DC and AC 1
Advantages and disadvantages of direct and alternating current

Advantages and disadvantages of DC and AC The source of electricity in any system is divided into two types: alternating current (AC) power supply, A constant current power source.
In most cases, we find on any electrical device the value of the supply voltage and next to it, DC or AC, In order to define that this device must be fed with alternating current (AC), or direct current (DC).
It is worth noting that the type of current used to feed household appliances is alternating current (AC), not direct current (DC), Therefore, you should avoid connecting the battery directly to the power socket without using a suitable charger.
In this article, we will learn about the most important advantages and disadvantages of DC and AC, and what is the difference between them?
alternating current (AC)
The letters AC are short for “Alternative current.” It is the current whose value and direction change with time, and its frequency is 50 or 60 Hz, according to the system followed in the country.
Advantages and disadvantages of alternating current
Advantages:
- The source voltage can be raised or lowered by the transformer as needed.
- It can be generated in huge quantities with less space than solar power plants.
- Its loss is low compared to DC.
- It can be transported long distances from the power plant to the consumer with minimal losses.
- It can be converted to direct current with simple and inexpensive circuits.
- It can be moved at minimal costs.
- More cost effective and reliable.
Defects:
- It cannot be used directly in the charging process.
- It causes some power loss inside the coils.
- When the transmission voltage is raised, cables need to be supported with sufficient layers of insulators and take safety measures.
constant current (DC)
The letters DC are short for “Direct Current.” Also called direct current. It is the current whose value and direction remain constant. That is, the value of the voltage remains constant, The positive side remains positive and the negative side remains negative.
Advantages and disadvantages of direct current (DC)
Advantages:
- does not reverse polarity like alternating current, Rather, the positive pole remains positive and the negative pole is negative.
- It can be obtained by full unification bridge circuits, It converts alternating current to direct current at the lowest costs.
- He has no hesitation.
- The power factor is always one right.
- It can be stored in electric batteries for use as a backup source.
Defects:
- It is very expensive to store in large quantities and requires a lot of batteries.
- Difficult to obtain in large quantities.
- The process of raising or lowering constant voltage needs complex circuits.
- It results in high loss when transported over long distances.
- High costs of DC cables.
- High maintenance costs for batteries.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
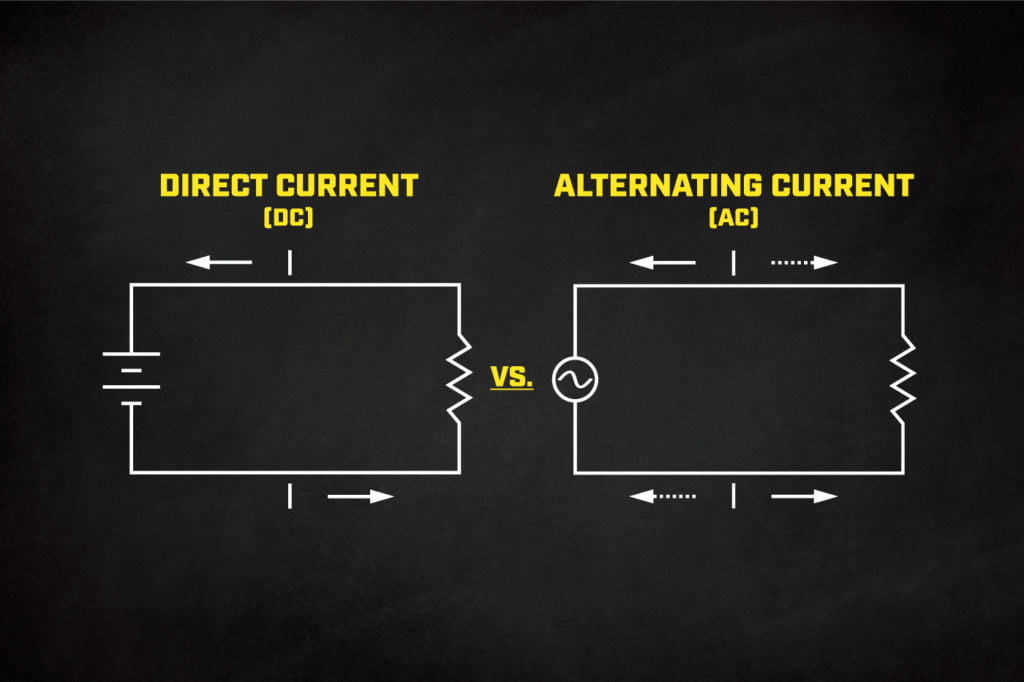
The difference between alternating current and direct current
The difference between alternating current and direct current, flowing electric current through circuits either in the form of alternating current or direct current, As each type of electric current has its uses and advantages, Let’s find out in this topic the difference between Alternating current and direct current in terms of its generation and uses.
