What is e-commerce?
What is e-commerce?
 Electronic commerce or electronic commerce refers to transactions that take place over the Internet.
Electronic commerce or electronic commerce refers to transactions that take place over the Internet.
Every time individuals and businesses buy or sell products and services online, they are engaging in e-commerce.
The term e-commerce also includes other activities including online auctions, online banking, payment gateways and online ticketing.
Now, a little history first.
How did e-commerce become?
The first e-commerce transaction was made in 1994.
A guy named Phil Brandenberger used a Mastercard to buy Sting’s Ten Summoners’ Tales online for $12.48.
This special transaction made history and demonstrated to the world that the “open Internet” For e-commerce transactions.
why?
Because it was the first time that encryption technology was used to enable online purchasing.
Needless to say, e-commerce has grown by leaps and bounds since then.
The emergence of e-commerce giants like Amazon and Alibaba in the mid-1990s changed the face of the retail industry.
They have greatly benefited from the penetration of the global Internet and the digitization of the financial system which has contributed to declining sales for many traditional companies.
The growth of e-commerce has also transformed the retail workforce.
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) revealed that from 1997 to 2016, employment in the e-commerce sector increased by 80%.
The BLS also expects that the number of e-commerce jobs will continue to grow and will reach 450,000 in the United States by 2026.
With this in mind, it is clear that the highly competitive nature of e-commerce will continue to change the retail industry and influence customer behavior.
Starting an online business nowadays seems like an attractive idea to many smart entrepreneurs
But before anyone dives into this dynamic business sector, they first need to learn the ropes of the e-commerce industry.
This is exactly the purpose of this guide.
- In this resource, we’ll take a deep dive into the e-commerce industry – how it came to be, the types of merchants that exist, and the platforms that allow online selling.
- We’ll also highlight notable e-commerce success stories and flops to give you a better idea of what it takes to succeed in this industry.
- Whether you’re someone who wants to start an e-commerce site or you already run an online store and just want to learn more about the industry, you’ll find plenty of pieces in our guide.
- Dive below or jump to a specific section:
- How did e-commerce become?
- The most important e-commerce statistics for 2020
- Types of e-commerce businesses
- E-commerce platforms: A look at where and how e-commerce happens
- Examples of e-commerce: success stories and failures
- E-commerce Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The most important e-commerce statistics
If you are interested in doing business online, it is important to stay up to date on the latest e-commerce statistics
We all know that the best way to understand any business sector is through hard facts and data.
We’ll start with 99Firms’ 2020 e-commerce statistics, which prove that e-commerce is growing at a steady rate around the world.
Moreover, experts expect retail e-commerce sales to reach US$4.13 trillion in 2020.
It is predicted that by 2040, 95% of all purchases will be via e-commerce.
The fastest growing e-commerce market in the world is China where e-commerce was valued at $672 billion in 2017.
The United States has the highest rates of e-commerce penetration, with about 80% of all Internet users making at least one purchase.
The main reason people make purchases online is so they can shop whenever they want, 24/7.
About 43% of e-commerce traffic comes from Google search (organic).
Slow-loading websites see 75% abandonment.
Finance Online’s 2020 data and engagement market analysis shows that e-commerce is not only thriving in the B2C sector
But sales are also expanding in the B2B segment and could even overtake B2C profits by the end of 2020.
Here are some of the more interesting stats from this report:
It is estimated that about 35% of Google product searches convert to purchases within 5 days.
About 51% of digital buyers make purchases via their smartphone.
Digital buyers are more likely to spend more if they are offered free shipping.
About 93% of online shoppers declared that the visual appearance of an online store plays a major role in their purchasing decisions.
It is estimated that about 80% of online shoppers do not make purchases from e-commerce sites that have problematic return policies.
It is estimated that 85% of all products purchased via social media platforms come from Facebook.
According to Statista, e-retail sales accounted for 14% of total retail sales worldwide
These numbers are expected to continue to grow, reaching 22% by 2023.
Mobile e-commerce retail sales are expected to reach $3.5 trillion by 2021.
In 2017,
About 42% of online shoppers said they prefer to pay by credit card.
Online stores with an active presence on social media platforms generated 32% more sales.
Generation
About 30% of digital buyers are millennials.
