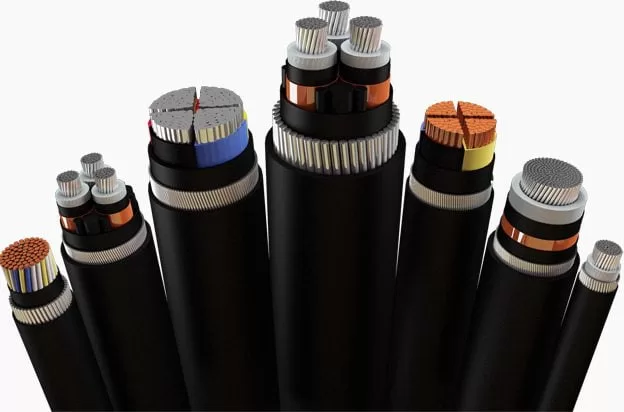
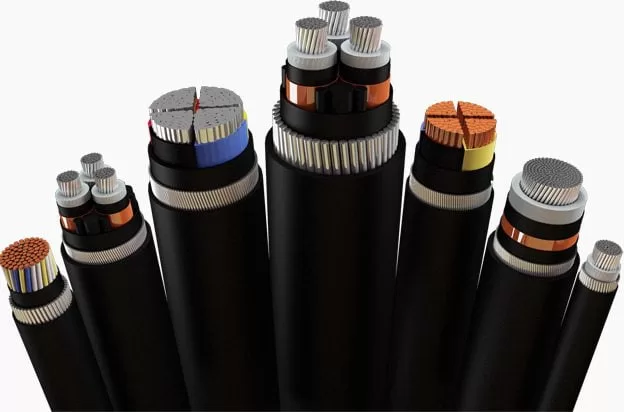
All types and sizes of electrical cables
All types and sizes of electrical cables
When we enter the world of electricity, we find thatcables form the vital artery that supplies energy and signals in most electrical installations and devices. Cable types and sizes vary depending on the intended use, and understanding these details becomes vital to ensuring efficient and safe performance of electrical systems.
When we look at the complex electricity system that extends into most corners of our daily lives, we discover that power delivery depends primarily on an interwoven network ofelectrical cables. These hidden wires play a vital role in directing electrical current from its source to its intended destination. In this article, we will explore the world of electrical cables, taking a look at their different types and sizes that determine their performance and effectiveness.

1.Copper cables: types and sizes
2. Aluminum cables: types and sizes
Aluminum cables are considered an essential part of electricity transmission and communications systems. These cables are characterized by their light weight and ability to transmit high currents, making them a popular choice in various fields. In this article, we will discuss the types of aluminum cables and the importance of choosing the appropriate sizes to meet different needs.
1. Types of aluminum cables:
A. Aluminum power cables:
It is used to transmit electricity through electrical networks. This category includes distribution and feeder cables, where aluminum is used as the main conductor.
b. Aluminum communication cables:
Used to transmit data and signals in communications systems, aluminum is integrated as an effective conductive material.
t. Aluminum control cables:
They are used to control industrial machinery and equipment, ensuring that control signals are routed efficiently.
2. Aluminum cable sizes:
A. Core diameter:
Core diameter measurements are one of the main criteria for determining cable size. Cable performance is greatly affected by increasing core diameter.
b. Connector clips:
Conductor cross-sections define a cable’s elbow area, and directly affect its ability to transmit current efficiently.
t. Current rating:
The current rating determines the maximum power that a cable can safely transmit without overheating, and is usually measured in amps.
3. Benefits of Aluminum:
Aluminum is lightweight and high strength, making it an excellent choice in cable application sites. It also has good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for use in diverse environmental conditions.
3. Fiber optic cables: types and sizes
Fiberoptic cables are key to providing fast and efficient data transfer in our digital age. These cables are characterized by their ability to transfer data at high speeds using infrared rays. In this article, we will look at fiber optic cable types and sizes to understand how this technology can meet the growing needs of modern communications.
