Wind energy and how to use it to generate electricity 1
Wind energy and how to use it to generate electricity
A search for wind energy. Wind energy is classified as one of the types of renewable energy sources because it relies on the wind source instead of using fossil fuel sources, oil and natural gas. These sources are harmful to the environment because of the toxic gases they produce when burned, in addition to being available only in limited areas. In the world.
Where the importance of using wind energy in European countries and America came to reduce dependence on traditional energy sources and reduce environmental pollution and costs.

What is energy
Energy means (English: energy) in the science of physics the ability to do something by converting energy from one form to another to produce different forms of energy such as: converting energy into electrical, thermal, radiation, nuclear or chemical energy, whose work depends on kinetic energy or energy lurking.
Definition of wind power
Wind energy is defined as a source of transformable energy, which results from exploiting the movement of wind and converting it into another form of energy such as electricity energy, where its work relies on the movement resulting from the wind in generating electrical energy by moving wind turbines. Mechanical energy, which in turn is converted into electrical energy. Wind energy is one of the renewable energy sources, which is used as an alternative source to traditional energy sources.
uses of wind energy
Wind energy has been used since ancient times at the level of different civilizations, as the ancient Egyptians used this energy to run their boats on the Nile River in Egypt, and the Muslims used it to grind various grains, while the Chinese exploited it to pump groundwater in particular.
As for the Arab countries, there are no development studies on increasing reliance on this energy to generate electricity, and the weakness of cooperation and coordination between countries has led to weak reliance on this energy and other renewable and non-polluting energy sources.
The idea of wind energy to generate electricity
The idea of its work depends on the kinetic energy of the wind through the rotation of the blades that are installed on the turbine, which is installed on a hub that is based on the main rotating shaft connected to a gear box to raise the rotational speed, as the movement is transmitted to the fast rotating shaft, and its rotation cuts off a magnetic field inside the generator, which results in the generation of electricity, and thus During which we can provide electricity in all public and private places.
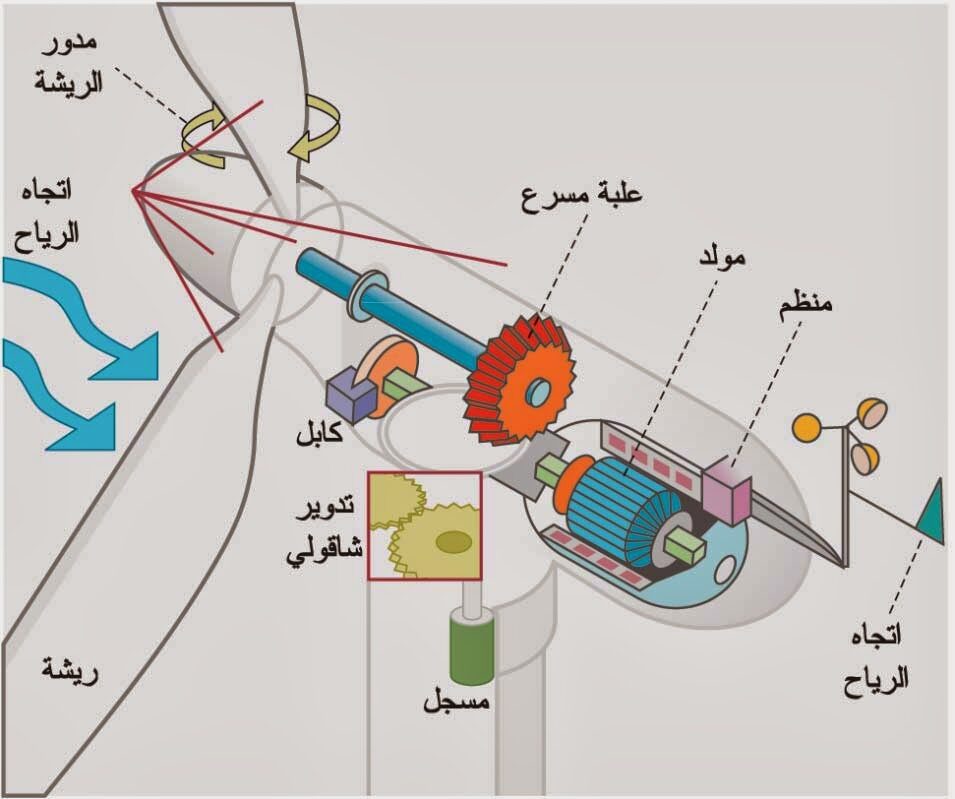
Advantages of wind energy
- Its low cost compared to other traditional energy sources.
