DC Generator Maintenance Full Guide 2023
DC Generator Maintenance Full Guide 2023
 DC Generator Repair- All of your industrial AC & DC electric motor and generator repairs can be handled by several service providers; this includes anything from assets weighing 145 tons and rated to 15kV to small, fractional HP, low-voltage devices (690V).
DC Generator Repair- All of your industrial AC & DC electric motor and generator repairs can be handled by several service providers; this includes anything from assets weighing 145 tons and rated to 15kV to small, fractional HP, low-voltage devices (690V).
A thorough list of DC generator services for all OEM fleets is available on Gahzly’s website. Gahzly vendors can assist you with this. Please get in touch with DC Generators Experts to find out more about how to find a wide range of service providers who continuously deliver high-quality goods.
A DC generator needs MMF to create flux in its magnetic circuit. The MMF necessary to establish flux in a dc generator’s magnetic circuit is obtained through field excitation. A DC voltage applied to the field windings of a DC generator causes current to flow through the windings, producing a steady magnetic field. This phenomenon is known as field excitation. Manufacturers, distributors, suppliers from a wide range of industries, as well as Gahzly, who has a big assortment of DC Generators for Sale, are all able to provide DC generators.
A DC generator can only be evaluated through testing. Your emergency DC generator system will function and you will be prepared for a power outage if you test it frequently. If you work for a business that has a commercial-sized generator, please learn more about full-load bank testing services.
What is DC Generator Repair?
It’s time to schedule generator repair if you observe any of the following symptoms:
- Your generator’s electrical components are broken: Be careful to pay attention to the wiring, buttons, and other parts of your generator when inspecting it. Your generator certainly needs to be fixed if they show any signs of corrosion or wear. Wet weather has the potential to significantly damage these parts, which could lead to a power outage.
- Your generator leaks fuel: Leaks are more likely to occur in a generator that is beginning to age. These leaks can be coolant leaks, fuel leaks, or oil leaks, and they all work to keep your generator from overheating while it’s in operation. Make sure to thoroughly inspect the generator because leaks can happen practically everywhere. Pay particular attention to any puddles that have developed by the generator because they usually signal a leak. Be cautious if you discover any leaks because any substance that escapes could be dangerous.
- Your generator starts up slowly: Your generator shouldn’t start up slowly. Your generator needs to be serviced if it seems to be taking longer to start up than it used to. The battery is most likely the problem’s root cause because it can discharge after extended periods of inactivity.
- Your generator is physically damaged: Look for any damage that can be seen by looking at it, such as cracks, dents, or frayed wires. You would not think that a little scratch on your generator’s surface should cause much trouble, but it might have impacted the interior wiring. The performance of the generator could be impacted by even little dents or cracks.
Gahzly’s DC Generator Services provide the essential load-bank testing for commercial and industrial generators. This series of demanding tests are designed to put your generator through its paces and evaluate its performance. If there is even the slightest problem, your generator could operate poorly or perhaps stop functioning altogether in an emergency. DC Generator Experts at Gahzly can carry out these thorough examinations and resolve any problems that can prevent you from producing your maximum power.
At Gahzly, we can provide a lot of services for your DC generator. To track the operation of your DC generator, we can install monitoring equipment. When your generator takes an action or has a problem, these gadgets send you a text message and/or email to let you know. DC Generator Installation, DC Generator Repair & Maintenance, DC Generator Inspection, and several other services can be provided by Gahzly. To learn more about our 100% customizable notifications, get in touch with us today!
DC Generator Maintenance
An inspection, testing, cleaning, replacement, and lubrication plan are all included in a DC generator maintenance program, which is a preventative and corrective maintenance schedule that ensures the proper operation of D.C. motors and related equipment. Creating and implementing a maintenance program is quite simple. When routine maintenance checks are added to a shop’s work schedule, they quickly become apparent and produce cost savings that much outweigh the time and material costs incurred in maintaining them.
