with frequent power outages.
-
Low frequency and high frequency inverters
Low frequency vs High Frequency There are two types of inverters and without diving into theories, it can simply be said that there are differences in weight, cost, maximum capacity and noise.
- A low frequency inverter uses large copper coils to convert current and is therefore heavy and expensive
- A high frequency inverter uses electronic transistors to convert current.
The difference between high and low frequency inverters clause Low Frequency Inverter High frequency inverter Weight and size Large and heavy, weighing up to 10 kg per kilowatt capacity Small and light, weighing about 2.5 kg per kilowatt capacity price beloved Cheap Maximum power – Surge Power The maximum capacity is 4-8 times the continuous capacity. That is, the 3 kilowatt inverter has a maximum capacity of at least 12 kilowatts, and this number is valid for starting induction motors such as air conditioners and washing machines. For example, a 3 kilowatt inverter has a maximum capacity of 12 kilowatts. This number is sufficient to operate a 3-horsepower air conditioner The maximum power does not exceed twice the continuous power, and for the operation of rectifying motors, careful care must be taken in designing the size of the inverter the noise It causes a lot of noise, so it must be connected in a place far from living places He does not make noise and his voice is very low
Types of inverters (inverters)
-
On Grid Inverter

- This type is used in systems connected to the electricity grid
- There are sizes starting from 2 kilowatts to 1 megawatt
- Small sizes up to 5 kilos have a 1-phase 220 volt output type
- Sizes larger than 5 kilos have an AC output type of 3 phase, 380 volts
- This type of inverter disconnects the electric current automatically and turns off completely when the network is out of power, and this feature ensures safety for workers in the event of maintenance work on the electricity network during a power outage.
- It is not possible to benefit from solar energy electricity when the power is cut off from the network, as the inverter is completely turned off
- The inverter synchronizes the frequency of the output current (50-60 Hertz) with the frequency of the network current using an internal oscillator, and adjusts the voltage with the same network voltage, and this process is called Synchronization
- This inverter outputs a pure sine wave current , so that the electricity coming out of the inverter matches the network electricity in all characteristics.
- Most of the types of inverters connected to the network now come from the high frequency type that does not contain copper coils, as previously explained.
-
Off Grid Inverter and Hybrid

- Most types of off-grid inverters now come with an internal charging regulator
- The current output is either a modified or pure sine wave. Pure wave inverters have become the most common of all inverters after their low prices, except for small inverters intended for operating lighting units only.
- The voltage of the battery bank supported by the inverter is a specification found in the hybrid inverter or the Off Grid that contains the charging regulator inside it. The voltage of the batteries supported by the inverter is generally as follows: 12 volts for small inverters up to a capacity of 1 kilowatt 24 volts for inverters from 1 to 3 kilowatts 48 volts for inverters from 3 to 10 kilowatts 96 volts for inverters from 10 to 20 kilowatts 192 volts for inverters from 20 to 50 kilowatts 600 volts for inverters from 50 to 500 kilowatts. If it is 48 volts, for example, you will have to install 4 12-volt batteries or 8 6-volt batteries, so that they are connected in series. More than one battery can be connected to the same device, but in parallel, to give the same 12 volts, for example, with a longer operating time, which also depends on the device’s ability to charge the batteries at an appropriate time, as frequent power outages lead to insufficient time between the two outages to charge the batteries.
- Inverter Protection – Circuit Protection Protection must ensure that the device has sufficient protections, mainly protection against overloads, especially with an audio alert Protection against low battery voltage Protection against overheating
- Automatic switching when the power is cut off – UPS uninterrupted power support Hybrid devices support automatic switching when the power is cut off or back, which is called UPS. This feature is useful if a specific device is running on the inverter and you do not want it to stop running, such as a server or a medical device, for example.
- The possibility of programming priority in operation, whether from panels, batteries or mains electricity
- Some types have a circuit to operate a diesel generator in the absence of the sun, mains electricity, and low battery charge. .
-
Grid Tied with battery backup

- This system combines the previously explained connected and separate systems, as these inverters accept batteries with the possibility of connecting them to the electricity grid.