- Contribute to providing job opportunities, raising the economy and reducing oil consumption.
- You don’t need equipment to drill like fossil fuel sources.
- Sustainable and inexhaustible energy.
- It does not need any kind of raw fuel sources during its operation like thermal stations.
- Wind energy is a clean and non-polluting resource.
- Contribute to reducing carbon dioxide emissions.
- It can be used in many different applications.
Disadvantages of wind energy
- You need very large spaces.
- You need a place with high wind speed and relatively moderate.
- Makes noise throughout the day.
- Winds are not always available to move the mills but are seasonal.
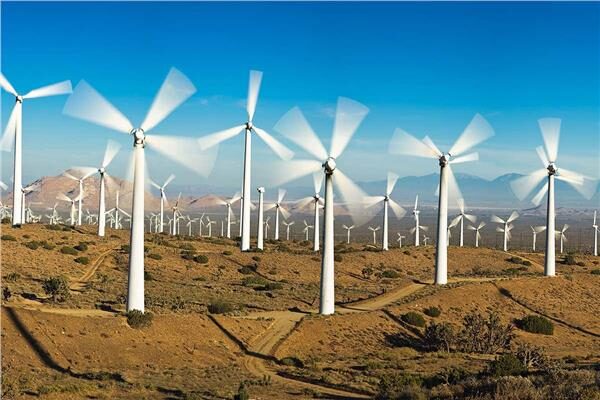
How do wind turbines work?
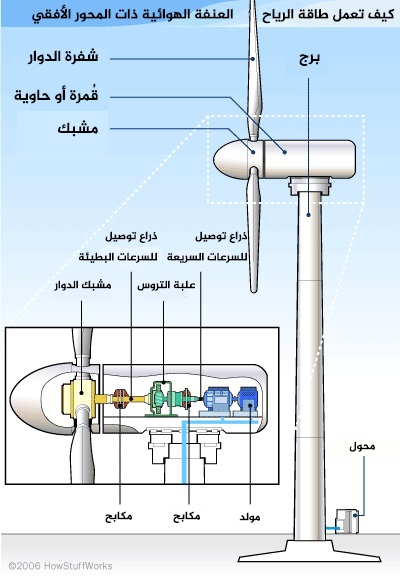
How do wind turbines work? Wind energy is one of the ways to generate electricity, and it is classified as an environmentally friendly renewable energy resource.
In this article, we will discuss how wind turbines work, and what is the best place to place the field?
How do wind turbines work?
A wind turbine contains rotating blades that are mounted on a shaft and a generator that converts the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical energy.
When the wind passes over the blades, it creates a dynamic air impulse that causes the blades to rotate. Thus, the generator operates, which produces electrical energy. These turbines are equipped with a device that controls the rotation of the blades to regulate their rotation rates and stop their movement if necessary.
The amount of energy produced from wind turbines depends on the wind speed and the diameter of the blades. That is why the turbines that are used to operate factories or lighting units are placed above the towers. Because wind speed increases with height above the ground, these turbines are placed in large numbers on large areas of land to produce as much electricity as possible.
Here is an example of a field around the world. The United States alone produces about 3 billion kilowatt-hours annually, and that amount is enough to meet the electricity needs of a million people, from wind fields located in California on the west coast of America.
Where is the best place to put wind turbines?
It is preferable to place wind turbines in a place where the average annual wind speed should not be less than 12 miles per hour, as most wind fields are located inside the water, and they are called offshore farms, as wind speeds are higher than on land.
And because there are times when the wind speed is slow, which makes it difficult to produce electricity, wind energy users must have a backup diesel or solar generator to use at those times.
We hope that you have been satisfied with what was presented for the work of wind energy turbines. If you have any questions, leave us a comment.
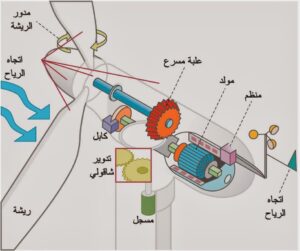
Components of a wind power plant
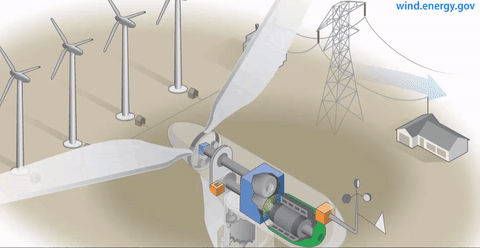
Components of the wind power plant. Each generating station has its own components. The plants that depend on wind energy contain blades, a box and a turbine, while solar power plants consist of panels and inverters.
In this article, we will get a quick look at the source of wind, and then mention the basic components of wind power plants.
