Information about plugs and sockets
Information about plugs and sockets
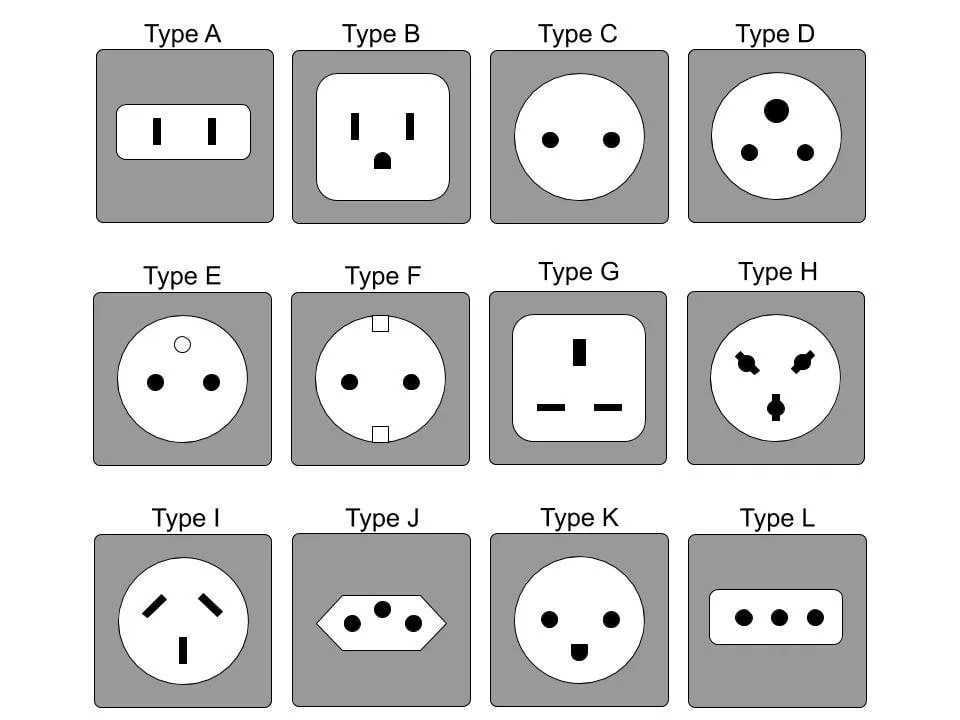 Information about plugs and sockets
Information about plugs and sockets
Plugs and sockets help meet the electrical need.
For the device to be connected to an alternating power (AC) source, there are two options:
Hard wire, power cable assembly or wiring harness.
Hardwiring, which makes a direct connection to an electrical circuit, requires a qualified electrician to connect/disconnect the device.
A power cable or wiring harness provides the user with a way to operate the device correctly and safely
By easily plugging/disconnecting the plug to/from the appropriate electrical outlet.
When electricity was first introduced in the late 19th century, it was used mostly for lighting purposes.
Home appliances began to be invented in the early 1900s, and new ways of connecting to a power source had to be created.
This led to individual countries developing their own style of plugs and sockets.
There were early efforts dating back to before World War II to try to start a single plug style globally
But the idea never caught on.
The discussion in the 1950s about standardizing a single plug worldwide came too late
, as many countries already had their own electrical connections in homes and businesses and were not willing to change to a new component design.
Today, manufacturers designing for global markets must realize that there are many different component styles.
They will need to specify which one is used in the country they are exporting to.
It is important to select the correct plug so that it connects securely to the power source.
Most plugs and sockets follow national and/or international standards that dictate physical and electrical characteristics
In addition, many countries have testing/certification agencies that specify specific plug/socket requirements that must be followed.
Jezly offers help in choosing the right plug style with a guide to plug styles, universal sockets and power switches (single phase).
This guide provides the most specific plug styles for electrical or electronic devices used in individual countries.
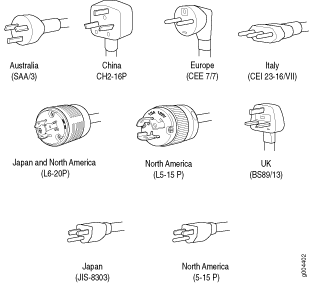 Basic elements in product design
Basic elements in product design
It is important to determine the following about plugs and sockets when designing and building a product.