1. Types of fiber optic cables:
A. Multimode fiber optic cables:
They are used to transmit optical signals across the cable core in multiple ways. It is characterized by its ability to transfer large amounts of data over long distances.
b. Single mode fiber optic cables:
Used to direct a single light beam through the cable core, it allows superior performance in applications requiring high precision.
t. Hybrid fiber optic cables:
It combines multimode and single-mode fibers in a single cable, providing a complete solution for various communications requirements.
2. Fiber optic cable sizes:
A. Core diameter:
The diameter of the core determines the size of the optical fiber, and plays a crucial role in determining the amount of light that can be transmitted.
b. Casing thickness:
The thickness of the jacket surrounding the core affects the cable’s flexibility, endurance and protection from environmental conditions.
t. Number of fibers in the cable:
Each cable can contain multiple fibers, which directly affects the data transmission capacity.
3. Technology development:
As technology evolves, fiber optic cables have seen continuous improvements in their performance and effectiveness. New designs are being developed to improve data transfer capacity and reduce signal loss over long distances.
4. Low voltage cables: types and sizes
Low voltage cables are used in a wide range of applications within homes, commercial and industrial buildings. These cables are an effective solution for power transmission in electrical systems that require low voltage. In this article, we will take a look at the different types and sizes of low voltage cables.
1. Types of low voltage cables:

A. Electric power cables:
It is used to transfer electrical energy from the power source to various appliances and equipment in the home or building.
b. Lighting cables:
They are specially designed to connect light bulbs to power sources, providing efficient and safe lighting.
t. Control cables:
It is used to transfer control signals and information between control devices and electronic systems.
w. Communication cables:
They are used to transmit data and signals in audio and television systems and communications networks.
2. Low voltage cable sizes:
A. Diameter measurement:
Low voltage cable sizes are usually measured by the diameter of the copper or aluminum core. The larger the diameter of the core, the more efficient the cable is able to transmit current.
b. Number of connectors:
The number of conductors determines the amount of wire inside the cable, and is affected by cable design and current needs.
t. Electric current endurance:
The electrical current carrying capacity determines the maximum current that a cable can safely transmit without overheating.
3. Materials and environmental factors:
A. Insulating materials:
The insulation materials used in cables, such as PVC or XLPE, vary and affect the insulation strength and resistance of the cable to environmental factors.
b. External protection:
The cables come with a coating that provides additional protection against abrasion, stress and weather conditions.
5.Medium voltage cables: types, dimensions and sizes
Medium voltage cables are considered one of the main elements in transmitting electricity over medium distances, and are usually used in distributing electrical energy and connecting transformer stations. Here is an overview of the types, gauges and sizes of medium voltage cables:
1. Types of medium voltage cables:
A. Paper insulated power cables:
It relies on paper as the main insulating material and is usually used in traditional systems.
b. Advanced Polyethylene (XLPE) Cables:
Advanced polyethylene is used as an insulating material and is more common in modern systems.
t. Oil and Paper (OIP) Cables:
These cables are used in some applications and are insulated using oil and paper.
2. Medium voltage cable gauges:
A. Operating voltage:
Medium voltage cables are available in different gauges and are classified according to their intended operating voltage. The operating voltage of medium voltage cables may range from 5 kV to about 35 kV.
b. Maximum current:
Medium voltage cables are classified according to the maximum current they can handle without overheating. This rating is specified in amps.
t. Length:
Cable length depends on the application and specific requirements, as the cable is available in a variety of lengths to suit different uses.
3. Medium voltage cable sizes:
A. Core diameter:
Core diameter sizes vary depending on design and application. The larger the diameter of the core, the more efficient the cable is able to transmit current.
b. Number of connectors:
The number of conductors in a medium voltage cable affects its ability to transmit power and its effectiveness in handling load.
4. Standards and specifications:
Medium voltage cables are designed and manufactured to strict standards and specifications that specify performance and safety requirements.
