Everything you need to know about cable tray systems
Everything you need to know about cable tray systems
Everything you need to know about cable tray systems
What are cable duct systems?
Cable trays are part of a cabling system and provide the physical infrastructure/support for various cables such as electrical or telecommunications. Cable trays are open in nature and the wiring inside the tray can still be accessed if required for any maintenance.
A cable duct system consists of different cable holders to provide the necessary protection and support for the wires inside. This system also allows for easy access to cabling as it is open and allows for any upgrade if necessary.
The materials used for cable trays are usually steel, stainless steel or aluminum most commonly as they have great corrosion resistance and lightweight properties when compared to steel.
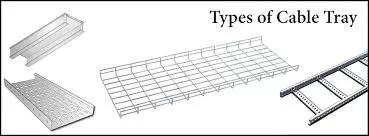
 Types of cable trays:
Types of cable trays:
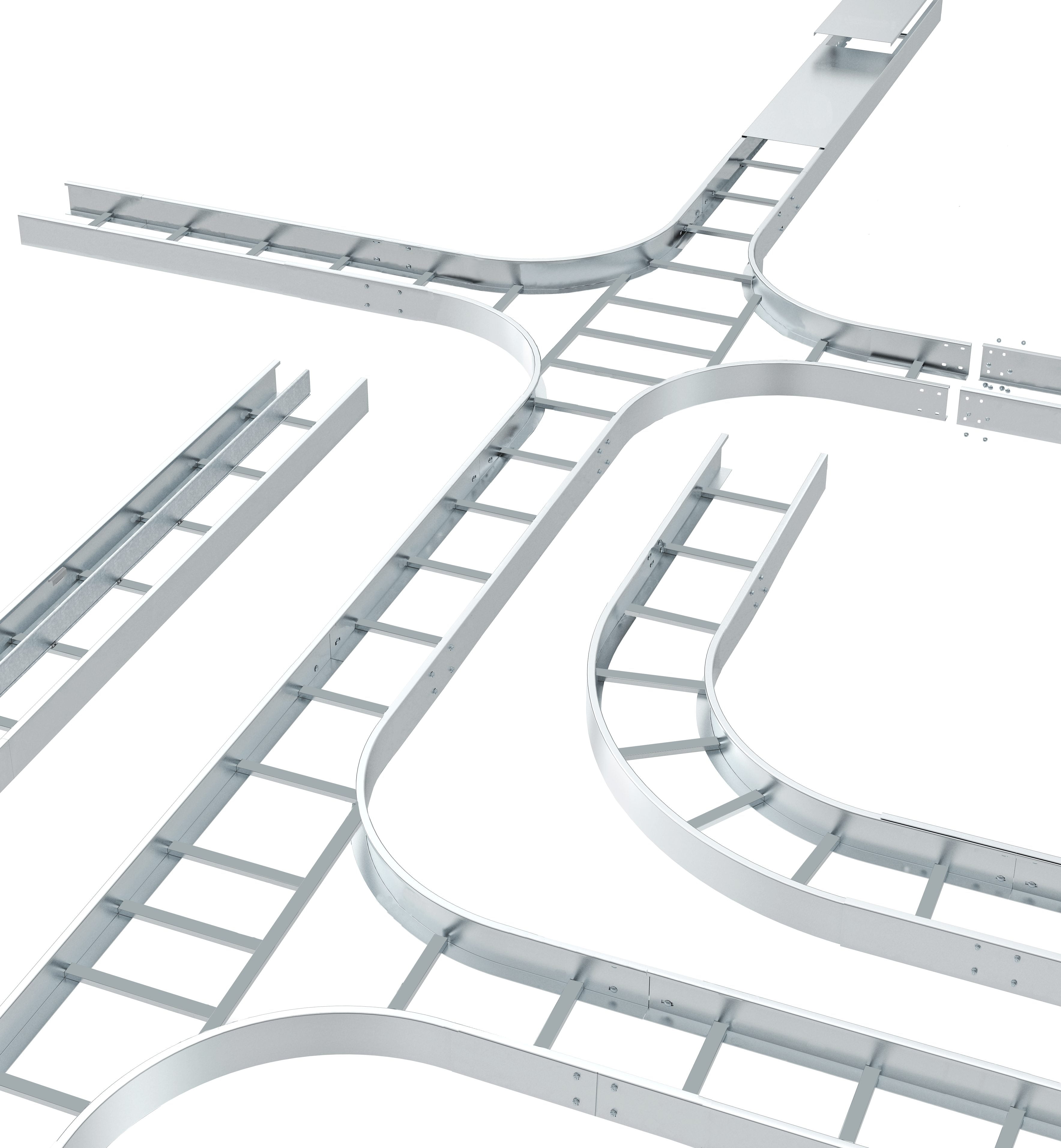
Cable ladder
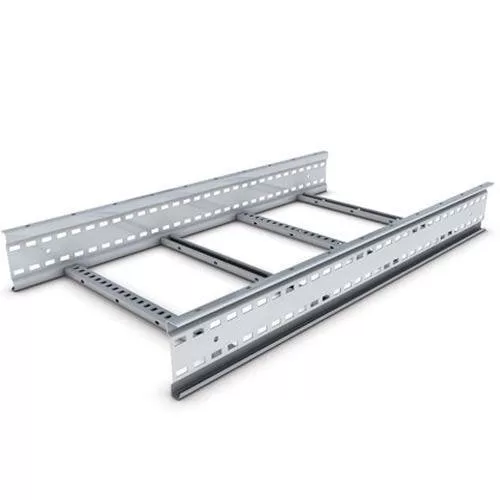 As the name suggests, ladder trays look like ladders and are suitable for a wide range of applications, such as appliances, communications and electrical cables.
As the name suggests, ladder trays look like ladders and are suitable for a wide range of applications, such as appliances, communications and electrical cables.
These ladder trays can support heavy cables and the advantages of ladder trays are that cables are free to enter/exit anywhere
Along the length of the stair tread and due to the open nature, it is able to allow the cables to “breathe” Avoid overheating problems.