Maintenance Guide Summary
This maintenance manual will go through typical maintenance practices for the majority of DC generators. Before performing maintenance, the maintenance technician should consult the manufacturer’s technical documentation to ascertain the maintenance needs of a specific device. The following subsections comprise this section:
- Noise and Vibration Inspections
- Reviewing the Service History
- Windings Tests
- Visual Inspection
- Bearings and Lubrication
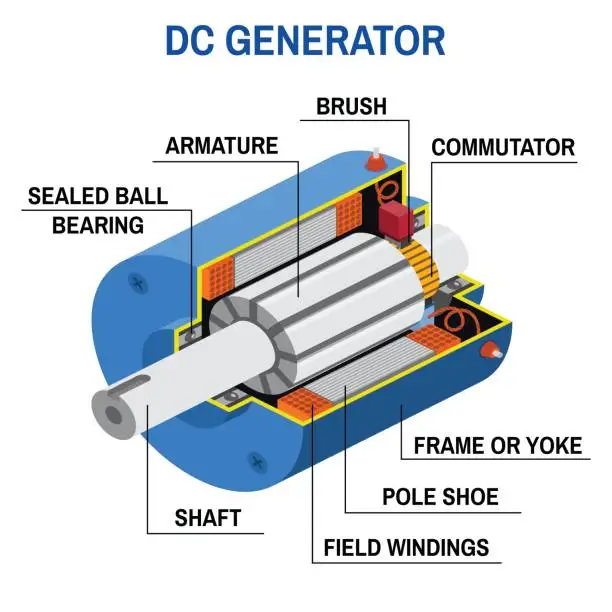
- Brush and Commutator Maintenance
Noise and Vibration Inspections
A noise and vibration inspection should be done before disconnecting the item and taking it to the shop or a repair facility for maintenance. For this, the motor must be activated, attached to its driving load, and used regularly (if possible). Mechanical noises or vibrations may be a sign of some issues, including electrical and/or mechanical imbalances, misalignments, brush chattering, bad bearings, bent shafts, mechanically loose windings (shaken loose by excessive vibrations, for example), a loose cooling fan, or something stuck in the vents or shroud. After it has been taken apart, inspect the lead and insulation for damage if the windings are loose. Excessive heat and brush sparking may also be caused by vibrations.
Electrical imbalances like open or shorted windings or unequal air gaps can produce noises or vibrations in addition to mechanical issues or imbalances. Power up the motor first, then cut power, to distinguish an electrical imbalance from a mechanical one. If the noise or vibration continues when the power is turned off, the issue is mechanical; if it stops when the power is turned back on, the issue is typically electrical.
Visual Inspections
Consult the manufacturer’s technical literature for suggestions on suggested inspection tests or procedures before disassembly. The information in this paper will help perform visual inspections.
Visual inspections are used to spot and document irregularities in a motor’s physical state while it is de-energized. A motor that looks dusty, rusted, or “beaten up” was likely used in a harsh environment and may be more problematic than typical. The “smell” test should be part of this assessment. Does the burning smell emanate from the motor windings? The insulation varnish on the motor windings is where the burnt smell is coming from. If so, there may be a problem with excessive heat. Under these circumstances, motor winding damage is probable, hence winding tests should be performed.
Overheating issues may not always be caused by the motor itself; instead, they may be the result of mechanical overloads like jams in the driven load or cold oil being pumped by a motor drive, running the motor at low speeds so that insufficient cooling airflow is present, electrical noise from DC drives heating the windings, or it may simply be the result of a dirty environment.
Since heat damage is the weakness of typical motor operating, dirt works as a heat insulator. Make that the cooling fan is working properly and that there are no obstructions in the channels. With a rag, wipe off all surfaces. Use a shop vac to blow out or vacuum the channels. Motor windings may be harmed by corrosion, which can also result in high-resistance wiring connections. If the winding tests show that winding damage has occurred, a motor rewind may be justified if the corrosion is persistent. It could also be necessary to re-plug the terminals on the motor connection box.
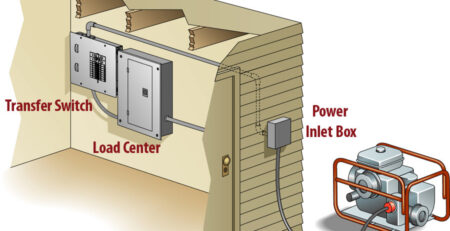
How to Test Your DC Generator
Do not be alarmed by a generator system. It is simple to perform periodic testing. In contrast to a portable generator, a home generator is directly attached to a power supply. The generator is then joined to the mainline circuit breaker. This main utility line may be located in a box outside, in the basement, or the garage when it enters your property.
- The incoming utility line will lose power when the main utility disconnect is flipped, requiring the generator to start.