What is alternating current?
 In electricity, it is denoted by the symbol AC, which is an abbreviation of the phrase (Alternating Current), and in Arabic it means alternating or alternating current.
In electricity, it is denoted by the symbol AC, which is an abbreviation of the phrase (Alternating Current), and in Arabic it means alternating or alternating current.
It relies on the idea of generating it in the form of curved lines in the opposite direction periodically, and it fluctuates during one second 50 or 60 times, and it is called frequency. The value of the frequency varies from one country to another.
It also changes its value by increasing from zero until it reaches the upper limit of the positive part and then decreasing until it returns to zero again and the same process in the opposite direction.
AC output waveform (sine wave)
The difference between alternating current and direct current
uses of alternating current
Alternating current is used to power most household electrical appliances. Like the motors in refrigerators and washing machines, In addition to televisions and computers in feeding battery chargers.
What is direct current?
It is denoted in electricity by the symbol DC, which is an abbreviation of the sentence (Direct Current) and in Arabic it means continuous current and is also called direct current.
Where the direct current flows in the circuit in the form of a current of constant value and direction, That is, the flow of direct current is in one direction with a specific voltage value only, unlike alternating current, which fluctuates between the positive and negative poles.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
What is alternating current?
 What is alternating current?
What is alternating current?
what is alternating current, Alternating or alternating current is classified as one of the following types: Electric current, which is transmitted from electric power stations through transmission wires to long distances under a high voltage.
The electric current is an important and influential factor in the establishment of industrial and commercial projects and the operation of electrical loads of all kinds. So what is alternating current, how does it work, and what type of output wave does it have?
What is alternating current?
Also called alternating current or sinusoidal, It is denoted by the symbol AC, which is an abbreviation for “Alternative current”.
It is defined as the electric current that periodically reverses its direction, oscillating in place repeatedly, 50 or 60 times during one second, depending on the type of electrical system used.
AC circuit with wave shape
What type of current is used in homes?
All residential homes are powered by alternating current. Most electrical appliances are powered by AC current
And when installing a solar energy system, an inverter must be added and connected to the system in order to convert the energy of DC batteries or solar panels into alternating current in order to operate all household electrical appliances.
AC function
The difference between alternating current and direct current
Alternating current generates its energy in the form of a pure sine wave with a maximum voltage and current, Where the wave begins to rise from the zero point to the top of the wave in the positive direction and then begins to decline to the value of zero again.
When the positive half of the wave is finished, the same thing begins to rise to the top of the wave, but in the opposite direction (negative), then the wave also returns to the zero point again.
This completes the full wave of alternating current.
This process happens quickly and without us noticing, Where alternating or alternating current oscillates during one second, 50 or 60 complete cycles.
AC sine waveform
The difference between alternating current and direct current
Features of alternating current
- It can be transported long distances with minimal losses.
- Its voltage can be raised and lowered using an electrical transformer.
- It can generate a changing magnetic field which is useful for moving electric motors.
- The method of generating it is easier than generating direct current, which requires panels and a charging regulator.
DC uses
DC is used in many low voltage applications, especially in all types of electric batteries that only generate DC. DC is also used in some solar energy systems such as Solar cells that generate electricity in the form of direct current only.
Constant linear constant voltage output
What type of current is stored in the batteries?
Some may wonder what kind of current is stored in the battery and can the battery be charged with alternating current.