About 55% of all online shoppers said that online reviews have an influence on their purchasing decisions.
So it’s clear – e-commerce is here to stay.
But how do we start?
 The first step is to make sure you are familiar with the basics.
The first step is to make sure you are familiar with the basics.
Types of e-commerce businesses
There are many ways to classify e-commerce websites.
You can categorize them according to the products or services they sell,
Or the parties they deal with, or even the platforms they work on.
In this guide,
We’ll take a look at all three aspects to give you a clear picture of the types of e-commerce sites out there.
Classification of e-commerce companies according to what they sell
Let’s start with the products and services typically sold online.
 Below is a list of e-commerce merchants according to what they sell.
Below is a list of e-commerce merchants according to what they sell.
- Stores that sell physical goods
These are typical online retailers.
Clothes, furniture, tools, and accessories are all examples of physical goods.
Shoppers can purchase physical items through online stores by visiting store websites, adding items to a shopping cart, and making a purchase.
Once the shopper makes the purchase, the store delivers the item(s) directly to their doorstep.
There are also online stores where customers can make a purchase online but go to the store themselves to pick up the products.
Some examples of such e-commerce stores include eyewear retailer Warby Parker
, men’s clothing store Bonobos, and shoe retailer Zappos.
- Service based e-tailers
Apart from products, services can also be purchased online.
Every time you hire tutors, freelancers and consultants through online platforms
, you are doing business with e-merchants that rely on the service.
The process of purchasing services depends on the merchant.
Some may allow you to purchase their services instantly from their website or platform.
An example of this comes from Fiverr.com, a freelance marketplace.
People who want to purchase services from Fiverr must place an order on the site before the seller will offer their services
.
On the other hand, some providers require you to contact them first (i.e. book a consultation) to determine your needs.
For example, Blue Fountain Media asks,
It is a company that develops digital strategies for large companies,
Clients contact them by first filling out an online form where they must describe their business needs.
- Digital products
E-commerce transactions take place over the Internet and for this reason
In the field of e-commerce, products are commonly referred to as “electronic goods”.
The term digital products refers to all items in a digital format including e-books
Online courses, software, graphics and virtual goods.
Examples of retailers that sell digital products include Coursera (an online learning platform)