- For distributing electricity throughout the home from an incoming utility or generated power, the transfer switch is the installation that is used the most frequently. The generator may run for a few seconds to a minute until the transfer switch clicks and power is distributed. This is because the transfer switch needs to verify that the generated electricity flowing in is stable.
- Give your generator some time to “work out” and “warm up.” It’s a good idea to check that the electricity has been fully restored by taking a walk around your home right now.
- Make sure to activate the mainline breaker after performing a test, then wait for the transfer switch to click and for the generator to restart.
Types of DC Generator Testing and Monitoring
If your building has an emergency generator, you should abide by these guidelines to maintain it operating properly. The following is a list of the standby generator testing requirements for each month and each year:
Monthly Type
A monthly test is performed on Level 1 and Level 2 generators. A generator classified as Level 1 is one whose failure could result in fatalities or serious injuries. A level 2 generator is one whose failure wouldn’t put lives in danger. During testing, a generator should run with the available load for at least 30 minutes. Successful testing occurs when the generator:
Reaches the minimum exhaust gas temperature necessary for the owner’s manual’s recommended monthly testing or operates at a minimum of 30% of the nameplate kilowatt rating while ordinarily operating.
A generator should only be tested for a brief period until its water and oil pressures have stabilized to avoid prolonging its downtime.
Yearly Type
If a generator fails the monthly test, it must be tested annually with a load provided by a load bank for two nonstop hours. During the two hours, the gadget should be utilized as follows:
- At 75% of the nameplate Kilowatt rating for 60 minutes.
- At 50% of the nameplate Kilowatt rating for 30 minutes.
- At 25% of the nameplate Kilowatt rating for 30 minutes.
The “training” offered by load bank testing can increase a generator’s operational capacity and make it more responsive during a real power outage.
Monthly and annual checkups are essential, but they shouldn’t be the only ones performed to ensure generators are prepared for power outages.
In addition to NFPA 110 emergency generator testing, building owners should make sure that their generators receive routine maintenance, yearly infrared scanning, modernization, and retrofitting, as needed. The efficiency of a generator can be assessed, but maintaining or increasing it necessitates a multidimensional approach that includes the aforementioned measures. For more information about DC generator repair, maintenance, and testing, visit this video.
DC Generators: Maintenance Tips for DC Generators to Ensure Maximum Reliability 2023
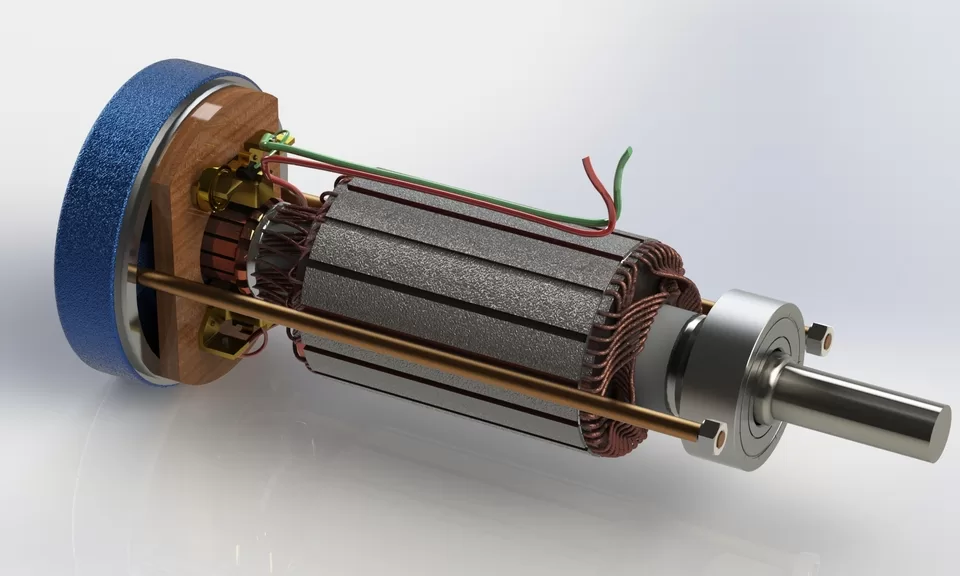
DC generators, also known as direct current generators, are devices that convert mechanical energy into direct current (DC) electricity. These generators are widely used in a variety of applications, including automobiles, power tools, and backup power systems.