It’s simple: all batteries have two terminals: the positive terminal (marked in red) and the negative terminal (marked with black or blue),
From these electrodes, we note that the type of electric current to be stored in the battery is direct current.
Because it has a constant value and direction, And also because DC has a positive terminal and a negative terminal.
When the two ends of the alternating current are connected in parallel with the battery poles (positive and negative), alternating current changes its nature,
This is because half of the positive wave cancels out half of the negative wave which causes the terminals to flip and this leads to the battery damage quickly.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
What is direct current?
 The difference between alternating current and direct current
The difference between alternating current and direct current
what is constant current,
A constant voltage source is commonly used as a power source for electronic circuits and can also be stored in all types of electric batteries .
Such as: car battery , gel battery and dry battery . So what is DC and how is it produced and stored inside the battery?
The difference between alternating current and direct current
What is direct current?
Known as direct current. Direct current) as a directed movement of electrons from one point to another through a conductor in one direction with a constant value within an electric circuit,
DC is denoted by the symbol “DC”.
As we note in the DC output, it is constant in value and direction with voltage and time. On the contrary, with alternating current whose value and direction change with the value of voltage and time.
DC output format
What are the characteristics of direct current?
- Constant value and direction over time.
- It is used in most devices that contain electronic boards.
- It is used in solar energy systems.
- It does not contain frequency.
- It cannot be transported long distances.
Constant current flowing in circuits
When a direct current source such as a battery is connected with an LED lamp,
The direction of direct current flow is from the negative electrode to the positive electrode, The direction remains constant with the constant value of voltage and electric current regardless of the change in time.
It has been termed that the direction of current is from the positive pole to the negative pole, which is used in some references and books.
DC transformers
Everyone knows that devices that contain electronic boards have special adapters that are plugged into a home electrical socket,
These transformers function to convert alternating current into direct current. An example of a transformer is:
- battery chargers
- Laptop chargers.
- Smart phone chargers.
- Screen converter.
- Inside the speaker board there is a bridge circuit whose function is to convert alternating current into direct current to feed the rest of the circuit components.
- feeding units, Like: computer power.
DC uses
- Direct current is used in solar energy systems where solar cells produce direct current when sunlight is shining on them.
- used in batteries, As DC current can be stored inside the batteries in the form of chemical energy, unlike AC, which cannot be stored.
- Direct current is used in most electrical devices that have internal electronic boards. like smart phones, and computers, and loudspeakers, and screens.
DC sources
- Electric batteries: And its types include gel battery, car battery, andLiquid batteries and dry batteries.
- Solar cells: The types of polycarbonate cells and mono cells.
- Nutrition sources or power supply.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
| Alternative current | DC | |
| value and direction | value and direction variable | constant value and direction |
| the magnetic field | It can generate a magnetic field | Cannot generate magnetic field (i.e. field constant) |
| Frequency | Generates a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz depending on the network system | There is no frequency |
| Power Factor | Its power factor ranges from zero to one | The power factor always has a right one |
| obstetrics | It is generated by electric generators | It is generated by solar cells and battery |
| pregnancy type | AC load can be capacitive, inductive or ohmic | DC load is usually resistive in nature |
| wave output type | The output wave can be sine, triangular, square or sawtooth | The output wave is a straight line |
| Transport | It can be transported over long distances with minimal energy loss | It cannot be moved because it causes a lot of energy loss |
| the transfer | It can be converted to DC using the bridge circuit | It can be converted to alternating current using an inverter. |
| stations | Requires few substations to generate and transmit current | Requires complex substations to generate and transmit current |
| the use | It is used in industries, factories, home appliances, and solar inverters | It is used in electronic circuits, automobiles and solar power system |
Table showing the difference between alternating current and direct current
AC and DC wires

The difference between alternating current and direct current
Why do you need both wires in a solar power system
Wiring is an important part of any electrical installation.
Which wire you have to choose mainly depends on the amount of current you want to pass through the wire and the flexibility and durability of the conditions you want to use it.
The common features of any wire are its material, and the thickness of the core wire in gauge or mm, and its insulation layer.
