What is an overload relay: its types and applications
What is an overload relay: its types and applications
 Overload is an electrical device used to protect an electric motor from overheating.
Overload is an electrical device used to protect an electric motor from overheating.
It is therefore essential to have adequate engine protection.
The electric motor can be started safely with the help of overload relays, fuses or circuit breakers.
But this relay protects the motor while the fuse circuit breaker protects the circuit.
More intentionally, fuses, as well as circuit breakers, are intended to detect excess current within a circuit
, while the relay is intended to detect overheating in the event of an electric motor heating up.
For example, it can troubleshoot overload without tripping the CB (circuit breaker)
. One does not restore the other.
This article discusses an overview of overload, its types and how it works.
What is an overload relay?
Overload can be defined as an electrical device designed primarily to mimic the heating patterns of an electric motor
, In addition to breaking up the current flow when the heat detector in the relay reaches a constant temperature.
An overload can be designed using a coupled heater with generally closed connections that open when the heater gets too hot.
The connections of this relay can be made in series as well as placed between the motor and the contactor itself to avoid restarting the motor on overload trips.
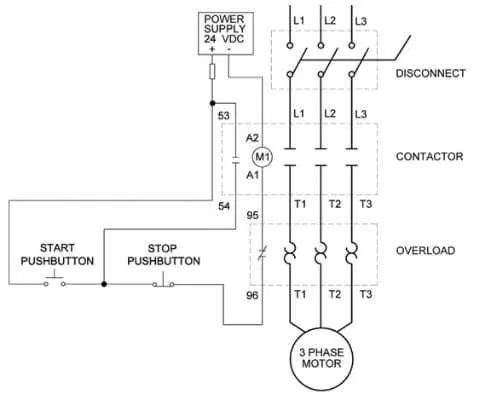
Contact diagram
The wiring diagram of the overload relay is shown below,
Overload relay symbol connections may look like two opposite question marks otherwise such as the “S”
. The working/function of Overload is discussed below.
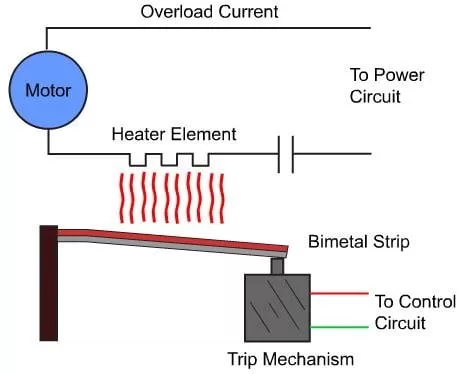
Although there are several types of overload relays available in the market, the most common type of relay is the “bimetal thermal overload”.
This relay can be designed using two different types of metal strips, and these strips can be mutually connected as well as enlarged at various rates during heating.
When the tape is heated to a certain temperature, the tape can twist enough to break this circuit.
 Overload relay diagram
Overload relay diagram
When the current flow towards the motor is more than what the heaters are being charged for,
The overload will be detected after a few seconds. Overload categories can be classified into three types based on the duration of exploration of the sequence.
Class 10, Class 20 and Class 30 overload relays can be probed after 10 seconds, 20 seconds and 30 seconds respectively.
One of the main safety properties of this relay is to prevent the engine from restarting immediately.
For example, when it detects an overload inside a bimetal relay, the NC (normally closed) bimetal connections will open the circuit until the strip cools down.
If anyone tries to press the start switch to close the contactor switches, the engine will not start.
Relay overload working
The operating principle of Overload is based on a thermoelectric property within a bimetallic strip.
This can be arranged in a motor circuit such that current flows to a motor using its electrodes.
When the current flow increases from the constant value, the bimetallic strip is heated and then bends.
These relays always work with contactors.
Once the bimetallic strips are heated, the contact trip can be energized and break the power supply towards the contactor coil, de-energized and break the current flow towards the armature.
The time taken for tripping is always inversely proportional to the current flowing throughout the relay.
Therefore, these relays are called current dependent relays as well as reverse time delay relays.
This relay can be connected to the motor in series so that the current flow is towards the motor.
When the motor is energized, the motor flowing throughout the OLR will be present.
Once the excess current flows through the relay, it will trip at a certain level, therefore, the circuit between the power supply as well as the motor will be opened.
After a preset period, this relay can be reset automatically or manually.
Once the overload is identified and corrected, the motor will be energized again.