A quick look at the source of the wind
Winds are generated as a result of the absorption of sunlight by the surfaces of the earth, seas and oceans, and thus the temperature of these surfaces rises by different degrees.
When the air heats up, this leads to a decrease in its density, and accordingly, the air moves from the high pressure area to the reduced pressure area, which leads to the emergence of winds.
Windmills have spread since the twelfth century until their number reached in the year 1750 AD to more than 8,000 mills in the Netherlands, and more than 10,000 mills in England,
The main purpose of its work at the time was to pump water from low areas to higher agricultural areas, or to manage stones for grinding wheat, corn, and other grains.
Components of a wind power plant
The generating fan consists of the following elements:
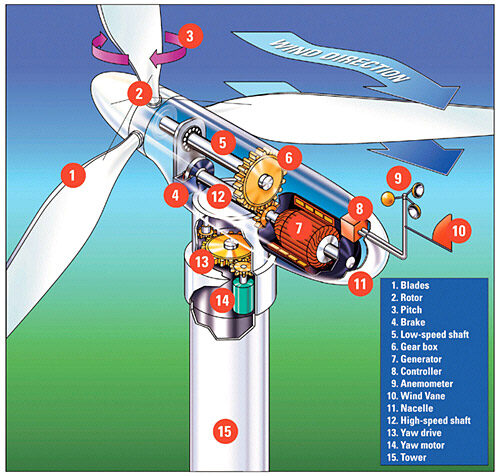
Turbine blades
The blade length reaches 20 metres, and in newer variants such as the 5-mega unit, the turning radius exceeds 130 metres.
Gearbox
Gears connect:
- The slow speed transducer on which the blades are mounted, rotates at about 30 RPM.
- The high speed shaft is the one that connects directly to the generator and rotates at a speed of 1500 rpm.
Cabin Room (Nacelle)
It includes the generator and the gears, as it is the housing for all the equipment, and it also includes the equipment that controls the vanes (blades), as it can change the inclination angle of the vane with respect to the wind by means of a motor, and thus controls the rotational speed, which in revolutions per second is affected by the wind speed, which must not be less than 5 meters per second, and it should not exceed 30 m/s.
Generator
The generator capacity ranges from 500 to 1500 kilowatts, and some generators have now reached 3, 5, 6, 7 megawatts, and more.
Power transmission transformer
The transformer of the unit transmits the power with a distribution voltage of about 24 kV through cables, and it is assembled with the other units, and then lifted to the transmission lines, and each unit is not connected directly with the transmission lines.
maternity tower
All equipment except the transformer is installed at the top of the generation tower, which is made of steel and has a height of 40 to 60 meters, and at the present time the height exceeds 140 meters, with capacities of 5 mega.
The tower is made of heat-treated iron to bear all the components of the container, which weighs up to 30 tons.
To ensure the maximum possible use of wind energy, a system is used to direct the turbine in the direction of the wind. If the wind speed rises above 25 meters/second, the brakes prevent the blades from rotating, lest the high wind speed lead to their shattering and breaking of the rotating parts in the container.
Factors affecting the production of electricity from wind
Factors Affecting the Production of Electricity from Wind There are several important factors affecting generation plants that depend on wind energy.
Follow the article with us to learn about the most important factors that affect the productivity of power plants that operate by one of the natural resources, which is the source of wind energy.
Factors affecting the production of electricity from wind
There are several factors that affect the productivity of electric energy by converting wind energy into kinetic energy, and then into electrical energy. Some of these factors are:
- Wind speed.
- rotational surface area.
- Feather speed ratio.
We will explain each factor separately.

Effect of wind speed on turbine
The production of wind turbines is directly affected by the wind speed, as the energy produced is proportional to the cube of the speed. To illustrate this relationship, we give the following example:
If the wind speed is 5m/sec, the resulting energy is approximately 125 energy units, while if the speed increases to 6m/sec, the resulting energy increases to 216 energy units.
What we can conclude from the example is that an increase in the wind speed by 1 meter/sec led to a significant increase in the energy produced. In this regard, the energy produced from turbines is affected by several other factors, including:
- air density.
- Tower height.
- rotational surface area.
- The effect of repentance on each other.
However, the direct and largest impact of the generation system is with wind speed.
rotational surface area
The rotation surface area expresses the area resulting from the rotation of the blades, which is determined by the length of the blade, and the volume of air that strikes the plane of rotation. The rotational surface area is also called the diameter of the turbine.
Feather speed ratio
It is the ratio between the speed at the end of the vane and the speed of the wind, which increases with the increase in the length of the vane, and determines its optimal limits between 60-80.