The conductivity and resistance of a material can explain how easily electricity can pass through the material. The higher the conductive material,
It was easier to let electric current pass through. The higher the resistance of the material, The greater the resistance it will show against the electric current passing through it.
The conductivity of a wire made of any material increases with increasing wire thickness and decreasing wire temperature.
The resistance of a wire made of any material increases with the increase in the length of the wire, the decrease in the thickness of the wire, and the increase in the temperature of the wire.
 Some metals have very high electrical conductivity and low resistance, While others are characterized by low electrical conductivity and high resistance. for example
Some metals have very high electrical conductivity and low resistance, While others are characterized by low electrical conductivity and high resistance. for example
Silver is our most conductive metal with a conductivity of 6.30 x 107 s/m and a resistance of 1.59 x 10-8.
Ω • m. Copper is the second most conductive metal and has a resistivity of 5.98 x 107 s/m and 1.68 x 10-8 Ω•m respectively.
Aluminum has a conductivity and resistance of 3.5 x 107 s/m and 2.82 x 10-8 Ω•m respectively and is therefore less conductive than copper.
Copper wires are more electrically conductive than aluminum wires and are also much more expensive.
AC cord vs. DC cord
Electricity, DC, or AC can flow through each wire, Whether it is cheap or expensive. Electricity only need conductor, Any connector will work for it.
The main reason for the rise in AC and AC wires is the difference in the amount of current in the case of the AC supplied in our homes and the DC we get from batteries and solar panels. The AC power supplied to our homes ranges from 20 Amps to 40 Amps and 240 Volts,
While the DC current generated by a single inverter battery can exceed 100A, Solar panels connected in parallel can also give more than 100 amps even if the voltage is 12 to 96 volts.
Low amperes of higher voltage can be easily passed through any wire easily but higher amperage can only be passed through thicker wire which results in better conductivity.
Passing high-ampere electricity through a thin or weak conductor wire will raise the temperature of the wire and will result in heavy losses.
Since the current is very high in the case of home production, The DC power is very high, We have to use wires with high conductivity, Which. Thick copper wire and good insulation.
On the other hand , AC wires can be made of aluminum, copper, or any other good conductive alloy.
The aluminum wire of some devices using 240VAC 1A can be up to 2mm thick while the copper DC wire for a 12V 150Ah battery is 5mm thick.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
Thicker copper wires are also used to power heavy AC appliances where ordinary alloy wires cannot power the load.
Thin wires can also be used to transmit DC power if the voltage is high and the current is as low as the AC power supplied to our homes.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
The conclusion is that 3-7 mm thick and highly conductive copper wires are used when the device requires high current or produces high current by the source. When talking about photovoltaic installations
, we need thick copper wires to connect the panels and batteries to the inverter because the current is more than 100A with low voltage like 12-96V
, Both batteries and solar panels produce DC power, hence the thick copper wires connecting these three components are called DC wires.
DC solar cables are the cables which have very good insulation, So that it can last long in outdoor conditions.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
Also in photovoltaic installations,
When referring to 1-3 mm thinner copper/aluminum/alloy wires to connect the inverter to AC appliances consuming 1-20 A and a total power of 1-5000 watts
, We call these wires AC wires.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
The information I wrote above is only in the case of PV systems.
DC wires have a different meaning when you talk about different systems. DC wires have different structures for different situations.
The difference between solar cables and ordinary cables
The difference between alternating current and direct current
The difference between solar cables and ordinary cables,
There are some who may think that ordinary cables, such as the ones we use in electrical installations, can be used in the solar energy system, specifically to connect solar panels with the inverter designated for the solar system.
This is a misconception because there are several reasons why we should avoid relying on regular cables and stick to solar cables.
Let’s get acquainted with the most important differences between the two types in terms of preference, composition, age, and others.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
solar cables
These cables are specially designed for solar energy systems, specifically direct current (DC) with premium specifications and are TUV and UL approved,
The solar energy cables are also manufactured according to international standards from high quality tinned copper filaments.