However, like any mechanical device, DC generators require regular maintenance to ensure they continue to operate at optimal levels. In this article, we will discuss the importance of maintenance for DC generators, and provide tips and best practices to ensure maximum reliability.
Our purpose is to help you understand how to maintain your DC generator so that you can prolong its lifespan and avoid costly repairs.
Types of DC generators
DC generators, also known as direct current generators, come in a variety of types, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. In this section, we will discuss the three main types of DC generators: series generators, shunt generators, and compound generators.
| Type of Generator | Armature Winding | Field Winding | Voltage Output | Current Output | Applications |
| Series Generator | Series | Series | High | Fluctuating | High voltage applications |
| Shunt Generator | Parallel | Parallel | Constant | Fluctuating | Constant voltage applications |
| Compound Generator | Series & Parallel | Series & Parallel | High and Constant | Fluctuating | High and Constant voltage applications |
Series Generators: Series Generators have a high internal resistance and are used in applications where a high voltage is required. The armature windings in these generators are connected in series with the field windings, which results in a high voltage output. The high internal resistance also causes the output voltage to fluctuate with changes in the load.
Shunt Generators: Shunt Generators have a low internal resistance and are used in applications where a constant voltage is required. The armature windings in these generators are connected in parallel with the field windings, which results in a constant voltage output. However, the low internal resistance means that the output current will fluctuate with changes in the load.
Compound Generators: Compound Generators combine the characteristics of series and shunt generators to provide both a high voltage and a constant voltage. These generators have both series and shunt windings in the armature, and the output voltage is determined by the combination of the two. Compound generators are commonly used in applications where both a high and constant voltage are required.
It’s important to note that regular maintenance and proper usage are important to keep DC generators working at optimal level. Consulting with the manufacturer’s recommendations and seeking professional help if needed, can ensure the longevity and reliability of the generator.
When choosing a DC generator, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of your application. The table above provides a quick comparison of the different types of generators and their applications. It’s also important to consult the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure that the generator you choose will meet your specific needs.
Maintenance tips for DC generators
To ensure the longevity and reliability of your DC generator, it is important to perform regular maintenance and follow best practices. In this section, we will discuss a variety of maintenance tips for DC generators, including:
- Regular inspections,
- Cleaning and lubrication,
- Electrical testing,
- Cooling system maintenance,
- Brush and commutator maintenance,
- Generator load testing.
Regular Inspections:
Regular inspections are crucial to maintaining the overall health of your DC generator. During an inspection, you should check for any visible signs of wear or damage, such as frayed wires or loose connections. You should also check the oil levels and look for any signs of leaks. It is recommended to have a regular inspection schedule, depending on usage and environmental factors.
Cleaning and Lubrication:
Cleaning and lubrication are important to keep your DC generator running smoothly. Dirt and debris can accumulate on the exterior of the generator and in internal components, which can cause problems if not removed. Lubricating the moving parts of the generator will help to reduce friction and wear. It is recommended to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific lubrication requirements.
Electrical Testing:
Electrical testing is necessary to ensure that your DC generator is producing the proper voltage and amperage. Testing the generator’s output will help to identify any problems with the electrical system and to determine if any repairs or adjustments are needed.
Cooling System Maintenance:
The cooling system is crucial for preventing overheating in your DC generator. It is important to keep the cooling system clean and free of debris. You should also check the coolant levels and make sure that the system is functioning properly.
Brush and Commutator Maintenance:
The brush and commutator are key components in the electrical system of your DC generator. They need to be kept clean and properly lubricated to ensure optimal performance. The commutator should also be checked for any signs of wear or damage, and the brushes should be checked for proper alignment.
Generator Load Testing:
Load testing your DC generator is necessary to ensure that it is capable of handling the load it is expected to carry. The generator should be tested under different load conditions to determine its overall performance and to identify any potential problems. It’s recommended to consult the manufacturer’s instructions for load testing your generator.
Regular maintenance and proper usage are crucial for the longevity and reliability of your DC generator. By following these maintenance tips and consulting with the manufacturer’s recommendations, you can ensure that your generator continues to operate at optimal levels.