- The main difference between this type and the hybrid inverter is that this inverter can pump electricity to the grid in addition to using electricity from the grid. That is, the alternating current runs in both directions to and from the network, as shown in the picture. As for the hybrid inverter, it takes current from the network in one direction only, and it cannot pump electricity to the network.
- This inverter performs the Synchronization process previously explained in the inverters connected to the network
- This inverter separates the pumping of electricity to the network when the power is cut off, but it does not turn off, so here lies the benefit from solar energy electricity when the power is cut off from the network and relying on cells and batteries
-
Solar pump inverter

- It is known that the power of the solar beam is variable during the day, which results in the need to change the speed of the solar-powered pump throughout the day. These inverters are characterized by the ability to control the speed of AC pumps from the moment they are turned on at sunrise to the moment they are turned off at sunset, passing through their normal operating period during the day.
- Solar pump inverters receive a series of cells connected to each other in series with a total voltage of up to 800 volts. Where there can be 20 solar panels connected to each other in series, and there will be 60 groups of these 20 panels, so they are all connected inside the inverters, whose capacity in large sizes may reach 300 kilowatts.
- The inverter controls the start of the motor by gradually raising the voltage and frequency from zero until it reaches the programmed initial speed or the required reference speed within a percentage of time called the acceleration time that has been determined and programmed in advance, as well as the process of stopping the motor, it gradually reduces the voltage and frequency from the value which it is at the moment of the stop request until it reaches zero within a percentage of time called the acceleration time that has been determined and programmed in advance.
- Inverters for pumps less than 2 HP usually have a single phase current output
- All inverters for pumps greater than 2 HP have a three phase AC output
- Many modern types of solar pump inverters have a diesel input and AC electricity from the network, to obtain a hybrid system that works as a backup source of energy other than the energy of the panels.
- The inverter outputs a current of variable frequency, starting from 0 to 60 Hz, according to the instantaneous intensity of sunlight.
- The inverter is equipped with a soft starter device, which performs soft rectification of motors with large and medium capacities to reduce the starting current, which is high when direct operation of the motor through a contactor, and to gradually raise the load speed from zero to maximum speed. This feature eliminates the need for a large inverter to withstand the large surge power that occurs at the start of induction motors.
Solar inverter specifications
Solar power inverter specifications, for each inverter (inverter) used in solar systems, there is a set of values that you should know because they describe the electrical characteristics of it.
Let’s get acquainted with the most important specifications that must be taken into account when choosing the appropriate inverter in the design of solar systems, because the wrong choice of inverter may lead to clear energy losses, or may cause malfunctions in the inverter itself.
Types of solar system inverters
There are three types of solar system inverters:
- ON-Grid system.
- Off-grid system.
- Hybrid System.
The two most popular types that are used are: the grid-connected system (ON-Grid) and the off-grid system (OFF-Grid). which may last for a long period of time.
Solar inverter specifications
The companies that manufacture these inverters include all the details inside the “data sheet” for each inverter (inverter), as they give sufficient information about it in order to assist the competent person while using these inverters to generate electric power in an efficient manner and feed the electric loads.
The types of solar power inverters available in the market differ in terms of brand, technology (online and offline), capacity, programming mechanism, and many other differences.
The most important electrical specifications of the solar inverter
It is necessary to know the most important values that are dealt with when choosing an inverter for solar systems, which are as follows:
First: The inverter technology used: Is the solar system connected to the grid (ON-Grid) or separated from the grid (OFF-Grid).
Second: The maximum amount of DC power at which the inverter (inverter) works: that is, the capacity of the solar panels entering the inverter, which is the highest value of DC power at which the inverter can work without any malfunctions, and it is usually a few percent higher than the rated (nominal) capacity of the inverter (inverter). ).
Third: The maximum operating voltage of the point (MPP): It is the maximum voltage value that the inverter input (inverter) can bear and work within the working period of the maximum capacity until we get the highest efficiency from the panels.
Fourth: The maximum continuous current (DC) that the inverter can work at: It is the maximum current value that the inverter can work at without damaging its internal electronic elements, and this value often determines the number of rows that we can connect with the inverter so that it works efficiently and without malfunctions.
Fifth: The output value of the inverter (AC): As it is known, the output power of the inverter is alternating power (AC) with alternating voltage (220V) for 1-phase inverters, and 400 volts for 3-phase inverters, with a fixed frequency of 50Hz. Note that these values are fixed for power inverters connected or isolated from the network.
