Explanation of MCB circuit breakers
Explanation of MCB circuit breakers
 Explanation of MCB circuit breakers
Explanation of MCB circuit breakers
Explanation of MCB electrical breakers. There are many types of electrical breakers that are frequently used in electrical installations
Some of them are used with medium voltages and are known as “Power Circuit Breakers”.
There is another type used in the low voltage network and is abbreviated with the three letters MCB.
What are MCB electrical breakers, how do they work, and what are the categories of breakers that are used in electrical installations?
MCB circuit breakers
MCB circuit breakers
 MCB: Short for “Miniature Circuit Breaker”.
MCB: Short for “Miniature Circuit Breaker”.
This type of breakers is available with several poles, such as: a single-pole breaker (1Pole), a two-pole breaker (2Pole),
3-pole breaker, 4-pole breaker.
The MCB circuit breaker is used with 3-phase circuits and 1-phase circuits.
Its main mission, in short, is protection from the palace current.
It can also be said that it is used to separate faults with low current and continuous for a long period.
MCB circuit breakers poles
Electrical circuit breakers come with a variety of rated current capacities, starting from 1 amp up to 125 amps. The most popular capacities that are used in electrical installations are:
| 6A | 10A | 16A | 20A | 25A | 32A | 40A | 50A | 63A | 80A | 100A | 125A |
Rated current capacity of MCB circuit breakers
The MCB electrical breakers used in home installations are called semi-automatic breakers because they disconnect automatically, but
When connecting it again, the connecting rod must be lifted up manually.
It is wrong to call the breakers used in homes automatic breakers
Rather, we should say semi-automatic circuit breakers because they only disconnect automatically.
What is the role of the MCB circuit breaker?
It is used to protect final distribution circuits.
That is, the breaker is located in the closest place so that it protects the electrical load from any possible fault, such as a short circuit.
The relationship between the fault current (measured in multiples of the rated current) and the trip time (measured in seconds) is determined through the three categories:
D, C, B according to the international standard specifications IEC Standard with some related data.
Categories of MCB circuit breakers
 There is a category for each cutter, including:
There is a category for each cutter, including:
Class B breaker: The operating limits of the magnetic trip for this type range from 3 to 5 times the rated current of the breaker.
Which makes it suitable for protecting resistive loads such as: heaters and tungsten bulbs.
Class C breaker: It has the same characteristics as type B, but the delay time for this type is greater and the instantaneous disconnection current is higher.
As its start ranges between 5 to 10 times the rated current of the breaker, it is suitable for protecting inductive loads, such as:
Motors, air conditioners and fluorescent lamps.
Class D breaker: This class is characterized by a longer instantaneous disconnection time than Class C, as it ranges between 10 to 15 times the rated current of the breaker.
This makes it suitable for loads with high inductance, such as transformers or electric welding machines.
Categories of MCB circuit breakers
Explanation of MCB circuit breakers
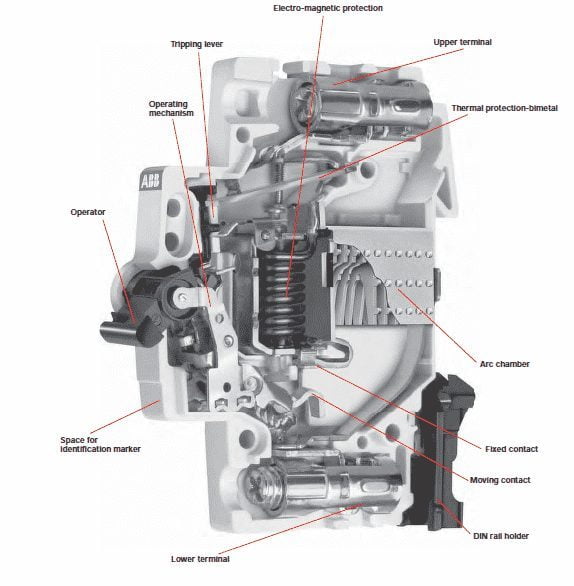
The MCB circuit breaker consists of the following parts:
- Plastic lever: used to connect the circuit manually, and disconnect it manually or automatically when a short circuit occurs or when the load increases exponentially.
- Movement mechanism: It connects and separates the cutter’s internal contact points.
- Metal contact point: It connects and separates the current entering the breaker.
- Poles or connection terminals: There are two terminals, one of which connects to the phase line of the electricity source, and the other connects to the load.
- Bi-metallic strip: Its function is to separate the circuit from the load, by stretching one of the two strips more than the other according to the value of the overload current. The more the load current exceeds the rated breaker current, the greater the disconnection time decreases.
- Electromagnetic coil: Its function is to automatically disconnect the breaker as soon as a high short current passes through it.
- Arc divider or damper.
MCB circuit breaker components
MCB circuit breakers data
Usually, important data is written on electrical circuit breakers, which are:
Rated current: symbolized by the letters In,
It is the maximum value of current that it can withstand at a certain temperature without disconnecting or heating up.
Example: If the rated current In of a circuit breaker is 100 amps at a temperature of 40 degrees Celsius,
We expect that at a temperature of 50 degrees Celsius, the rated current will decrease to 92 amps, and so on with the rest of the various breakers.
Instantaneous separation current: It is symbolized by the letters Im,
It is the lowest value of the short circuit that activates the breaker within a very short period (fractions of a second).
The value of the current ranges from 3 to 10 times the value of the rated current.