Troubleshooting common problems
Despite regular maintenance, DC generators may still experience problems from time to time. In this section, we will discuss some common problems that can occur with DC generators and provide tips for troubleshooting them. The common problems are:
- Voltage regulation problems
- Overheating
- Loss of power
- Abnormal noises
To help you understand these problems and their solutions better, I have also included a table which lists the common causes and solutions for each problem.
| Problem | Common Causes | Solutions |
| Voltage Regulation Problems | Loose connections, worn out brushes, damaged voltage regulator | Check and tighten all connections, replace worn out brushes, replace damaged voltage regulator |
| Overheating | Dirty or clogged cooling system, low coolant levels, malfunctioning thermostat | Clean and flush the cooling system, refill coolant, replace malfunctioning thermostat |
| Loss of Power | Low battery voltage, loose or corroded connections, worn out brushes | Charge or replace the battery, check and tighten all connections, replace worn out brushes |
| Abnormal Noises | Loose or worn out parts, poor lubrication | Tighten all connections, replace worn out parts, lubricate all moving parts |
Voltage Regulation Problems: Voltage regulation problems can occur when the generator’s voltage is not being regulated properly. This can be caused by loose connections, worn out brushes, or a damaged voltage regulator. To troubleshoot this problem, you should check and tighten all connections, replace worn out brushes, and replace a damaged voltage regulator if necessary.
Overheating: Overheating can occur when the generator’s cooling system is dirty or clogged, the coolant levels are low, or the thermostat is malfunctioning. To troubleshoot this problem, you should clean and flush the cooling system, refill coolant, and replace a malfunctioning thermostat if necessary.
Loss of Power: Loss of power can occur when the generator’s battery voltage is low, the connections are loose or corroded, or the brushes are worn out. To troubleshoot this problem, you should charge or replace the battery, check and tighten all connections, and replace worn out brushes if necessary.
Abnormal Noises: Abnormal noises can occur when the generator’s parts are loose or worn out, or the moving parts are not properly lubricated. To troubleshoot this problem, you should tighten all connections, replace worn out parts, and lubricate all moving parts as necessary.
It is important to note that regular maintenance and proper usage are important to keep DC generators working at optimal level. Consulting with the manufacturer’s recommendations and seeking professional help if needed, can ensure the longevity and reliability of the generator.
The above table provides a quick reference for common problems and solutions. However, it’s always recommended to consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide or seek professional help if you’re unsure about anything.
FAQs
Q: What are the different types of DC generators?
A: The three main types of DC generators are series generators, shunt generators, and compound generators. Series generators have a high internal resistance and are used in applications where a high voltage is required.
Shunt generators have a low internal resistance and are used in applications where a constant voltage is required. Compound generators combine the characteristics of series and shunt generators to provide both a high voltage and a constant voltage.
Q: How often should I perform maintenance on my DC generator?
A: It is recommended to have regular maintenance schedule for your DC generator, depending on the usage and environmental factors. It’s best to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for the specific maintenance schedule for your generator.
Q: What are some common problems that can occur with DC generators?
A: Some common problems that can occur with DC generators include voltage regulation problems, overheating, loss of power, and abnormal noises. These problems can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor maintenance, worn out parts, and environmental factors.
Q: How can I troubleshoot common problems with my DC generator?
A: Troubleshooting common problems with a DC generator typically involves performing regular inspections, cleaning and lubrication, electrical testing, and load testing. It’s also helpful to consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide and if needed, seek professional help.
Conclusion
DC generators are essential devices that convert mechanical energy into direct current electricity. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure their longevity and reliability. This article has provided an overview of the different types of DC generators, their applications and the importance of maintenance.
We also provided tips for regular inspections, cleaning, lubrication, electrical testing, cooling system maintenance, brush and commutator maintenance, generator load testing and troubleshooting common problems. It’s important to note that regular maintenance and proper usage are important to keep DC generators working at optimal level.
Consulting with the manufacturer’s recommendations and seeking professional help if needed, can ensure the longevity and reliability of the generator. For more information and resources, it’s recommended to consult the manufacturer’s manual, user guide, or seek professional help.
Don’t hesitate to take action and start maintaining your DC generator today for maximum reliability in 2023 and beyond.
Summary
Although it is recommended that you test your DC generator twice a year, you can do so whenever you need to. Conducting a test before hurricane season or a major storm can be useful. So that you have it, make a note of your test in a notebook. If you experience any problems, get in touch with a residential generator specialist for a more thorough test and inspection.
electric fuse
We are pleased to have you visit our pages on social networking sites,
where we publish exclusive offers on our website.
Our Facebook page here .
Our Twitter account is here .










Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.