and Audiobooks (a website where you can purchase audiobooks).
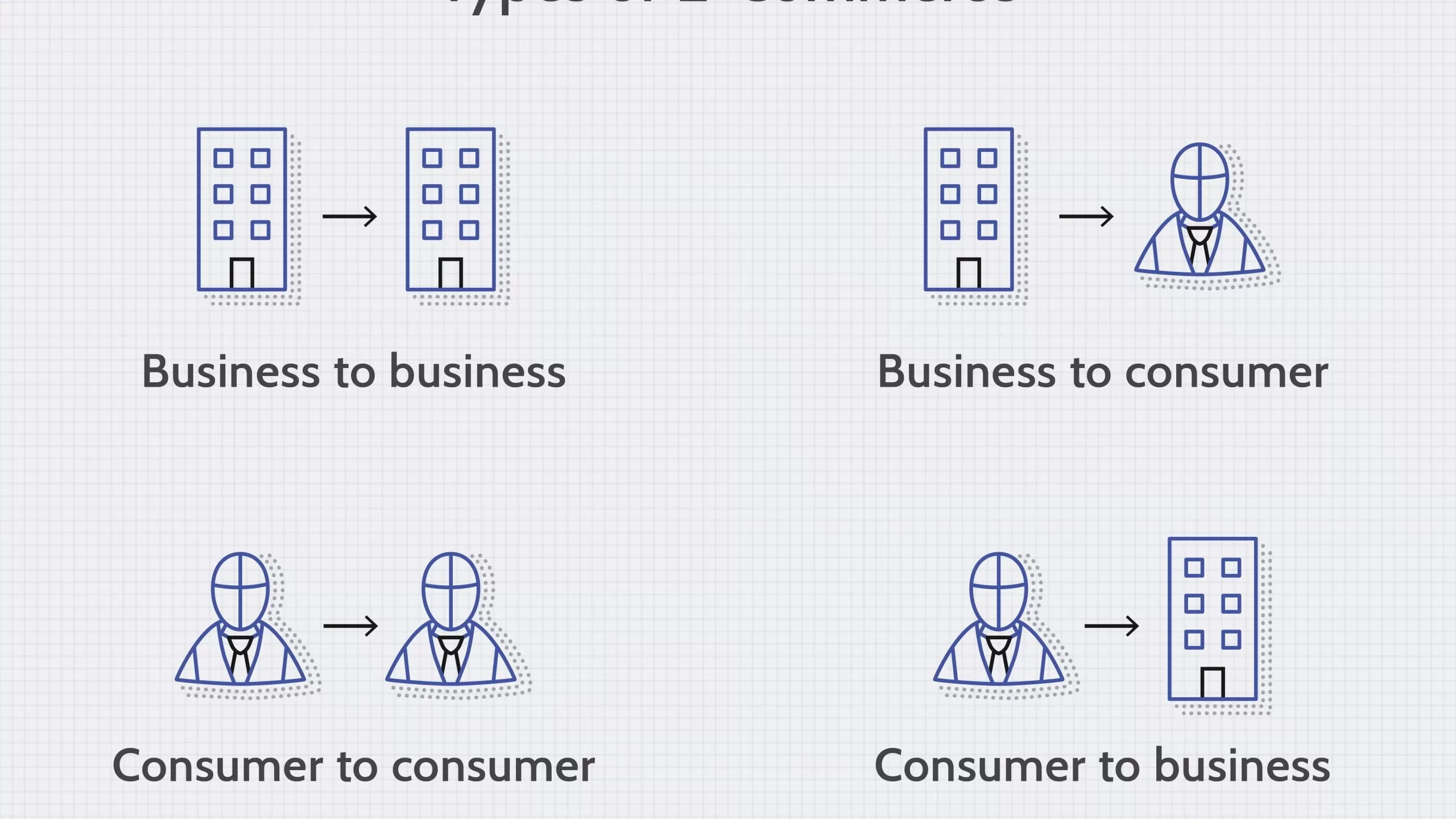
Classification of e-commerce according to the parties involved
Looking at the parties involved in the transaction is another way in which e-commerce sites can be categorized. These usually include:
-
Business to consumer (B2C)
As the name suggests, the B2C e-commerce model represents a transaction between businesses and individuals
. B2C e-commerce is the most popular business model among brick-and-mortar and online retailers.
Nike, Macy’s, IKEA, and Netflix are all examples of companies involved in business-to-consumer e-commerce.
-
Business to Business (B2B)
In the B2B e-commerce model, both parties involved are businesses.
In this type of transaction, one company provides another with products and/or services.
Slack, a platform for communication between remote companies, and Xero,
It is a cloud-based accounting software for businesses, examples of B2B companies.
-
Consumer to business (C2B)
The C2B business model represents a transaction in which individuals create value for a business
, unlike the traditional consumer business model where companies are the ones who provide value.
Consumers provide companies with products and/or services,
They collaborate on projects, and ultimately help companies increase their profits.
Freelancer, is a freelance platform that connects remote workers and companies
, an example of a company bringing together two parties to engage in C2B transactions
.
4. Consumer to Consumer (C2C)
C2C e-commerce occurs when the two parties involved are consumers who trade with each other.
eBay and Craigslist are examples of online marketplaces where individuals buy and sell products to each other.
5. Government to Business (G2B)
G2B e-commerce models occur when the government provides businesses with goods and services.
Government procurement, data centers, and e-learning are all examples of G2B e-commerce.
6. Business to Government (B2G)
The B2G model refers to businesses and companies that provide goods and services to the government.
For example, OpenGov is a company that provides governments with cloud-based platforms for communication, reporting, and budgeting.
7. Consumer to Government (C2G)
Every time consumers pay taxes, health insurance, or…
Electronic invoices or request information related to the public sector, they participate in C2G.
Note that we have included all of these sections to give you a general idea of e-commerce classification, although models such as G2C or C2G
It is part of e-commerce only in its loosest definition.
80% of the time, when we talk about e-commerce, we’re talking about the B2C or B2B model.
E-commerce platforms:
A look at where and how e-commerce occurs
We’ve talked about the types of e-commerce transactions on the web as well as the products and services that are sold online.
But where and how do these transactions take place?
Answer: It varies.