Parts of overload relay
Apart from the contacts as well as the bimetallic strip, there are some other parts available in the overload which are discussed below.
the parties
In the relay diagram, the input terminals are denoted as L1, L2 and L3 which are mounted directly towards the connector.
The motor supply can be connected to terminals T1, T2 and T3.
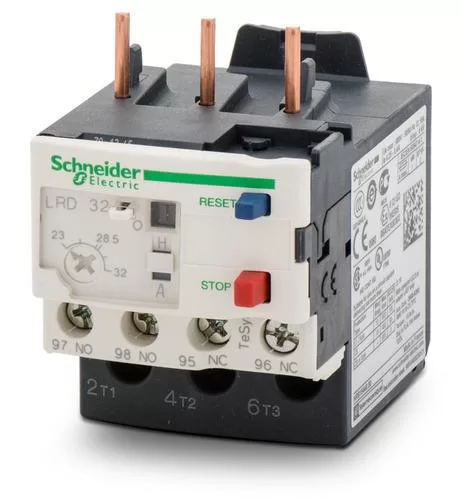
Ampere range setting
Old style rotary knob can be available.
By taking advantage of this, the rated flow of current towards the motor can be adjusted.
The current flow can be adjusted between the upper and lower limits provided. In electronic OLD, an additional knob is also provided to disable the separation selection
Reset button
This button is available via OLD which is used to reset the relay once per trip and clear faults.
Manual or automatic selection button
Using these buttons, one can choose between manual and automatic reset of the relays after a trip.
Once the device is repaired for automatic reset, a remote reset of the relay can be achieved
Assistance point of contact
This relay includes two auxiliary contacts such as one is NO and the other is NC
. For trip signals, no contact is used while for contactor disconnection, NC contact is used
. NC contacts are capable of direct switching of contactor coils.
Test button
The test button is used to check the control wiring.
Types of overload
It is classified into two types: thermal overload and magnetic overload.
Thermal overload
Thermal type relay is a protective device, which is mainly designed to cut off the power when the motor uses too much current for a long period of time.
To achieve this, these relays include an NC (normally closed) relay.
. Once intense current is supplied throughout the motor circuit, the relay opens due to the enhanced motor temperature
, the relay temperature, and the detected overload current, based on the relay type.
 Thermal Overload Relay
Thermal Overload Relay
These relays are connected to circuit breakers in construction as well as application; However, most circuit breakers will disturb the circuit if an overload occurs even momentarily.
These are equally designed to account for the heating profile of the engine; Thus, the overload must occur for a full period before the circuit is disconnected.
Thermal overload relays are classified into two types namely solder pot as well as bimetallic strip.
Magnetic overload
The magnetic overload relay can be operated by detecting the intensity of the magnetic field generated by the flow of current towards the motor.
This relay can be built with a variable magnetic core inside a coil carrying the armature current.
The arrangement of flux within the coil pulls the core upward. When the core gets large enough, it trips a set of contacts on top of the relay.
 Magnetic Overload Relay
Magnetic Overload Relay
The main difference between thermal type as well as magnetic type relays is that magnetic type overload relays do not respond to the ambient temperature.
Generally, these are used in areas that exhibit extreme variations within the ambient temperature.
Magnetic overload relays are classified into two types namely electronic as well as drive plate.
Bi-metallic thermal overload
The operation of the bimetallic thermal overload mainly depends on the heating property of the bimetal strip.
In straight heating technique, the complete flow of current towards the armature can be provided using overload which is also called OLR.
As a result, they are heated directly due to the flow of current.
However, in the absence of direct heating, the strip can be arranged in close contact through the conductor inside the relay.
The intense flow of current towards the electric motor is heated by the conductor and the bimetallic strip.
Here, the conductor must be insulated, hence there will be no flow of current throughout the strip.
 Electronic Overload
Electronic Overload
Typically, electronic overload relays are referred to as solid-state overload relays.
The interior of these types of relays does not contain a bimetallic strip.
Alternatively, it includes current transducers, or temperature sensors to observe the total current flow towards the motor.
For protection, this type of relay uses microprocessor-based technology. Here PTC plays a major role in detecting the temperature and also tripping the circuit once overload faults occur.
Some types of overload relays come with Hall Effect sensors as well as current transformers to detect current flow directly.
The main benefit of an electronic overload over a thermal overload is that it lacks the bimetallic strip which results in less heat loss in the relay.