Sixth: Inverter efficiency: It is a very important point, as it determines the ratio between the power coming out of the inverter to the power entering it in relation to the standard values, where the efficiency measures the extent to which the inverter is used, and the efficiency is often represented by a percentage (%), and the efficiency of the inverters currently reaches to more than 92%.
Important note: The efficiency of inverters associated with the network is often greater than those independent of the network.
What is the best inverter?
What is the best inverter? With the rapid technical progress in the manufacture of inverters , there are many different types of inverters currently available in the market, including old inverters that cannot be programmed and modern inverters that can be programmed, such as solar energy inverters.
Many may search for “what is the best inverter” on which electrical loads can be operated without any problems. There are several tips that must be recognized in this article before buying any inverter.
What is the best inverter on the market?
The best inverter in the market is chosen based on the following specifications:
- Inverter type
It is one of the most important options that are presented before the decision to buy any inverter. There are inverters dedicated to solar energy, some are dedicated to electric batteries only, and finally you may see some small-sized inverters for cars.
- Inverter brand
- Inverter input and output voltage
It is always preferable to go to internationally accredited and recommended companies that have guarantees about their inverter products, as there are some inverters that are adulterated in terms of quality and that an inverter with a capacity of one kilowatt does not bear more than half a kilowatt.
It is always advised, before buying an inverter, to read all its specifications in terms of capacity, input and output voltages, the maximum current that it can withstand at the moment of loading it, and what is the current of the charger if it is available, and all of these things make it easier for you to determine the inverter that suits you.
- Inverter capacity
There are many inverters available in the market with different capacities, and the capacity that suits you is determined according to the capacity of the electrical loads to be run on the inverter, and it is always preferable to choose an inverter capacity that is 30% higher than the total capacity of the electrical appliances.
The best solar inverters
The best solar power inverter for your solar system is chosen based on the type of use. There is a solar power inverter with an on grid system that works to save consumption in public electricity energy in order to reduce the payment of the monthly bill, and it can also sell surplus energy produced from the panels to the electricity company.
There is also a solar power inverter designed with an off grid system designed to be independent of the public electricity grid, and it can be installed in any place where there are no public electricity grid lines.
Important note: Use the inverter correctly by avoiding overloading, and installing circuit breakers to protect the inverter from short current.
The most important specifications of the inverter
There are several specifications that determine the type of inverter you want to buy, which are:
- The maximum capacity of the inverter.
- Peak Surge value, which is the maximum capacity value that the inverter can bear at the moment it is loaded.
- Is the inverter for a solar energy system or just a battery?
- It is preferable to buy an inverter that is also equipped with a battery charger and an inverter system between the electricity grid and the battery.
- It is preferable to choose an inverter with a pure sine wave output.
- If you want an inverter dedicated to solar energy, there are two types that you can choose between, depending on the type of system you want: the off grid system, and the “on grid” system.
- Ensure that the inverter is equipped with overload and palace current protection.
- Knowledge of inverter efficiency and power factor.
- Know the input and output voltage of the inverter.
You may find all of these specifications in the inverter data sheet, through approved websites, or from the same company that manufactures the inverter.
Types of inverters
The inverter is one of the most important elements used in the solar energy system, as the main function of the solar energy inverter is to work on converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to benefit from it in running household loads, and we will show you some types of inverters, their method of connection, advantages and disadvantages.