In this section, we will highlight some of the most popular platforms on which e-commerce takes place.
A visual representation of the percentage of websites that use e-commerce technologies. Source: Career Cliff
What are the best e-commerce platforms?
Using shopping carts and e-commerce platforms, retailers build online stores where they display their products and services.
Having an online storefront is one of the most straightforward ways to do e-commerce.
There are a large number of e-commerce solutions out there and choosing the right one for your business depends on your budget, preferences, and company needs.
Below we have listed the best e-commerce solutions currently available on the market
 Shopify
Shopify
Here are some Shopify facts:
Shopify supports more than 2,921,565 websites worldwide.
Shopify has 21% e-commerce market share.
A popular choice among many small and medium businesses, Shopify allows customers to build effective online stores and scale their businesses.
This platform is created with an easy-to-use and intuitive interface
In addition to many templates,
It offers flexible shipping rates, automatic taxes, and more than 100 payment gateways. Shopify allows social media integration,
It is packed with built-in SEO features
It is fully hosted.
Best for: Small businesses looking for an all-in-one eCommerce solution.
Magento
Here are some Magento facts:
To date, Magento has powered over 772,000 websites worldwide.
There are over 5,900 extensions that integrate with Magento.
Magento is a highly flexible e-commerce solution used by medium-sized businesses ready to scale.
This platform offers powerful features that allow retailers to customize all aspects of their online store including custom templates, plugins, and modules.
If customers need to expand the functionality of their Magento store, they can always use add-ons to turn their online store vision into reality.
As many complex e-commerce platforms, Magento
Supports customers by maintaining an active community of developers and experts in the Magento ecosystem who are ready to help beginners maintain their online store.
Best for: Brands looking for a highly customizable e-commerce solution.
Sales force
Here are some Salesforce facts:
As of 2020, the platform has 150,000 active users.
Salesforce has been awarded several times with prestigious recognition including the GSMA Glomo Award – Best Mobile App for Business,
DMN Awards 2017, and AOTMP Mobility Awards.
This fully hosted solution allows you to run a powerful e-commerce store in the cloud.
Traders who use will not have to
Salesforce has to worry a lot about maintaining and developing the platform because it’s hosted
Entirely owned by the company (although this may limit your freedom slightly).
One of the strengths of Salesforce is that it was designed with omnichannel retailers in mind and the features it enables merchants to offer
Easily sell across physical and digital storefronts.
Best for: Large companies that need integrated, scalable CRM software
 Oracle Commerce
Oracle Commerce
Here are some Oracle Commerce facts:
Most companies that use Oracle Commerce are in retail, computer software, and information technology.
Oracle Commerce has 0.36% of the e-commerce market share.
Oracle Commerce is a powerful e-commerce solution suitable for both B2B and B2C retailers
. It’s packed with out-of-the-box features that enable you to sell more complex items and data-rich offers.
This is a highly customizable e-commerce platform that allows retailers to customize every aspect of their online store and campaigns.
Best for:
Growing businesses looking for a flexible and scalable e-commerce platform.
Maryam Al-Dakhil wrote for the Wealth Academy
Here are some WooCommerce facts:
WooCommerce powers 3,876,748 live websites.
CodeCanyon sells over 1,773 plugins designed to integrate with WooCommerce.
WooCommerce is one of the largest open source e-commerce platforms.
Specially designed to integrate with WordPress, WooCommerce has tons of templates that can help you create a unique online store.
You’ll get all the essential features including unlimited products, unrestricted customization, order management, and free shipping.
Best for: Small businesses with a WordPress-powered website.
BigCommerce
Here are some BigCommerce facts:
BigCommerce powers over 150,000 websites worldwide.
Pandora, a popular jewelry retailer, is built with BigCommerce.
BigCommerce
It is a popular e-commerce solution that provides online retailers with a powerful online store builder to create a fully functional online store and sell an unlimited number of products.
One thing that particularly sets BigCommerce apart from other ecommerce solutions is its powerful business management features like shipping, reporting, and product and order management
, as well as the fact that it is fully hosted.
in addition to ,
BigCommerce has a built-in B2B offering for businesses involved in B2B e-commerce.