Also, these types of relays are more accurate compared to thermal relays.
Some manufacturers redesign older electronics by including additional features such as ground fault protection and motor stall.
Electronic overload relays are used where motors need to be turned on and off frequently.
These relays can be designed in such a way that they withstand the primary current of the motor for a limited time
Overload eutectic
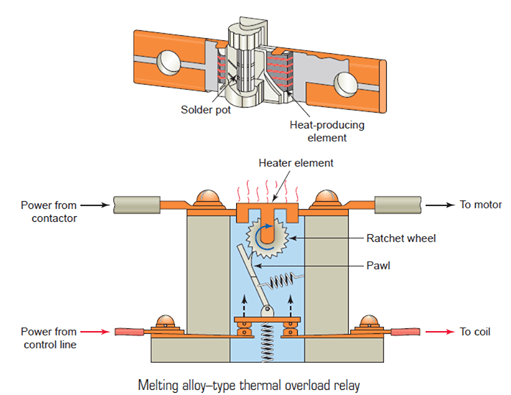
The eutectic overload includes a coil heater, the eutectic alloy and a mechanical device to activate the tripping mechanism.
Here, the eutectic alloy is a mixture of two additional materials
, which would otherwise melt, and solidify at a specific temperature. In OLR,
The eutectic alloy is placed inside a tube for repeated use through a spring-loaded ratchet wheel to activate the tripping device during the overloading process.
Current flows in the motor through the small heater winding during overload,
The eutectic alloy tube can be heated by turning the heater and the alloy melts due to the heat so that the ratchet wheel rotates.
This act begins to open the auxiliary contacts closed within the OLR. This type of relay can be manually reset once tripping is complete.
Therefore, usually, this reset can be done using the reset button, which is arranged on the relay cover.
The heating unit connected via the relay can be selected based on the full load current of the motor.
 Overload for the refrigerator
Overload for the refrigerator
A protective device such as overload is used inside the refrigerator compressor circuit.
The power supply to the compressor motor windings is provided using the overloaded machine.
This type of relay is mainly used to include the starter winding within the circuit so that the compressor runs at operating speed.
How does the OLR guard against phase failure work?
In normal operation of OLR, the current flow through each electrode to the electric motor remains similar every time.
If any phase is interrupted, the current flow through the remaining two phases increases to the usual value.
So the relay and trips are heated.
Phase failures are also called phase loss, otherwise single phase of the motor.
These relays cannot protect against short circuit but must be used with short circuit protection devices to protect them
Otherwise any short circuits inside the electric motor could easily hit it.
These relays can protect against phase loss, phase imbalance, and overload, but not from short circuits.
What causes OLR trip?
From the above discussion, there are three main cases of over-trip:
Engine overload.
Input phase loss
Phase imbalance
There are also some additional security features available but these vary from one designer to another
Overload Trip
The time used to unlock the contactor during overloads can be indicated by the trip class.
Generally, it is divided into different categories such as Class5, 10, 20 and 30.
This relay trips at 5 seconds, 10 seconds, 20 seconds and 30 seconds correspondingly at full load current towards the electric motor.
Commonly used overload relays are class 10 and 20 while class 30 OLR are mainly used to protect motors while operating high idle loads.
Type 5 relays are mainly used for motors that require very rapid tripping.
 Applications
Applications
Overload applications include the following.
It is widely used for engine protection.
It can be used to detect both overload conditions as well as fault conditions and then announce trip commands to the protective device.
This relay has evolved into microprocessor systems as well as solid-state electronics.
These relays de-energize the device when it draws excessive current.
Hence, this is all about Overload overview.
From the above information finally, we can conclude that these are electromechanical overload protection relays used in circuits.
These devices provide consistent protection for motors during an otherwise phase failure.
Here is a question for you, what is the function of Overload?
What is the function of overload?
Overload is widely used to protect electric motors in particular, and it consists of two internal parts:
- Part consisting of a temperature sensor that connects in series with the motor windings.
- Another part consists of connection points to control the connection and disconnection of electrical circuits.
The overload function generally depends on disconnecting the electrical circuit when the motor current exceeds the normal current or when one of the three fuses falls.
What is an overload relay (overload): its types and applications

We are pleased that you visit our social media pages, where we publish exclusive offers on our website.
Our Facebook page Here.
Our Twitter account Here.











Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.