Ventilated cable runner
 A lighter duty type of cable trays are ventilated cable trays which are
A lighter duty type of cable trays are ventilated cable trays which are
Metal plate with lots of holes/slots so that wires on the tray can be easily fixed and provide a means of ventilation.
Wire network cable runner
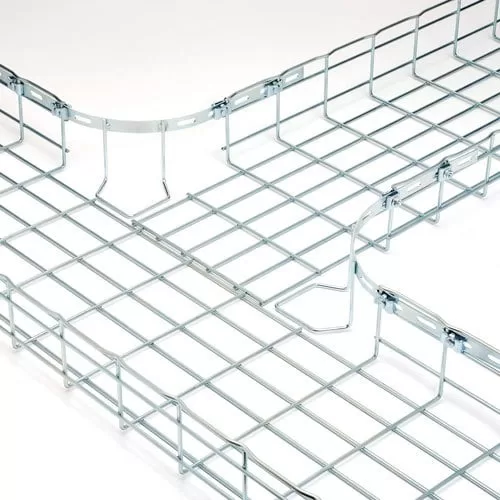 Also known as trey basket cables,
Also known as trey basket cables,
It is made of stainless steel wires welded together and forming a square basket
The shape is crisscrossed to support lighter load wires such as low voltage or Internet cables.
Why do you need to use cable runners to install cables?
A cable tray is an important element to add to any wiring setup.
By adding a cable tray, you can organize, support and move your cables efficiently.
 Most people would think their homework is done when they find the right professional to install the wiring system at their business.
Most people would think their homework is done when they find the right professional to install the wiring system at their business.
In fact, the job is only half done if you haven’t looked up the difference between a conduit system versus a conduit (tray) cabling system.
The TRA cable market is growing in size and popularity for a reason.
There are great advantages that make you consider installing three-way cables.
Keep reading to learn what it is and why choosing it will benefit you now and in the long run.
What are cable trays?
Cable trays are one way you can organize and support your cables.
They are increasingly used, and are often a better alternative to channels.