6. High voltage cables: types, standards and sizes

High voltage cables are used to transmit electrical energy over long distances in electricity networks. These cables are characterized by their ability to withstand high electrical voltages, making them an ideal solution for transmitting energy in large quantities. Here is an overview of high voltage cable types, gauges and sizes:
1. Types of high voltage cables:
A. Oil and Paper (OIP) Cables:
It is used in some systems and relies on oil and paper as insulating materials.
b. Advanced Polyethylene (XLPE) Cables:
Advanced polyethylene is used as an insulating material and is commonly used in modern systems.
t. Optical Fiber Cables:
They are used to transmit data as well as power, and are designed to provide fast and efficient transmission of optical signals.
2. High voltage cable gauges:
A. Operating voltage:
High voltage cables are available in different gauges and are classified according to their intended operating voltage. The operating voltage of high voltage cables can range from several tens to hundreds of kilovolts.
b. Maximum current:
They are rated according to the maximum current that the cable can handle without overheating. This rating is specified in amps.
t. Length:
High voltage cables are manufactured in a variety of lengths depending on the application requirements, ranging from several meters to hundreds of kilometres.
3. High voltage cable sizes:
A. Core diameter:
Core diameter sizes vary depending on cable design and current and voltage requirements.
b. Number of connectors:
The number of conductors affects the efficiency of a high voltage cable and its ability to transmit power.
4. Environmental applications:
A. Insulating materials:
Insulation materials are affected by the insulation strength and resistance of the cable to environmental factors. Materials are selected based on application requirements.
b. External protection:
The cable is designed with an outer jacket that provides additional protection against corrosion and environmental effects.
7. Single core or core cables
Single-core cables Typically used to transmit data individually, they feature a single core carrying one or multiple signals. This type of cable is widely used in communications and networking technology. Here’s a look at the types, gauges, and sizes of single core cables:
1. Types of single core cables:
A. Fiber optic cables:
- Used to transmit data by optical fiber.
- It can be made of glass or plastic.
- It is characterized by its ability to transfer large amounts of data over long distances.
b. Electrical connection cables:
- They are used to connect electrical appliances to power sources.
- It may be made of copper or aluminum.
- They vary in core diameter and number of conductors depending on the specific use.
2. Standards of single core cables:
A. Core diameter:
- It is determined by measuring the diameter of the main core of the cable.
- Varies depending on cable type and expected usage.
b. Data transfer capacity:
- Depending on cable technology and core type, optical fiber usually increases data transmission capacity.
3.Single core cable sizes:
A. Fiber optic cables:
- They vary in size and design according to needs.
- It can be thin and lightweight.
b. Electrical connection cables:
- Available in multiple sizes to suit different loads.
- They can be great for meeting high electrical power transmission needs.
8. High temperature cables:
High temperature cables are designed to withstand high temperatures and harsh environmental conditions. These cables are used in applications where there is significant heat generation or in environments exposed to high temperatures. Here is an overview of high temperature cable types, gauges and sizes:
1. Types of high temperature cables:
A. Silicon cables:
- Used at temperatures exceeding 200°C.
- Resistant to UV rays, oils and chemicals.
b. Fiberglass cables (thermal glass):
- Withstands very high temperatures up to 1000 degrees Celsius.
- Resistant to chemicals and extreme heat.
t. Rubber insulated heat cables:
- Designed to withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions.
- Used in industrial applications and factories.
2. High temperature cable gauges:
A. Maximum temperature:
- Determines the cable’s ability to withstand high temperatures.
- The cable should be selected based on the temperature expected in the application.
b. Insulation measurement:
- The type and quality of insulation affects the cable’s ability to withstand heat.
3. Sizes of high temperature cables:
A. Core diameter:
- It can vary depending on application requirements and the cable’s ability to withstand temperatures.
b. Cable length:
- Determined based on site requirements and application in which the cable is being used.
9. Afor fire resistant cables:
Fire Resistant Cable is a type of cable that is designed to remain effective in fire situations, helping limit the spread of flame and minimizing damage. This type of cable is used in applications that require a high level of fire safety. Here’s an overview of fire-resistant cable types, gauges, and sizes:
1. Types of fire resistant cables:
A. Ordinary fire resistant cables:
- Designed to remain effective at high temperatures resulting from fire.