Inverter types
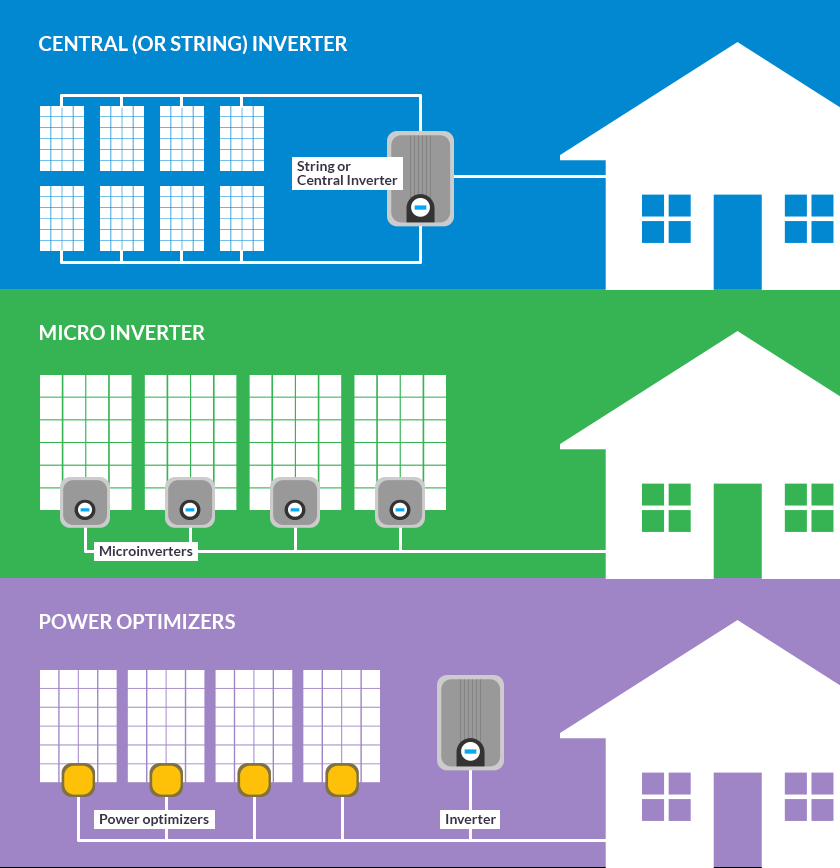
- Micro-inverter
- String-inverter
- Central inverter
Micro-inverter
The micro-inverter converts the energy produced by the solar panels from DC current (voltage) to AC current. As for the connection process, each inverter is connected to each panel, as it is installed and placed directly behind the panel. Each inverter takes full advantage of the production of each individual plate; The energy generated from each panel is then transferred to the solar system grid.
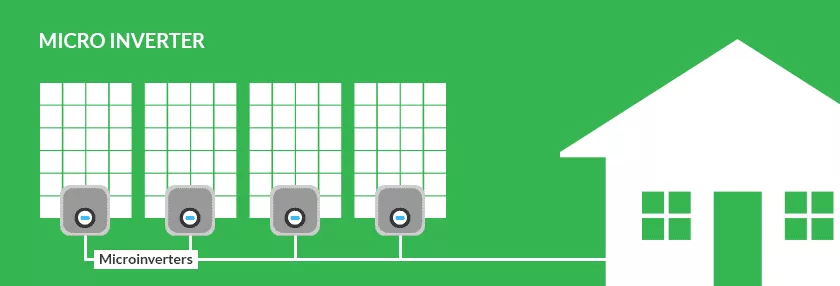 Micro-inverter features
Micro-inverter features
- Through it, electricity can be obtained from the panels with high efficiency.
- Suitable for solar system facing multiple angles.
- Suitable for places where there is partial shade on solar panels.
- The production of each solar panel can be tracked, while the inverter connected to several panels – which we will mention in this article – follows the production of the entire system.
- The default life of the mini inverter extends up to 25 years.
Micro-inverter defects
- The high cost compared to a string-inverter connected to several panels.
- When installing additional solar panels, you need one micro-inverter for each panel.
String-inverter
This is the most widespread and best type of small inverter. It is known as the inverter series or the small central inverter. It is an independent box that is usually installed in an empty, clean, well-ventilated place, in order to cool the device by means of fans during operation.
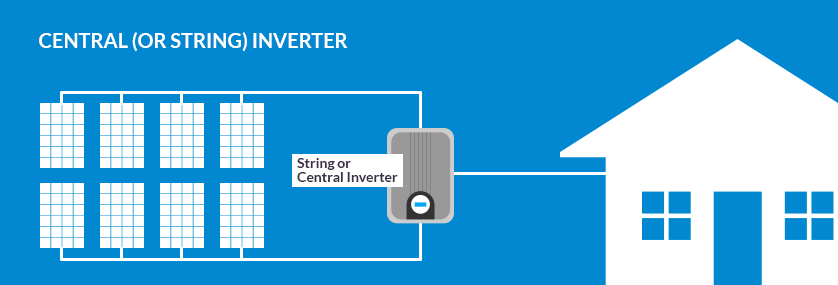
The inverter connected to several panels contains a screen to give information about the loads that you have operated, such as (the device’s capacity in VA or KVA, network voltage, electric load current, and the status of connecting and disconnecting panels, batteries, and general electricity automatically), with the possibility of grounding the system.