The main problem with duct systems for distributing telecommunications cables is that they are often complicated to install and thus become expensive.
A great deal of time and skill is required to install good level duct.
Conduits can be expensive to implement and service when you get them.
This can take away any of the strengths that channel systems have.
On the other hand, tri-cable systems offer much more advantages and require additional safety cabling.
There are a variety of types you can choose from when you want cable trays to install your company’s infrastructure. there:
Ladder trays
Conduit and wire cable trays
Solid bottom slot cable trays
Basins
 If you’re not sure which type of trey cable is right for you, you should talk to a professional before adding it.
If you’re not sure which type of trey cable is right for you, you should talk to a professional before adding it.
- You get greater savings
When you want to save money as a business, choosing cable trays is the perfect choice.
This starts right away because cable trays offer a lower installation cost.
Installing cable trays takes less time.
Since a professional can complete the work faster, you pay less for time and labor.
This is ideal for those who want to install seamless fiber optic cables or copper cables.
Another way you can save money is that cable trays will help preserve the life of your cables and improve their performance in the long run.
The design of the cable trays also results in significant savings.
It has unique features that allow any cable to enter or exit along the way.
This provides further convenience or modification of wires and cables whenever you need them.
Cable trays simplify the process of the entire wiring system as details need to be reduced before installation.
This is the opposite of standard duct systems which need a more complex design due to the need for splice or pull boxes, and tighter tolerances on capacity.
- The wires will look neat and clean
Cable trays have an advantage over standard wire installations because they provide a neater, cleaner look.
Although you may need several types of cable to run different systems, that doesn’t mean you need to see all those differences in size and color.
The bundles of wires you leave outside can be unattractive to look at.
However, with the addition of cable trays, you can eliminate that.
The clean appearance will be attractive to your eyes as well as other visitors.
If you have people – especially customers and potential customers – visiting your place, you want to make the area look as inviting as possible.
A clean residence or working environment can only benefit you.
- Enhance safety
When you expose your wires, not only do you have to deal with them getting in your way, but you also put your overall safety at risk.
Poorly installed cables can pose a significant risk.
When you have wires lying around, especially on the floor, you increase your chances of slips, falls, and other accidents.
These are the types of accidents you want to avoid in businesses when you have workers and customers.
Good cable management can prevent these accidents from occurring in your company.
You can also reduce the chances of spills on wires that could damage them or the equipment connected to them.
 More flexibility options
More flexibility options
Tri-cable systems are also convenient because they offer flexible options for those who want to switch now or later.
If you already have a conduit system and want to switch to cable trays, you can do so without major complications.
If you decide to move your devices, cable trays are adaptable and can meet the requirements.
While you may have to limit the number of wires or cables you can install in conduits, there is less of a limit with cable trays.
Installing cable trays is also quick and less labor intensive compared to a conduit system.
Returning “online” To do your work easier. With proper installation, cable trays will cost you less to maintain.
- It is perfect for indoors or outdoors
The quality of the cable holders is durable and you can install them almost anywhere.
If you decide you want your cable trays indoors
You will be happy to know the support it provides and how useful it is in reducing risks.
The same goes if you want to install cable trays outdoors.
The right cable runners will withstand environmental elements such as wind, snow, rain or ice.
Even outdoors, the right cable runners resist corrosion.
Order high quality TRA cable online
Millions depend on quality companies and professionals who can install their own conduit (tray) cabling system.
Construction sites, companies, manufacturers, and even the typical homeowner depend
To receive energy, telecommunications, IT and television services using a ducted (Tray) cabling system.
You should always work with an experienced professional to help you install cable trays the right way.
It’s more than worth the cost.
You can supply them with the parts you want or install the cable trays yourself if you feel comfortable.
Jezly distributes a variety of cable duct solutions.
If you’re not sure what type you should get and what to look for, you can get the help you need by contacting us.
Talk to the team for help choosing the right products for your requirements.
 Cable duct materials:
Cable duct materials:
Most cable conduit systems are manufactured from corrosion-resistant metal
(low carbon steel, stainless steel or aluminum alloy) or of a metal with a corrosion-resistant finish (zinc or epoxy).