- May contain heat-resistant insulating materials.
b. Fortified fire resistant cables:
- It is characterized by its sturdy design and resistance to mechanical influences and heat.
- May contain additional lengths of fire resistant material.
2. Fire resistant cable gauges:
A. Heat resistance degree:
- Determines the cable’s ability to resist high temperatures during a fire.
b. Flame resistant:
- It relates to the ability of the cable to remain effective in the presence of flame.
3. Fire resistant cable sizes:
A. Core diameter:
- Varies depending on cable design and current requirements.
b. Length:
- Determined based on site needs and security guidelines.
4. Safety standards:
A. Fire standards:
- Determines the cable’s resistance to fire, flames and smoke.
b. Industrial approvals:
- Some applications may need special approvals and evaluation from safety bodies.
10. Portable Power Cables:
Portable power cables are an essential part of our daily lives, used to charge mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets and laptops. These cables are flexible and easy to carry, making them an essential travel product. Here’s an overview of portable power cable types, gauges, and sizes:
1. Types of portable power cables:
A. USB-A to USB-C cables:
- Used to charge many modern devices such as smartphones and tablets.
- Provides high data transfer speeds.
b. Lightning cables:
- Especially for Apple devices such as iPhone and iPad.
- Supports charging and data transfer.
t. Micro-USB cables:
- It is used in many old devices and some modern devices.
- Allows charging and data transfer.
2. Portable power cable gauges:
A. Length:
- They are available in different lengths, from a few inches to several feet, to suit your application needs.
b. Power of current:
- They are designed with guidance for specific devices, and the current strength changes according to needs.
3. Portable power cable sizes:
A. Cable thickness:
- It varies depending on the cable design, and affects the flexibility of the cable and how well it can withstand daily use.
b. Cable flexibility:
- It is preferable to choose highly flexible cables for durability and ease of storage.
11. Double shielded cables:
12. External cables:
Outdoor cables are essential for connecting devices and applications in outdoor environmental conditions, and are resistant to weathering and corrosion. Their types, sizes, and sizes vary based on the specific applications and environments in which they are used. Here’s an overview of some outdoor cable types, gauges, and sizes:
1. Types of external cables:
A. Fiber optic cables:
- Used to transmit data by optical fiber.
- Provides excellent performance and resistance to electromagnetic interference.
b. External power cables:
- Used to connect power devices in outdoor environments.
- It has weather-resistant insulation and casing.
t. External Ethernet cables:
- Used to transfer data in external environments.
- They may be protected with water and corrosion resistant casings.
2. External cable standards:
A. Core diameter:
- It is determined by the size of the main core of the cable.
- Depends on current and application requirements.
b. Weather resistant:
- Determines the cable’s resistance to weather factors such as water, sun, and abrasion.
3. External cable sizes:
A. Cable length:
- Varies depending on site and application requirements.
b. Insulation thickness:
- It affects the cable’s resistance to environmental factors and general protection.
4. Protection classifications:
A. Wear tolerance:
- Evaluates the cable’s strength against wear and tear caused by weather conditions.
b. Water bearing:
- Determines the cable’s water resistance and ability to operate in wet environments.
13. Earth cables:
Ground cables They are used to connect electrical systems to the ground in order to provide protection from excessive electrical currents and get rid of excess charges. These cables play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of electrical systems and protecting against electrical shock. Here’s an overview of underground cable types, gauges, and sizes:
1. Types of underground cables:
A. Copper ground cables:
- Made of copper to provide good conductivity and withstand high currents.
- It is used in grounding electrical systems in buildings and facilities.
b. Aluminum ground cables:
- It is made of aluminum and is used to connect electrical systems to the ground.
- They may be lightweight and offer an economical solution.
t. Insulated ground cables:
- It comes with an insulating layer to provide extra protection and reduce the chances of shorts.
2. Underground cable gauges:
A. Conduction resistance:
- It determines the cable’s ability to withstand short-circuit current and ensure an effective connection.
b. Diameter:
- Depends on endurance current and application, and changes according to safety requirements.
3. Underground cable sizes:
A. Cable length:
- Determined by location and distance between the connection point and the ground.
b. Insulation thickness:
- It affects the cable’s resistance to weather conditions and general protection.