Voltages and frequencies
In addition to the different delivery styles available,
There are also different voltages and frequencies that play a role,
Which varies in different regions of the world.
In many industrialized countries, voltages run at 120V or 230V (except Japan which uses 100V),
But it can operate at voltages between 100-250V.
Some countries use multiple voltages.
North America, part of South America, part of Japan, and a few other countries operate on 60 Hz.
Most of the rest of the world runs on 50 Hz.
There are some countries that work on both, such as Japan.
Ratings
The plug and socket have a maximum voltage and amperage rating.
Rankings are determined by national and/or international standards.
They are set for safety purposes and are often higher than the actual voltage measurement when in use.
For example, if a continental European plug is rated for 16 amps at 250 volts,
It is unlikely that there will be a constant current of 16 amps at 250 volts flowing through the electrical connection.
European voltage is standardized at 230 volts.
In the United States, the National Electrical Code specifies a standard for common household use to be 120 VAC.
The first category and the second category
Plugs and sockets can be classified for Class I or Class II applications.
In a Class I application, the component must have the ability to provide grounding.
In a Class II application, no basis is required.
Although some electrical systems in developing countries may not be grounded
It is not recommended to cut the ground pin of a Class I plug so that it can be installed in an ungrounded two-pole receptacle.
This eliminates the safety ground connection and will cause the plug or socket to lose its compliance. It is best to use a class plug
II in a power cord or wiring harness, rather than changing a Class I harness.
Polarized and non-polarized
Polarization can have two meanings: electrical or pin.
Electrical polarization means that there is a standard way to connect a plug or socket to a circuit’s wiring.
The circuit wires need to be properly connected to the line, neutral and ground contacts on the plug and socket.
Components reflect the electrical circuit.
Pin polarization means there is a custom alignment of the pins — there is only one way to fit the plug into the socket.
Note: Even though a plug is pin polarized, it does not necessarily mean it is electrically polarized as well.
All polarized and non-polarized plugs will fit a polarized socket, but polarized plugs will not fit a non-polarized socket.
The need for one or the other is specific equipment – what is needed within the internal circuitry of the device.
It depends on whether the final product requirements need a specific electrical path for the line current
, or whether it doesn’t matter which part of the power is connected to the internal circuit.
![]()
Approvals
It is also necessary to include the correct plug and socket in the product design in order to follow the specific standard of the export country.
In most countries, approval documents are required for the final product to be accepted in that country.
Country-specific information
NEMA numbering system
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) has a variety of standards for electrical manufacturers.
This is so consistency and safety can be achieved.
A numbering system was created to standardize the description and classification of NEMA plug and socket styles.
The NEMA pattern and numbering system consists of four main identifiers.
First identifier
The first identifier can be empty or contain the character “L.”
This determines whether the machine will use straight blades or locking blades.
The second identifier
The second identifier is the number that identifies the voltage rating. For example:
The number “1” The configuration is rated for 125VAC, Class II
Defines the number “5” The configuration is rated for 125VAC, Class I
Defines the number “6” The configuration is rated for 250VAC, Class I
The rating given is the highest voltage allowed for use with the device according to ANSI/NEMA WD-6 standard
. In a Class I application, the component must have the ability to provide grounding.
In a Class II application, grounding is not required.
The third identifier
The third identifier is also a number. This determines the current rating.
Current rating, such as voltage rating,
It is the highest current allowed to be used with the device by the standard.
The fourth identifier
The fourth identifier is a letter.
The letter “P” stands for to the plug while the letter “R” stands for To the receptacle (also referred to as an outlet or socket).
Examples
The 1-15R is a 125-volt, Class II, 15-amp receptacle.