Characteristics of the inverter connected to several panels (String-inverter)
- It needs one device to transform the current in order to feed the electrical loads.
- Multiple solar panels can be installed on one inverter.
- Cheaper than installing a Micro-inverter.
- high efficiency; Where it reaches 98%.
Faults of the inverter connected to several panels (String-inverter)
- The cost is higher compared to a small inverter.
Central inverter
The central inverter, or what is also known as the high-capacity inverter; It is similar to a string-inverter system.
As it was designed for use with large solar energy systems, such as the solar power station, a large series of panels are installed in order to produce electrical energy with high capacities of up to megawatts to handle large loads such as feeding residential communities and others.
 Features of the central inverter
Features of the central inverter
- A large series of solar panels can be installed to the central device.
- High efficiency.
- Large electrical power can be produced compared to the previous types.
Central inverter defects
- The high cost compared to the inverter connected to several panels and the small inverter.
In this way, we have reviewed all types of inverters for you, and we have shown you illustrations, advantages and disadvantages of each type of inverter, in addition to an overview of each type.
Inverter: How to connect, mechanism of action, and types of waves
What is an inverter
It is a device specialized in converting direct current “DC” from solar panels or batteries into alternating current “AC” with the aim of using it to operate household appliances or pumps or to connect the solar energy system to the public electricity grid.
inverter connection
The process of connecting a small inverter is easy, and you do not need much experience. Where the source of continuous current (voltage) (DC), such as batteries, is connected to the inverter device, and this device converts the continuous current (voltage) (DC) to alternating current (voltage) (AC), and from it the output of the device is connected to the electrical loads in proportion to the voltage The current and capacity of the inverter.
How to convert energy to the “inverter”
DC power is converted to AC power using two methods:
- In the first method: the low voltage DC power is converted into high voltage DC power, then in the second step, the high voltage DC power is converted into AC power.
- In the second method: low DC power is converted to low voltage AC power, and then this output is stepped up to high voltage AC power.
As they both perform the same conversion in the end.
Types of output waves
pure sine wave
It is the real or pure wave, which we get from the power station or big generators. This type is created by rotating machines (AC). The main advantage of a sine wave is that all devices and equipment sold in the market are designed for sine waves. This ensures that the equipment is used according to full sine wave specifications; such as motors, microwave ovens.
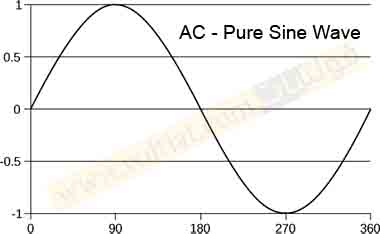
Features of the pure sine wave inverter
- Available in different capacity sizes.
- It works on sine wave output, which is suitable for electrical devices.
Disadvantages of a pure sine wave inverter
high cost.
Modified sine wave
This type of modified sine wave is similar to square wave, but with better enhancement than square wave.
A modified sine wave inverter works well with most equipment, although the efficiency is low, i.e. not as perfect as a pure sine wave. For example, when using a refrigerator motor, pumps or fans, it will consume more energy by approximately 20% due to the lower efficiency of the Modified sine wave inverter.

Modified sine wave features:
Cheap price compared to pure sine wave inverter.
Modified sine wave negatives:
- low efficiency.
- Not suitable for engines of all types.
Square wave:
This is one of the three types, is the cheapest type and does simple things. It is not suitable for motors and pumps, and customers often do not look at it, because this type damages electrical appliances.
Square wave features:
The cheapest type of inverters.
Square wave cons:
- Not suitable for running electric motors.
- Harmful to sensitive devices.
Solar panel wiring guide
We are pleased to have you visit our pages on social networking sites, where we publish exclusive offers on our website.
Our Facebook page here .
Our Twitter account here .















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.