4. Protection classifications:
A. Overcurrent tolerance:
- Determines the ability of a cable to withstand excessive currents for short periods of time.
b. Withstand weather conditions:
- Determines the cable’s resistance to environmental factors such as water, sun, and corrosion.
14. Coaxial cable:
Coaxial cables are types of cables used to transmit signals between devices, mainly used in telecommunications systems and television broadcast networks. Coaxial cable is known as an essential component in connecting antennas, cameras, internet systems, etc. Here’s an overview of coaxial cable types, gauges, and sizes:
1. Types of coaxial cable:
A. Coaxial Cable (RG-6):
- It is widely used to transmit digital TV and Internet signals.
- It features internal and external isolation to protect signals from electromagnetic interference.
b. RG-59 cables:
- It is mainly used in old television system and transmission of video signals.
- It features internal insulation and an external casing.
t. RG-11 cables:
- It is used to transmit signals over long distances.
- Features a larger diameter to deliver improved performance.
2. Coaxial cable gauges:
A. Resistance:
- Determines the cable’s ability to withstand interference and signal loss over distances.
b. Frequency tolerance:
- Determines the signal frequency that the cable can transmit efficiently.
3. Coaxial cable sizes:
A. Cable length:
- It changes depending on the location of use and the distance between devices.
b. Cable diameter:
- It depends on the cable type and application, and affects the signal performance.
4. Usage classifications:
A. For TV and video:
- Used to connect televisions and video players.
b. For Internet systems:
- Used to connect networking equipment and provide Internet services.
15. Control cables:

Control cables Includes a variety of cables used to connect and connect control devices to electronic systems and mechanisms. These cables play a vital role in transmitting signals and data between control devices and other components in the system. Here’s an overview of some control cable types, gauges, and sizes:
1. Types of control cables:
A. Active control cables:
- Used to transmit signals between controllers and motors or other devices.
- It features effective isolation to reduce electromagnetic interference.
b. Network control cables:
- Used in control networks and industrial control systems.
- They usually contain several pairs of wires to support efficient data transfer.
2. Control cable gauges:
A. Number of wires:
- Varies depending on cable design and connection requirements.
b. Wire diameter:
- Determined based on control current and transmission requirements.
3. Control cable sizes:
A. Cable length:
- Determined by the distance between controllers and other components.
b. Insulation thickness:
- It affects the cable’s resistance to interference and environmental conditions.
4. Usage classifications:
A. For industrial control:
- Used in industrial control systems and machine control.
b. For home control systems:
- Used in home control and home automation systems.
16. Signal cables:
Signal cables are used to transmit electrical signals between components of electronic systems. These cables vary based on different uses, and you need to choose the right cable depending on the signal type and application requirements. Here’s an overview of some signal cable types, gauges, and sizes:
1. Types of signal cables:
A. Audio Cables:
- Used to transfer audio signals between devices such as headphones and amplifiers.
- Examples: RCA cables, XLR cables, and TRS cables.
b. Video cables:
- Used to transmit video signals between signal sources and monitors.
- Examples: HDMI cables, DisplayPort cables, and VGA cables.
t. Data cables:
- Used to transfer data signals between electronic devices.
- Examples: USB cables, Ethernet cables, Thunderbolt cables.
2. Signal cable gauges:
A. Signal frequency:
- Determines the cable’s ability to transmit specific signal frequencies.
b. Conduction resistance:
- It affects signal loss during transmission and needs to be compatible with application requirements.
3.Signal cable sizes:
A. Length:
- It varies depending on the distance between system components and connectivity requirements.
b. Cable diameter:
- It depends on the cable type and affects the connection resistance and signal quality.
4. Usage classifications:
A. Studio cables:
- Used in studios to connect audio and recording equipment.
b. Network communication cables:
- Used to connect computers and networks.
17. Afor solar cables:
Solar energy cables are used to transfer solar electrical energy from solar panels to the control system or connect it to the electrical grid. Choosing the right solar cables is vital to the efficient and safe performance of your solar energy systems. Here’s an overview of some solar cable types, gauges, and sizes:
1. Types of solar cables:
A. Internal connection cables (PV Wire):
- Used to connect solar panels to each other within a solar system.