L5-20P is a locking, 125 volt, class 1, 20 amp plug
6-15P is a 250 volt, class 1, 15 amp plug
NEMA connection patterns
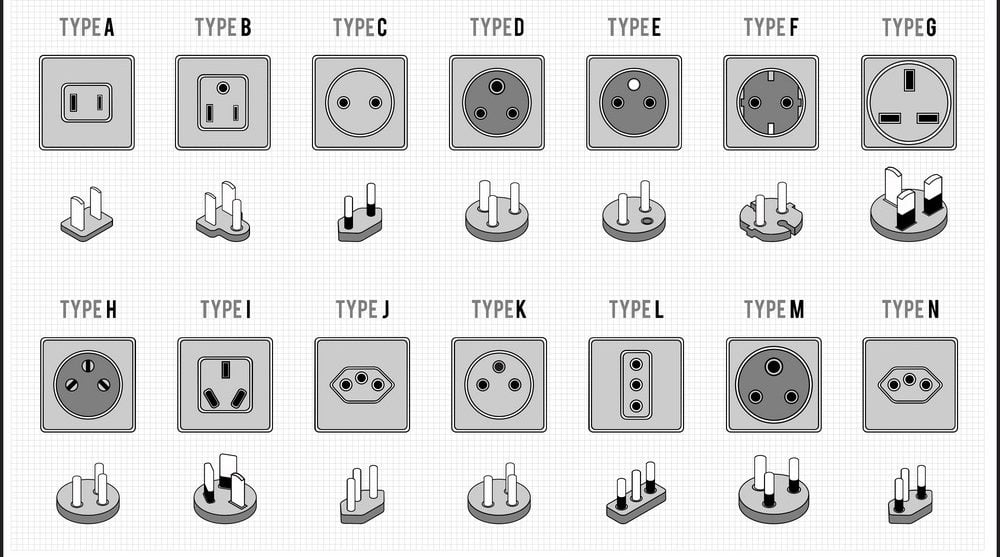
| NO 1-15P | NO L1-15P | ||
| NO 5-15P | NO L5-15P | NO 5-20P | NO L5-20P |
| NO 6-15P | NEMA L6-15P | NO 6-20P | NEMA L6-20P |
UK Plug and Ring Wiring System
The UK plug and socket system began before World War II at a time when there was a shortage of copper for cables.
This lead ring system is designed to help reduce the amount of copper needed for cable wiring within homes and buildings.
Part of the purpose of this system is to enable the ground circuit to handle the current that could blow the fuse in the plug due to a sudden short circuit.
Circuits leave the local branch protection device, travel to loads (outlets or lamps, for example), and then return to the circuit protection device.
 A fault condition in an outlet, for example, will be obtained by current from both directions.
A fault condition in an outlet, for example, will be obtained by current from both directions.
This helps reduce the amount of heat generated in the conductor, where the fault condition occurs, but before the circuit protection device can clear the fault.
By reducing the heat generated, insulation degradation (which accompanies overheating due to frequent fault conditions) is also reduced.
, leading to improved long-term safety of the insulation system.
Until the circuit protection device clears the fault, the fault condition is obtained from two different directions in the supply system.
So there is a much larger potential fault current condition at the socket/wire junction.
Having a secondary protective device in the plug helps reduce the safety risks created by this case;
Hence, the power plug fuse.
The fuse installed in UK sockets complies with BS 1362
. The time-current characteristic of this group of fuses does not necessarily conform to any other standard, but it appears to have most of the characteristics of a fast-acting fuse.
Hospital grade plugs and sockets
When designing, building or maintaining hospital-grade products,
It is necessary to know whether there are medical standards or other requirements in the product of the country being used.
While some countries/regions have medical standards or recommendations, some hospitals may also have requirements that they choose to follow that are specific to their facilities.
For more information about the hospital-grade products offered by Jezly, see Design, Build and Maintain Hospital-Grade Products and Hospital Grade Products.
Design for global markets
It is necessary to offer products that can be easily adapted to the needs of the export market, without the need for rebuilding by the user.
Today’s customers expect to unpack the product and start using it as is, so knowing the electrical requirements of where the product will be used is crucial.
 Plugs can be shaped or re-plugged.
Plugs can be shaped or re-plugged.
Cast (non-rewireable) parts cannot be modified after they are manufactured.
The reconnectable part can be disassembled and wired again after initial assembly with a different cable.
Jezly carries a variety of plugs and sockets designed to meet electrical needs around the world.
Most plugs are available as part of a power cord or molded cord set and many are available as re-pluggable.
Product specifications can be found on the website for both plugs and sockets available through Jeezly.
These may include dimensions, panel cutouts, wire strip lengths,
and proper wiring information, flammability ratings, maximum current and voltage ratings.
Most of Jezli products have agency approvals.
Jezly provides free technical support.
For further assistance, contact customer service
 To know our latest products and special offers, please subscribe to our social media pages:
To know our latest products and special offers, please subscribe to our social media pages:
Our Facebook page=> Gahzlystore
Our Twitter page=> Gahzlystore












Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.