Best for:
Grow a business that wants to take advantage of multi-channel selling.
spilling
Here are some Volusion facts:
The total volume of purchases made through stores created with Volusion was 13.8 million in 2018.
There are over 11,000 websites powered by Volusion in 2020.
Another popular e-commerce solution, Volusion enables
Merchants can create online stores, display their merchandise, and take payments all on one platform.
Volusion comes with standard features including a website builder, shopping cart software, marketing tools, and more.
Best for:
Small businesses that need a simple, easy-to-use e-commerce platform
.
Drupal Commerce
Here are some Drupal Commerce facts:
Drupal Commerce has 0.11% of the e-commerce market share.
Most companies using Drupal Commerce are in computer software and retail stores.
This is an open source e-commerce framework
It enables users to create online stores and applications on Drupal. Drupal Commerce
It is highly flexible and provides hundreds of modules that allow users to improve and extend its functionality.
Drupal Commerce also offers a Commerce Kickstart package
Which integrates with the latest versions of Drupal.
It’s packed with out-of-the-box features that allow developers to quickly set up and customize all aspects of their online store.
Best for:
Large businesses that require a robust, feature-rich e-commerce solution.
 What are the largest online marketplaces?
What are the largest online marketplaces?
Online marketplaces are platforms that facilitate e-commerce transactions between buyers and sellers
, enabling buyers to display their products and reach a larger audience.
These platforms are very popular among customers due to their wide range of products and services from various vendors and suppliers from all over the world.
Let’s dive into the best online marketplaces on the web:
Amazon
Here are some facts about Amazon:
Statistics show that Amazon is the largest e-commerce seller in the United States
Its net sales reached $280.5 billion in 2019.
The e-commerce giant has about 101 million Amazon Prime members on
Americans spend an average of $1,400 annually on online purchases.
A company that needs no introduction, Amazon is one of the largest online marketplaces in the world.
It offers customers a wide range of products from retailers around the world and enables businesses to reach a large audience.
Best for:
Large companies that want to expand their sales channels.
Chances are
Here are some eBay facts:
eBay has a total of 1.4 billion live listings.
eBay had about 182 million active users in 2019.
eBay connects retailers and customers from all over the world,
It is an online marketplace that can help small and medium-sized businesses create an international customer base.
eBay is easy to use, intuitive, and offers a number of payment options.
One thing that particularly sets eBay apart from other online marketplaces is that it allows merchants to conduct online auctions.
Best for:
Established brands that sell unique items are looking to expand their audience base.
Etsy
Here are some facts about Etsy:
Etsy had 2.5 million sellers and 45.7 active buyers online in 2019.
Etsy had 60 million items for sale in 2019.
Etsy is the perfect platform for creatives looking for an online marketplace to showcase their unique, handcrafted products.
They are especially popular among independent creatives and people looking to purchase unique, exclusive and rare items.
Best for:
Small businesses that sell handmade and vintage items.
Ali Baba
Here are some Alibaba facts:
About 960 million people made a purchase on Alibaba in 2019.
Alibaba recorded revenues of $54.5 billion in 2019.
Alibaba is one of the largest online marketplaces in the world.
The platform is particularly effective for accessing large manufacturers and purchasing products in bulk.
Alibaba dominated the Chinese market in 2019, with an estimated 960 million active customers.
Best for:
Large, established brands looking to expand and reach a global audience.
Pfeiffer
Here are some Fiverr facts:
Fiverr recorded an average monthly transaction count of 50 million in 2019.
Fiverr generated revenue of $27.9 million in the third quarter of 2019.
Unlike the other marketplaces mentioned above, Fiverr offers freelance services.
This platform connects businesses with remote workers who specialize in all types of services including digital marketing, video editing, programming, and graphic design.
Joining Fiverr is free for freelancers and costs to hire a remote worker for a specific job start at $5.
Best for:
Small businesses looking to hire freelancers for outsourcing.
Even work
Here are some Upwork facts:
Upwork reported revenue of $67.3 million in the fourth quarter of 2018.
With 12 million registered freelancers, Upwork is the largest job marketplace for freelancers in the world.
Upwork, formerly known as Elance and oDesk,
It is a freelance services marketplace that connects businesses and businesses with remote workers from around the world, whether part-time or for long-term engagement.
Remote workers who use Upwork specialize in all types of services including accounting, expert marketing, content writing, and web development.