- It comes with insulation that is resistant to UV rays and harsh environmental conditions.
b. DC (direct current) cables:
- Used to transfer electrical energy from solar panels to the inverter or controller.
- They usually have improved insulation to withstand high currents.
t. AC cables:
- Used to connect the solar energy system to the public electricity grid.
- It contains insulation that is resistant to heat and electrical currents.
2. Solar cable gauges:
A. Endurance current:
- Specifies the maximum current that the cable can safely handle.
b. Effort Rating:
- Specifies the maximum operating voltage that can be tolerated by the cable.
3. Solar cable sizes:
A. Cable diameter:
- It affects cable resistance and power loss when transmitting electricity.
b. Cable length:
- It changes depending on the distance between the solar panels and the system components.
4. Usage classifications:
A. Underground cables:
- Used to connect solar panels to the grounding system.
b. Network connection cables:
- Used to connect the solar system to the public electricity grid.
18. Welding cables:
Welding cables They are used in welding operations to transfer electrical current between the power source and the piece being welded. Types of welding cables vary based on their applications and the conditions they may encounter. Here’s an overview of some welding cable types, gauges, and sizes:
1. Types of welding cables:
A. Copper welding cables:
- They are commonly used because they provide good conductivity and carry high currents.
- It comes with resistance suitable to withstand high electrical currents.
b. Aluminum welding cables:
- They are used in some applications because of their light weight and low cost.
- They may be less effective at conducting high currents than copper.
t. Insulated welding cables:
- Comes with an insulating layer for extra protection.
- Used to avoid electrical short circuit or electricity leakage.
2. Welding cable gauges:
A. Endurance current:
- Specifies the maximum electrical current that the cable can safely handle.
b. Voltage:
- Specifies the maximum welding voltage at which the cable can be used.
3. Welding cable sizes:
A. Cable diameter:
- It affects cable resistance and heat loss during welding operations.
b. Cable length:
- It varies depending on the welding location and cutting locations.
4. Usage classifications:
أ. لحام MIG/MAG:
- Used in argon or mixed gas welding operations.
b. TIG welding:
- Used in tungsten arc and gas welding processes.
19. Flexible cables:

Flexible cables are used in applications requiring frequent movement or bending, and are designed to withstand mechanical impacts without compromising their performance. Flexible cables vary in type, gauge, and size depending on the applications and environment in which they are used. Here’s an overview of some types, gauges, and sizes of flexible cable:
1. Types of flexible cables:
A. Rubber Cables:
- They are used in harsh environments where they are exposed to mechanical influences and difficult environmental conditions.
- Resistant to oils and chemicals.
b. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Cables:
- Used in light applications that are not exposed to extreme conditions.
- They are available at a lower cost and are used in less heavy duty applications.
t. Flexible Control Cables:
- Used in control systems where flexible movement and precise connection are required.
- Available in several gauges with different currents.
2. Flexible cable gauges:
A. Endurance current:
- Specifies the maximum electrical current that the cable can safely handle.
b. Voltage:
- Specifies the maximum operating voltage at which the cable can be used.
3. Flexible cable sizes:
A. Cable diameter:
- It affects the cable’s flexibility and endurance to movement.
b. Length:
- Depends on installation needs and system requirements.
4. Usage classifications:
A. For industrial applications:
- Used in factories and machinery where cables need to withstand periodic movement.
b. For medical applications:
- Used in the medical field where cables need high flexibility and tolerance to mechanical impacts.
20. Submarine cables:
Marine cables They are designed for use in the marine environment, where they are exposed to unique challenges such as salt water, strong mechanical influences, and thermal changes. These cables are used to connect and transmit data and power in marine applications. Here is an overview of some submarine cable types, gauges and sizes:
1. Types of submarine cables:
A. Marine power cables:
- Used to transmit electrical energy in the marine environment.
- It features improved insulation and corrosion protection.
b. Marine communication cables:
- Used to transmit signals and data in marine applications.