The choice of material for any given installation depends on the installation environment (corrosion and electrical considerations) and cost.
(1) Aluminum:
Extruded aluminum cable trays are often used due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, superior resistance to some corrosive environments, and ease of installation.
They also offer the advantages of being lightweight (about 50% lighter than tri-steel) and maintenance-free
And, since aluminum cable trays are non-magnetic, electrical losses are reduced to a minimum.
Tri cable products are machined from 6063 series alloy which is, by design, a copper-free alloy for marine applications.
These alloys contain silicon and magnesium in appropriate proportions to form magnesium silicate, allowing them to be heat treated.
This silicon-magnesium alloy has good formability and structural properties, as well as excellent corrosion resistance.
The extraordinary resistance to corrosion, including weathering, that aluminum exhibits is due to the self-healing aluminum oxide layer that protects the surface.
Aluminum’s resistance to chemicals should be tested in the application environment prior to installation.
(2) Steel:
Steel cable trays are manufactured from high quality steel using a continuous roll forming process.
Forming and extrusion increases mechanical strength.
The main benefits of trey steel cable runs are their high strength and low cost.
Disadvantages include high weight, low electrical conductivity, and relatively poor corrosion resistance.
The rate of corrosion varies depending on many factors such as the environment, coating or protection applied and the composition of the steel. T & B Finishes and coatings to improve steel’s resistance to corrosion.
These include pre-galvanized, hot-dip (after fabrication), epoxy and specialty paints.
(3) Stainless steel:
Stainless steel provides high yield strength and high creep strength, at high ambient temperatures.
The stainless steel cable tray is made of AISI Type 316 stainless steel.
Stainless steel is resistant to dyeing, organic chemicals and inorganic chemicals at high temperatures.
Higher levels of chromium and nickel and a lower level of carbon increase corrosion resistance and facilitate welding.
Type 316 includes molybdenum to increase resistance to high temperatures and improve corrosion resistance
, especially for chloride and sulfuric acid. The carbon content is reduced to facilitate welding.
 Hungarian finishing (Tray) cables
Hungarian finishing (Tray) cables
(1) Galvanized coatings
The most commonly used coating for trey cable conductors is galvanization.
It is cost effective, protects against a wide range of environmental chemicals,
It self-heals if the area becomes unprotected through cuts or scratches.
Steel is plated with zinc through electrolysis by dipping the steel in a bath of zinc salts.
A combination of carbonates, hydroxides and zinc oxides forms a protective layer to protect the zinc itself.
Corrosion resistance is directly related to the thickness of the coating and the harshness of the environment.
(2) Pre-galvanized:
Pre-galvanized, also known as mill galvanized or hot mill galvanized is produced
, in the rolling mill by passing steel coils through molten zinc.
These files are then slit and manufactured.
Areas not normally covered during manufacturing, such as cutting and welding, are protected by adjacent zinc
, which acts as a positive electrode. During welding, a small area is also left directly affected by the heat, but the same self-healing process occurs.
G90 requires a coating of 0.90 ounces of zinc per square foot of steel, or 0.32 ounces per square foot on each side of sheet metal.
According to A653/A653M-06a, pre-galvanized steel is not recommended for outdoor use or in industrial environments.
(3) Hot-dip galvanized:
After the steel cable tray is fabricated and stripped, the entire container is immersed in a bath of molten zinc
, which leads to the coating of all surfaces, as well as all edges, holes and welding.
The thickness of the coating is determined by the length of time each part is immersed in the bath and the speed of removal.
Post-fabrication hot-dip galvanization produces a thicker coating than the pre-galvanized process,
A minimum of 3.0 ounces per square foot of steel or 1.50 ounces per square foot on each side of the plate (according to ASTMA123, Grade 65).
This process is recommended for cable trays used in most outdoor environments and many harsh industrial environment applications.