They can create an account on Fiverr and offer their knowledge and services to companies from all over the world.
Best for:
Companies that need freelance services and competent remote workers who can stand out in a highly competitive job market.
Social media and e-commerce
Social media platforms can help e-commerce businesses expand their reach and create a recognizable brand identity.
They can also increase sales and smoothen the buyer’s journey by either directing consumers to a retailer’s stores via
online or by enabling shoppers to purchase items directly from retailers’ social media pages.
How social media facilitates e-commerce
 The most popular social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and Pinterest are not usually used by sellers as an alternative to online stores.
The most popular social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and Pinterest are not usually used by sellers as an alternative to online stores.
Instead, retailers use these platforms to showcase their products using visuals
, such as photos, videos, and engaging social media copy to attract customers and reach a wider audience.
Consumers who come across an item that interests them are then directed to social media platforms
Social to the online retailer so they can make a purchase.
Conduct e-commerce transactions on social sites
Is there anything else to say about e-commerce on social media or e-commerce on social media?
Well, some social media platforms take things further by enabling customers to sell products directly from their social media accounts.
For example, retailers who showcase their products on Instagram can use Instagram’s checkout option
. This feature allows customers to purchase items they like without having to leave Instagram.
Since September 2018, businesses can also use Instagram Shoppable Stories, a feature that allows businesses to add product stickers to a Story.
Customers who come across a product they like can just click on a label that will redirect them to the product page with more details about the product.
The above initiatives are certainly interesting, but it is important to note that not all social selling projects are successful. Take Twitter’s buy buttons.
In 2014, this social media platform launched a feature that allowed customers to purchase items directly from a tweet.
It was not a huge success so the company officially closed the project in 2017.
Examples of e-commerce:
Stories of success and failures
At this point, you have a solid idea of what e-commerce represents,
The types of e-commerce transactions that are made, and the type of platforms that sellers use to reach their audience.
Let’s now go through some of the most successful e-commerce examples as well as those that haven’t worked in the industry
In order to learn from winning strategies and mistakes.
This section lists some of the best e-commerce sites on the web, and highlights what makes them successful.
Amazon e-commerce example
Amazon is not only one of the largest e-commerce platforms,
It is also the most valuable company in the world, surpassing even Microsoft in terms of market capitalization.
Amazon is a thriving and competitive marketplace for third-party sellers and a platform where customers enjoy a wide range of products from providers from all over the world.
What makes Amazon successful
Brian Eisenberg is a bestselling author who recently co-authored his latest publication Be Like Amazon:
Even a lemonade stand can do that with Jeffrey Eisenberg and Roy H. Williams. In the book, he talks about the four pillars of Amazon’s success.
Be customer-centric – “Amazon doesn’t try to force customers to fit how they want to sell to them.” , he says.
“Amazon wants to fit the way customers buy today and will change their purchasing behavior in the future.
” They address all customer concerns by providing them with a detailed help center where they can get information regarding purchases, refunds, and shipping rates.
Be creative – Amazon is always experimenting and coming up with ways to improve the shopping experience.
Amazon regularly conducts online surveys via email where they ask customers to rate their shopping experience with Amazon.
This gives the company guidance on areas they should work on in order to improve customer experience.
Focus on customer experience – Amazon focuses on engaging customers and making them a vital part of the purchasing process.
A good guide is the huge number of reviews.
Customers want to share their experience with the platform because they feel that their opinion is important.
Continuous improvement and optimization – Amazon uses its data well. The company is always crunching numbers,
Data is used in almost every aspect of a business, including customer experience, warehousing, operations, finance, and marketing.
However, when you are trying to create an e-commerce company from scratch,
It is difficult to relate to one of the biggest giants of the digital age.
That’s why we’ll also take a look at Birchbox.
Birchbox ecommerce example
Birchbox has a two-fold business:
It offers a subscription in which the company charges $10 per month to receive
“A personal blend of 5 samples of hair, makeup, skincare and fragrance” ,
It also has an online store that allows customers to purchase full-size products.
As of 2015, Birchbox has over 800 brand partners and over 1 million subscribers.
What makes Birchbox successful
Several factors contribute to Birchbox’s success, but data is one of the most important.