- They usually carry extra layers to protect against harsh environmental conditions.
t. Submarine fiber cables:
- It is used to transmit data using fiber optic technology in the marine environment.
- It is highly resistant to electromagnetic interference and environmental influences.
2. Submarine cable gauges:
A. Endurance current:
- Specifies the maximum current that the cable can safely handle.
b. Operating voltage:
- Specifies the maximum operating voltage that can be used for the cable.
3. Submarine cable sizes:
A. Cable diameter:
- It affects the cable’s resistance, flexibility, and tolerance to environmental conditions.
b. Cable length:
- Depends on connection locations and installation needs in the marine environment.
4. Usage classifications:
A. Underwater (Subsea):
- Used for underwater connections and applications.
b. On the surface:
- Used for water surface connections and applications.
21. Hardware cables:
Instrumentation cables refers to the cables used to connect electronic devices to each other or to the electrical network. Their types, gauges and sizes vary according to different uses and hardware requirements. Here’s an overview of some instrument cable types, gauges, and sizes:
1. Types of instrumentation cables:
A. Power cables:
- Used to connect devices to electrical power sources.
- They are available in different sizes and measurements depending on the needs of the device.
b. Data cables:
- Used to transfer data between devices, such as USB and HDMI cables.
- The type and size of the cable varies depending on the data type and connection requirements.
t. Audio and video cables:
- Used to connect devices to speakers or monitors.
- May include RCA cables, AUX cables, and HDMI cables.
2. Instrumentation cable gauges:
A. Endurance current:
- Specifies the maximum electrical current that the cable can safely handle.
b. Operating voltage:
- Specifies the maximum operating voltage that can be used for the cable.
3. Instrumentation cable sizes:
A. Cable diameter:
- It affects the cable’s ability to transmit current and data.
b. Cable length:
- Varies based on location and delivery needs.
4. Usage classifications:
A. Charging cables:
- Used to charge mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets.
b. Network connection cables:
- Used to connect devices to computer networks and the Internet.
t. Audio and video cables:
- Used to connect devices to audio systems and televisions.

If you have any inquiry, please contact us freely and we will be happy to serve you.

Gahzly website for purchasing electrical appliances
When we say Gahzly website, we are talking about one of the most famous Arab websites that was able, in a very short period of time, to achieve a very large demand for purchases from it by people from various parts and sectors of the Arab world.
On the Gahzly website, you will find a joint look and all the products that you may need in your home, starting with those for kitchens or bathrooms, but even those for gardens, you will find them on this wonderful site.
So, if you were lost before and did not know where to go to buy your products on the Internet, now you have the perfect solution, and all you have to do is go to the Gahzly website and start choosing the products you want.
 What are the features of Gahzly?
What are the features of Gahzly?
Since we are talking about a site that is preferred by many people around the world, there is no doubt that it is a site full of various features and characteristics. Therefore, we have decided to devote our next paragraph to pointing out the most prominent features of the Gahzly site.
One of the most prominent features of the site is the proportionality of prices. On the Gahzly website, you do not have to worry about the imaginary prices of the products, as is the case with most sites that display their products on the Internet.
The price of delivering products is very reasonable and not expensive, and the site accepts delivery to various countries, without forgetting that it accepts free shipping on some products.
One of the features of the site is also the high quality of its products, as it is impossible to find a poor quality product. Rather, the Gahzly website deals with the major companies, Philips, for example, and other famous brands, so you must remove from your mind the idea of the poor quality of one of the products. Another advantage of the site is that it does not specialize in one type of product, but rather you will find various types of products on it, for example, electrical appliances, hand tools, mechanical devices, paints, packages for establishing apartments, and many other types.
Gahzly website also accepts what is known as the shopping cart, which makes it easy for you to filter the products you want to buy and put them in one package in order to be able to pay with the click of a single button.
Accepts multiple payment methods.
We are pleased that you visit our social media pages, where we publish exclusive offers on our website.
Our Facebook page Here.
Our Twitter account Here.












Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.