Conventional separation current: It is symbolized by the letters Ir or Irth, and it is also called thermal separation current.
It is the current resulting from overloading for a relatively long period of time, which leads to heating and expansion of the double metal strip, which results in the circuit breaker disconnecting.
Short circuit: It is symbolized by the symbol Icu or Icn, and it is the maximum value of the current that the breaker can disconnect without damage.
Rated Voltage: Symbolized by the letters Ue, it is the value that the breaker operates at in the normal state.
Insulation voltage: Symbolized by the letters Ui, it is the value that the breaker can isolate as long as it is less than the value of the insulation voltage.
It must be equal to or greater than the rated voltage (breaker voltage).
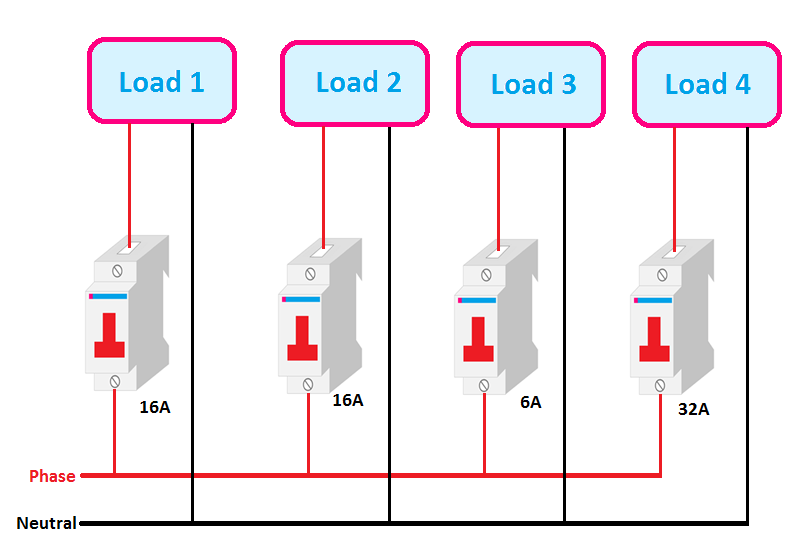
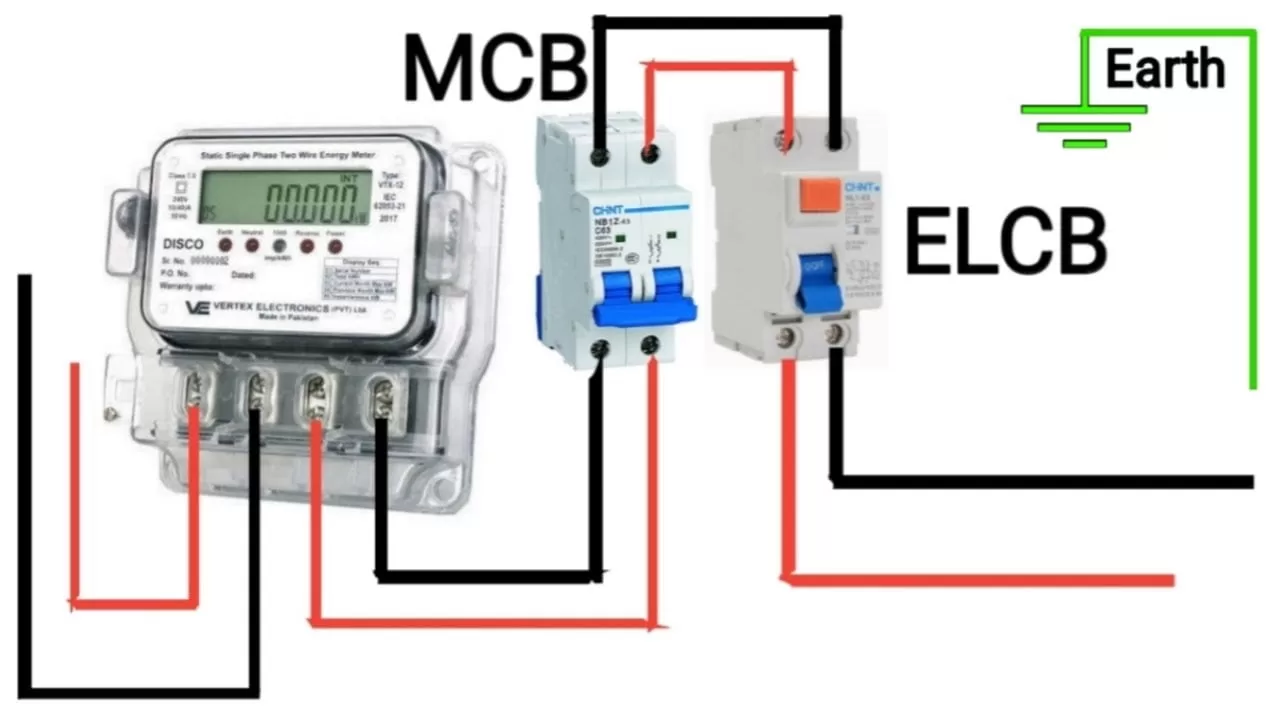 Connecting MCB circuit breakers
Connecting MCB circuit breakers
 To know our latest products and special offers, please subscribe to our social media pages:
To know our latest products and special offers, please subscribe to our social media pages:
Our Facebook page=> Gahzlystore
Our Twitter page=> Gahzlystore









Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.