The company’s co-founder, Katia Beauchamp, told Forbes that data has become their best friend.
Here’s one example of how a company uses data: Requests
Birchbox requires subscribers to review each item and uses this information to match customers with the best products.
Birchbox also sends data to their partners so they can determine what’s working and what’s not.
Another key to their success? Unlike most of their competitors, Birchbox isn’t just a box subscription service.
The company allows members to purchase full-sized products as well as samples, which is what sets it apart from the competition.
Wayfair ecommerce example
Wayfair is an American company that specializes in selling furniture and household items.
The company offers more than 14 million items from 11,000 suppliers worldwide and was the fastest-growing retailer in the United States in 2018.
What makes Wayfair successful
Wayfair is a dropshipper, so they barely carry any inventory.
However, the company does a tremendous job of managing suppliers, orders, and fulfillment.
Neeraj Agrawal of Battery Ventures says in an interview with Forbes:
“They figured out how to manage the 7,000 sellers and the express delivery process so that the sellers go directly to the consumer.”
It works like this.
Sellers upload their inventory data to Wayfair’s servers,
The company’s algorithm crunches the numbers and uses that information to determine shipping times and operations.
The system is very effective when it comes to informing suppliers of purchases made.
They are notified immediately of the type of application submitted.
In addition, the system evaluates the size of the order and decides whether to send it via FedEx or use a delivery company.
In addition to managing suppliers and orders efficiently, Wayfair also strives to get to know its customers.
The company encourages each shopper to create an account, and monitors user behavior in order to customize the shopping experience accordingly.
Example of e-commerce Zappos
Zappos is an online shoe and apparel retailer based in Las Vegas, Nevada.
It is currently owned by Amazon,
But it’s still worth taking a look at what makes this e-commerce site successful.
What makes Zappos successful
Zappos is known for its customer service.
The company’s main promise to customers is to provide great service.
Their popular slogan “Delivering Amazing Service Through Service” lives up to its popularity. We live up to this core value by always putting customers first.
For example, while other companies encourage call center agents to move away from the phone as quickly as possible, Zappos wants its employees to stay
On the phone as long as necessary.
 At one point, a Zappos employee spent 10 hours on the phone with a customer.
At one point, a Zappos employee spent 10 hours on the phone with a customer.
When asked how the company feels about this, Jeffrey Lewis, customer loyalty team supervisor at Zappos, said:
“Zappos’ number one core value is providing great service, and we feel that allowing our team members the ability to stay on the phone with…
A customer as long as they need a primary means of achieving this value.
Examples of e-commerce failure
I’ve seen success stories. Let’s now take a look at some of the industry’s biggest failures. Pay attention and learn from the mistakes of these companies.
Boo.com
Boo.com was a UK-based clothing and cosmetics e-tailer that failed just two years after launching.
It was just one of many Internet companies that closed its doors during the dot-com bubble in 2000.
The Nasdaq Composite (which was composed of many technology companies) rose in the late 1990s, but experienced a sudden decline after the bubble.
For starters, the bursting of the dot-com bubble occurred from 1997 to 2001.
The rapid growth of Internet use and adoption at the time fueled investments in incredibly high valuations and companies that did not generate profits until they went public.
However, the hype was not sustainable, and capital soon dried up.
As you will find out below, this was ultimately one of the reasons for Boo.com’s closure (among others).
Why Boo.com failed
Poor user experience, a faulty growth plan, and a high burn rate contributed to the failure of Boo.com. For starters,
The site needed JavaScript and Flash as well as several large files in order to run efficiently. This resulted in slow loading times and ultimately a poor user experience.
Boo.com also tried to expand way too quickly while operating expenses were very high.
Due to the collapse of technology stocks at the time, the company was not able to raise enough money to stay afloat.
eToys.com
As its name suggests, eToys.com was an online toy retailer.
It was launched in 1997 and then filed for bankruptcy in 2001.
Why eToys.com failed
Like Boo.com, eToys tried to expand too quickly and also incurred high operating expenses.
Due to market conditions following the dot-com bubble, eToys failed to obtain capital that would allow it to continue operations.
But this was not the only factor that led to its failure.
According to ABC News, the main failure of eToys was the inability to deliver all orders on time.