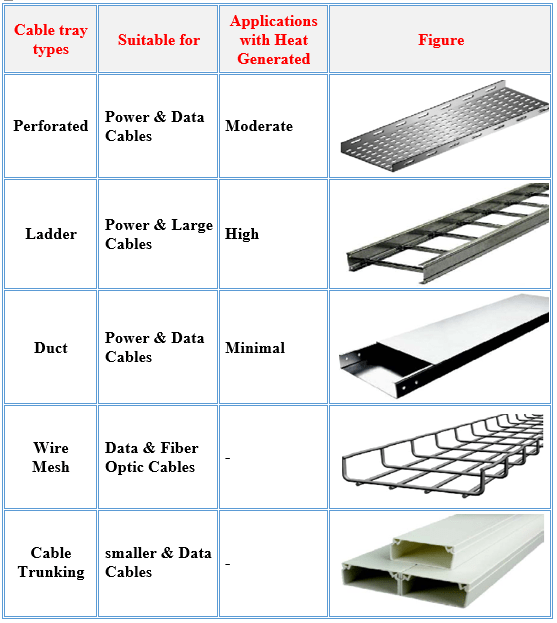
Types of cable trays:
- Cable trays are made of either steel, aluminum or fiber reinforced plastic (FRP) and are available in six basic types,
- Ladder type cable duct
- Bottom solid cable duct
- Dock cable duct
- Conduit cable runner
- Wire network cable runner
- Single rail cable runner
(1) Tray ladder cable
Generally used in applications with medium to long supports spanning 12 to 30 feet.
Ladder cable runners are used for approximately 75 percent of cable runner wiring system installations.
It is the prevailing cable tray type due to several desirable features:
Ladder cable tray without covers allows maximum free airflow through the cables.
This allows the heat produced in the cable conductors to dissipate effectively.
Under these conditions, the conductor insulation in a properly designed cable system will not exceed the maximum operating temperature.
Cables will not age prematurely due to excessive operating temperatures.
Ladder cable trays provide convenient fastenings for tying cables in non-horizontal cable trays or where cable positions must be maintained in horizontal cable trays.
This capability is necessary for single conductor cable installations.
Under fault conditions (short circuit), the magnetic forces generated by the fault current will force the cables
The individual conductor of the cable run if it is not securely fastened to the cable run.
Cables may exit or enter ladder cable trays through the top or bottom of the cable tray.
When cables enter or exit the conduit, the conduit clips to the cable tray may be installed loosely
Vertical or inverted to terminate channels at the top or bottom of the side rail of a cable tray.
Moisture cannot accumulate in ladder cable trays
 If cable trays are installed where there is a workspace problem
If cable trays are installed where there is a workspace problem
Manual access through a cable tray may help facilitate the installation of small diameter cables:
Control and signaling devices, etc.
The most common rung spacing for ladder cable runs is 9 inches.
This spacing can be used to support all cable sizes.
This spacing is desirable for small diameter cables of type PLTC and TC as at the support distance there is no visible drooping of small cables between the rungs.
12- or 18-inch rung spacing provides adequate cable support
, but a small amount of small-diameter cable droop between the rungs may be aesthetically unacceptable in some installations.
The maximum allowable spacing between supports for 1/0 to 4/0 AWG single conductor cables is 9 inches [1993 NEC Section 318-3(b)(1)].
Ducted ventilation (Tray) cables
The only reason to choose a ventilated tub cable tray over a ladder-type cable tray is aesthetics.
It shows no dangling of small cables.
The Ventilated Dock Cable Tray provides more support for cables than a ladder cable tray but this extra support is not significant.
It has no effect on cable service history or life.
features:
Solid side rail protection and system strength with soft radius mounts.
Maximum strength for long range applications
Standard widths 6, 12, 18, 24, 30 and 36 inches
Standard depths are 3, 4, 5 and 6 inches
Standard lengths are 10, 12, 20 and 24 feet
Step spacing is 6, 9, 12 and 18 inches.
(2) Solid base cable ducts:
Generally used for minimal heat generation for electrical or telecommunications applications with short to medium support spans of 5 to 12 feet.
The main reason to choose a solid bottom cable tray (with covers) is to take care of EMI/RFI shielding for highly sensitive circuits.