Despite the advice on using cables dedicated to solar energy, some people ignore these tips and use ordinary cables that are not intended to withstand weather conditions because of their poor insulation and their intolerance to high voltages and the arc phenomenon resulting from the constant current.
The main purpose of using solar cables is that they are designed and insulated with two layers of non-PVC insulation in order to provide adequate protection from extreme cold or hot weather conditions in order to last for long periods.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
normal cables
Ordinary cables are meant for household electrical extension cables and the cables that we use indoors that are away from sunlight,
As the insulation of these cables is weak and not suitable to withstand external weather factors in terms of high temperature.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
The difference between solar cables and ordinary cables
| solar cables | normal cables |
| The insulator is weather resistant and made of XLPE. | Single layer PVC insulation type |
| Can withstand high effort | limited tolerance |
| These cables have a lifespan of up to 25 years | It lasts for a short period of time, up to 8 years |
| Its efficiency does not drop more than 10% after long service up to 25% | Its efficiency decreases more and more over time |
| Made with high quality | Low quality |
| It can withstand extreme heat and cold | Cannot withstand harsh outdoor weather |
The difference between alternating current and direct current
Important note:
Solar cables (red and black) exposed to direct sunlight are recommended to be placed inside a suitable hose.
The difference between DC cable and AC cable in power cable
A DC cable has the following characteristics compared to an AC cable.
- The system used is different. DC cable is used in rectified DC transmission system, And AC cable is often used in power system with power frequency (50Hz).
- Compared with AC cable, The power loss during DC cable transmission is minimal. The power loss of the DC cable is mainly the DC resistance loss of the conductor, And the insulation loss is small (the magnitude depends on the current fluctuations after rectification); While the AC resistance of a low voltage AC cable is slightly larger than the DC resistance, The high voltage cable is clear, This is mainly due to the proximity effect and the skin effect, The loss of insulation resistance is a large proportion, Mainly generated by the capacitor and inductor.
- High transmission efficiency and low line loss.
- It is convenient to adjust the current and change the direction of power transmission.
- Although the transformer equipment price is higher than the transformer price, However, the cost of using a cable line is much lower than that of an AC cable. DC cable are positive and negative poles, simple structure; The AC cable is a three-phase four-wire or five-wire system, and high insulation safety requirements, the structure is complex, The cost of the cable is more than three times that of the DC cable.
- DC cable is safe to use:
1) The characteristics inherent in the transmission of DC current, It is difficult to generate induced current and leakage current, And it will not interfere with the electric field generated by other cables.
2) Single core extension cable does not affect the transmission performance of the cable due to the hysteresis loss of the steel structure bridge.
3) It has higher interception capacity and over-cutting protection than DC cables of the same structure.
4) An alternating direct electric field of the same voltage is applied to the insulation, The DC electric field is safer than the AC electric field.
- DC cable installation and maintenance is simple and low cost.
Requirements for insulation of the cable itself for the same voltage, AC and DC
When an electric field AC and DC of the same voltage are applied to the insulation
, the electric field of a DC cable is much smaller than the electric field of AC.
Due to the significant difference in the structure of the two electric fields, The maximum electric field when the AC cable is energized is concentrated near the conductor,
The maximum electric field when the DC cable is energized is mainly concentrated within the insulating surface layer, It is more secure (2.4 times).
Third , Mutual conversion relationship between AC voltage and DC current
There are many different understandings about the mutual conversion of AC and DC voltages.
However , Our company is uniformly accounted for in accordance with GB12528.1, ie the same AC cable, And the rated voltage of the DC cable is 1.5 times that of the phase voltage of the AC cable.
But our company’s 1500V DC cable is designed according to the voltage of DC3000V, Which has safe electrical insulation performance.
The difference between alternating current and direct current
The difference between alternating current and direct current
We are pleased to have you visit our pages on social networking sites, where we publish exclusive offers on our website.
Our Facebook page here .
Our Twitter account is here .





![قواطع مقولبة شنايدر [NSX] 3فاز 250B 25KA 5.2E](https://gahzly.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/قواطع-مقولبة-شنايدر-nsx-3فاز-250b-25ka-52e-450x231.jpg)








Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.