Contents
Electrical cable components
Electrical cable components play an important role in ensuring the proper performance and safety of the cable. Electrical cables must be made of high-quality materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, humidity, and other environmental conditions. Electrical cables consist of several components, each serving a specific purpose. These components include:- Conductor : It is the core and most important component of electrical cables. It is usually made of copper or aluminum, which transmits electrical current from the power source to the load.
- Insulators : Protect electrical wires and cables from contacting each other, as well as the ground. Common materials used for insulation include PVC, rubber, and Teflon.
- Shielding : Shielding is used to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) from affecting the electrical signals being transmitted through the cable.
- Sheath : The sheath is an essential layer for protecting cables because it prevents damage caused by corrosion and other environmental factors. Common materials used for jackets are PVC, nylon or rubber.
- Drain Wire : A small, bare copper wire used to ground the shield, providing a path for a static charge that can build up on the shield.
Types of electrical cables and their sizes
Each type of electrical cable has its specific uses and advantages, and the choice of cable depends on the transmitted voltage, the required current carrying capacity, and the specific requirements of the environment in which the cable is installed. Some of the most common electrical cables and types include: 1 . Copper cables : Commonly used in electricity and power distribution industries because they have great conductive properties and low resistance rating. 2 . Aluminum cables : Their use in transmission and distribution of electricity has become more common. This is because they are lighter and better in budget compared to copper cables, but they have lower conductivity and higher resistance than their counterpart also called armored cables.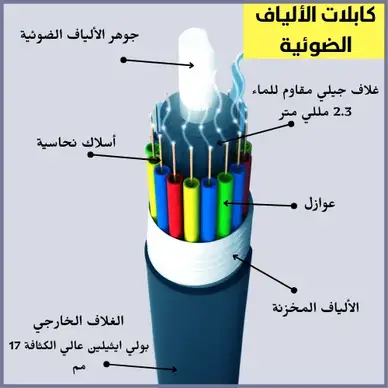
3 . Fiber optic cables : They are essential in sending optical signals over long distances. Made of glass or plastic, they have become indispensable for a variety of tasks and applications, such as high-speed data transfer and communications as well as industrial and military uses.
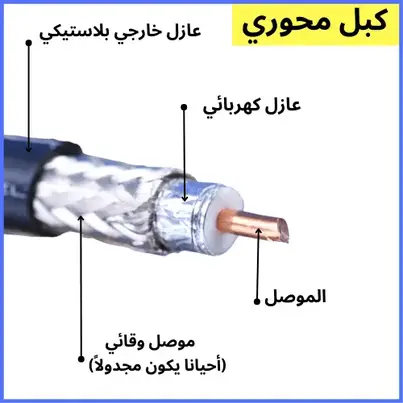
14 . Coaxial cable : Used for a variety of high-frequency tasks, such as television and radio broadcasting, and is also used to transmit data. Coaxial cables consist of a central conductor surrounded by insulating material, a metal shield, and an outer jacket.
Electrical cable sizes and sizes
Electrical cable size is the maximum amount of electrical current that the cable can safely carry without overheating. This rating is usually stated in amperes (Amperes), and is determined by conductor size, insulation type, and operating temperature. Electrical cables come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and it is important to understand these differences when choosing the right cable for your project. Knowing the size of cable you need and its current rating is essential to ensuring your electrical system operates safely and efficiently. The cable size is represented by a number that corresponds to the cross-sectional area of the conductor which is square millimeters (mm2). Common mm2 sizes range from 1.5mm2 to 500mm2.What are square millimeters (mm2)?
Square millimeters (mm2) is a metric unit used to determine the cross-sectional area of electrical conductors. The larger the mm2, the greater the cross-sectional area of the conductor, and the greater the electrical current it can carry. For example, a conductor with a cross-sectional area of 1.5 mm2 can carry a maximum current of 15 A, while a conductor with a cross-sectional area of 16 mm2 can carry a maximum current of 95 A. These are all examples of mm2 sizes and their corresponding current carrying capacities:| Cross-sectional area in: mm2 | Maximum current in amps | Cross-sectional area in: mm2 | Maximum current in amperes |
| 1.5 mm2 | 13 amps | 120 mm2 | 877 amps |
| 2.5 mm2 | 21 amps | 150 mm2 | 1088 amps |
| 4 mm2 | 33 Ampere | 185 mm2 | 1334 Ampere |
| 6 mm2 | 48 | 240 mm2 | 1721 |
| 10 mm2 | 77 | 300 mm2 | 2144 |
| 16 mm2 | 124 | 400 mm2 | 2880 |
| 25 mm2 | 195 | 500 mm2 | 3650 |
| 35 mm2 | 259 | 630 mm2 | 4620 |
| 50 mm2 | 385 | 800 mm2 | 6000 |
| 70 mm2 | 531 | 1000 mm2 | 7500 |
| 95 mm2 | 719 |
Important factors when choosing an electrical cable
Choosing the right electrical cable is an important decision that can have a significant impact on the safety, performance, and longevity of your electrical system. There are many factors to consider when choosing an electrical cable, such as:- Know the cable voltage rating and rating.
- Level of insulation material.
- Gauge of wire or conductors.
- Size and weight.
- The current or current carrying capacity of the cable.
- Evaluate the temperature it can withstand.
- Withstand the environmental conditions in which it will be used.
- Consider cable length and orientation when choosing it.
- The cost of the cable should be considered when choosing.
- The cable must meet national electrical codes and standards.
The difference between electrical cables and wires
Electrical cables and wires are among the most important components of any electrical system. Therefore, many confuse these two terms, but they differ in their understanding and design, and their construction and purpose remain different. Find out the differences in the following table:| Cables | Wires |
| – Electrical cables consist of one or more insulated conductors. | – Wiring consists of a single conductor, usually uninsulated. |
| – Cables are used for high voltage applications such as power distribution and high current. | – Used for low voltage applications such as connecting components in a circuit. |
| – Electrical cables consist of several wires bundled together and covered with an insulating material. | Wires are single cylindrical conductors used to transmit electrical current. |
| – Cables are thicker than wires, allowing them to carry more current over longer distances. | - Made of metal, such as copper or aluminum. |
Colors of electrical cables
Different colors of cable are often used to indicate different functions and to make it easier to understand and trace the types of wires, but they are not standardized and the understanding of their colors may vary from country to country. Here are some common color codes used for electrical wires:- Black and red: hot wire.
- White: White is used for neutral wires.
- Green: ground wire