The solid base steel cable tray with steel covers provides a good degree of protection when there are no breaks or holes in the completed installation.
A solid-base cable duct system has the disadvantage that moisture can accumulate in the cable trays.
This can be controlled by drilling 1/4 inch drainage holes in the bottom of the cable tray
At three-foot distances (in the middle and very close to the sides) if two strands of cable are not used for EMI/RFI shielding.
Some engineers and designers specify solid cable trays (often with covers) in the belief that all electrical circuits should be completely enclosed in metal.
Cable trays only support cables designed for such installations.
Cable failures rarely occur in cable ducts.
There are no cable failures due to cable support issues in cable trays.
features:
Continuous, breathable support for sensitive cables with additional cable protection available in metal and fiberglass
Solid metal bottom with solid metal covers for imperfectly rated cables in environmental areas
Standard widths 6, 12, 18, 24, 30 and 36 inches
Standard depths are 3, 4, 5 and 6 inches
Standard lengths are 10, 12, 20 and 24 feet
(3) Dock cable duct
Generally used for moderate heat generation applications with short to medium support spans – 5 to 12 feet
 features:
features:
Moderate ventilation with additional cable support frequency – with the bottom configuration providing cable support every four inches.
Available in metallic and non-metallic materials
Standard widths 6, 12, 18, 24, 30 and 36 inches
Standard depths are 3, 4, 5 and 6 inches
Standard lengths are 10, 12, 20 and 24 feet
Fixed step spacing of 4 inches on center.
(4) Conduit cable runner
Used for installations with a limited number of tray cables when conduit is not desired.
Support hesitation with short to medium support extending 5 to 10 feet.
features:
Economical support for cable drops and sub-cables runs from a core cable conduit system
Standard widths are 3, 4 and 6 inches in metal systems and up to 8 inches in non-metallic systems
Standard depths of 1 1/4 to 1 3/4 inches in metal systems and 1, 1 1/8, 1 5/8 in non-metallic systems
Standard length is 10, 12, 20 and 24 feet.
(5) Three-way wire network cable
Generally used for telecommunications and fiber optic applications, installed over short support spans – 4 to 8 feet.
features
Job site, adaptable field support system mainly for low voltage cables, telecommunications and fiber optics.
These systems are usually steel wire mesh and zinc plated
Standard widths 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 18, 20, 24 inches
Standard depths are 1, 2 and 4 inches
Standard length is about 10 feet.
(6) Tray monorail cable
They are generally used in low voltage and electrical cable installations where maximum cable freedom, lateral packing and installation speed are factors.
features
These aluminum systems are the quickest to install and provide maximum freedom for the cable to enter and exit the system
Suspended or wall-mounted systems in single or multiple layers
Standard widths are 6, 9, 12, 18 and 24 inches
Standard depths are 3, 4 and 6 inches
Standard lengths are 10 and 12 feet.
Thermal expansion and contraction of cable ducts:
The cable duct system may be affected by thermal expansion and contraction, which must be taken into account during installation.
To determine how many stretch splice panels you need,
Determine the run length of the straight cable tray and the total difference between the minimum winter temperatures
The maximum temperatures in summer.
To function properly, expansion splice panels require precise gap settings between the trays.
The support should be installed closest to the midpoint between the expansion splice panels, allowing longitudinal movement of the tray in both directions.
When using a cable duct system as an equipment grounding conductor,
It is important to use jumpers in all expansion joints to keep the electrical circuit continuous.
| MAX DISTANCE BETWEEN EXPANSION JOINTS (For 1” Movement) | ||
| Temperature Differential (oF) | Steel (Feet) | Aluminum(Feet) |
| 25 | 512 | 260 |
| 50 | 256 | 130 |
| 75 | 171 | 87 |
| 100 | 128 | 65 |
| 125 | 102 | 52 |
| 150 | 85 | 43 |
| 175 | 73 | 37 |
 To know our latest products and special offers, please subscribe to our social media pages:
To know our latest products and special offers, please subscribe to our social media pages:
Our Facebook page=> Gahzly store
Our Twitter page=> Gahzly store













Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.