They received a huge number of orders during their first holiday season, but most customers received late shipments that brought them a bad reputation.
The bad publicity didn’t stop there.
At one point, the company filed a lawsuit against Etoy, a Swiss art site.
eToys tried to acquire the etoy.com domain, saying it was too similar to eToys.com
. The move was met with widespread backlash, and eToys.com backed down.
Tuigaru
Founded in 2010, Toygaroo was an online game rental service dubbed the Netflix of games.
Toygaroo has enabled parents to rent toys for a period and return them once their children get tired of playing with them.
Tuigaru had a promising start.
Its founder, Nikki Pope, appeared on the popular TV show Shark Tank and received a $200,000 investment from Mark Cuban and Kevin O’Leary.
Unfortunately, this investment did not pay off. Toygaroo filed for bankruptcy in 2012 and subsequently closed.
Why Toygaroo Failed
While the exact details of Toygaroo’s closure were not clear, it appears that the company had problems dealing with its rapid growth as well as executing its business model.
Toygaroo may have had trouble scaling the business, Phil Smy, Toygaroo’s former CTO, told Shark Tank Blog.
The company has achieved tremendous growth in a short period of time which is both a huge success and a difficult one to handle.
Regardless of their experience, small businesses lack the ability to manage rapid growth.
If Toygaroo had slow organic growth, the company may have avoided bankruptcy.
Meanwhile, Kevin O’Leary, one of the Sharks who invested in Toygaroo, told Forbes that this was his worst deal on the show.
“Great concept but they proved unable to execute,” he said.
Frequently asked questions about e-commerce
How many e-commerce transactions are there worldwide?
Statistics show that there will be more than 2.5 billion consumers online by the end of 2020.
To put things into perspective, with a global population of 7.7 billion people
, it basically means that 25% of the world’s population conducts e-commerce transactions.
How much is e-commerce worth?
E-commerce generated about $3.5 trillion in sales in a year
2019, and the sector is expected to witness greater growth in the future.
 Is e-commerce still growing?
Is e-commerce still growing?
You bet it is!
Studies predict that e-commerce will see a growth rate of 265% in the future from $1.3 trillion
in 2014 to $4.9 trillion in 2021.
How many e-commerce websites are there in the world?
It is estimated that there are about 24 million e-commerce sites selling products online in 2020.
What are the largest e-commerce companies?
The largest e-commerce company is Amazon
, with an estimated market value of $993 billion in 2019. The largest player in the Chinese market is Alibaba
, which accounts for about 56% of the market share.
What is the proportion of mobile e-commerce?
In the United States, mobile devices accounted for 44.7% of all retail e-commerce sales in 2019.
What days do people shop the most?
Mondays and Sundays receive higher traffic than other days of the week.
When do people shop online the most?
The peak hour for customers to make purchases is between 8pm-9pm in 2020.
Put e-commerce knowledge into practice
And there you have it. Now you know what e-commerce is, the types of merchants who do business online,
And the biggest successes (and failures) in the industry. What then?
The answer: Take action.
Wherever you are now in your ecommerce journey, we hope this post gives you some ideas that you can apply to your project.
If you’re just starting out and need help choosing a platform or deciding on your target audience, go back and read the section on eCommerce types and solutions.
Already running a business and want to ensure your success?
Read the e-commerce stories above.
Finally, if that’s not enough, we suggest you check out the following resources on our blog:
How to start your first e-commerce business
Ecommerce Dropshipping Guide
GDPR: A guide to e-commerce
The complete guide to fraud and fraud prevention in e-commerce
E-commerce laws and regulations
If you need additional tips or insights, we’re here to help.
Entrepreneurs who want to start a new e-commerce project and need professionals to discuss their ideas with or solve a problem can…
Contact our consulting team at any time.
Our experienced e-commerce professionals can help new businesses implement the right strategy in this fast-growing industry.
Whether you need advice on
Search engine optimization, product promotion or tracking
advancement or brand, our team at EcommerceGuide will be happy to help your ecommerce business grow and prosper.
 Try Prepare me for a fun shopping trip
Try Prepare me for a fun shopping trip
We are pleased that you visit our social media pages, where we publish exclusive offers on our website.
Our Facebook page Here.
Our Twitter account Here.










Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.