The work of the turbine depends on the wind speed to manage the rotor according to the aerodynamic forces, and this movement is transmitted to the generator through two axes and a speed gearbox (the slow speed axis and the high speed axis), and the transmission ratio of the gearbox determines the speed that will reach the generator.
The amount of energy generated by the wind
The amount of energy generated by the wind depends entirely on the kinetic energy of the air, which is directly proportional to the mass of the air and its speed, and the following equation shows this in terms of the area of the fan and the density of the air as follows:

The relationship between the power produced by the turbine and wind speed

The relationship between the power produced by the turbine and the wind speed, it is important to know the relationship between the power output of the wind power turbine and the ambient air speed.
In this article, we show you a detailed and simplified explanation of the relationship between the power generated by the turbine and the wind speed.
A quick overview of the turbine’s relationship to wind speed
Some may think that once a fan is made and placed on the roof of the building, it will produce constant electrical energy, or that this design is practical and completely similar to the fields that you see in wind power plants.
This belief is wrong, because all fields of wind power plants are studied with high accuracy by experts specialized in this field at the scientific and practical level, and simulations are made by special programs before starting implementation to ensure the efficiency of the system.
Since the wind speed is variable, you will need control systems in order to deal with the change and maintain a constant speed of the turbine to keep it from high speeds, and to keep the turbine operating within the operating safety limits.
In sum, it is not possible to design, install, or choose the appropriate location except after conducting highly qualified studies and with the help of specialists in the field of wind energy, because every step that you will take affects the final result, whether it will be successful or not.
The relationship between the power produced by the turbine and wind speed
Without dwelling on the topic, note the curve that shows the relationship between power output and wind speed.

You notice that the curve is divided into three parts: the Cut-in area, the Rated Speed area, and the Cut-Out area, as the operating area of the turbine between the Cut in Speed and the Cut out Speed is within the limits allowed by its capacity and keeps it within operating safety limits, and helps in maintain its structure.
As shown in the curve, the first and second region when the wind speeds are low, the blades are adjusted to obtain the greatest power, while in the third region and at high speeds that are above the nominal wind speed on which the turbine is designed, the blades are modified to reduce the effect of wind speed and preserve the turbine from high speeds.
Advantages of placing wind turbines offshore
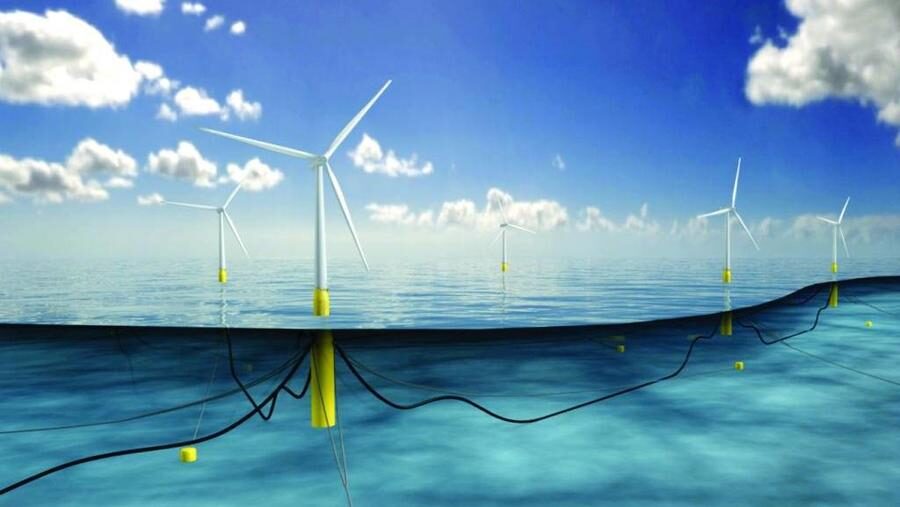

Advantages of placing wind turbines in the sea Some may ask about the repercussions that led to the preference for building wind turbines in the sea instead of on land.
In this article, we will learn about the direct reason behind the preference for building wind turbine plants in the sea? And what are the main advantages that we get behind the implementation of this.
Contents
Reasons for preferring offshore wind turbines
Offshore winds tend to flow faster and more forcefully than winds on land, because the roughness of the sea surface is less than on land, and the wind blowing obstacles are less, which allows wind turbines to generate more electricity.
As we know that the energy extracted from the wind is proportional to the cube of the wind speed, any small increase in the wind speed can achieve a significant increase in the electrical energy generated.
For example, a wind turbine located at a location with a wind speed of 16 mph (7 meters per second) produces 50% more energy than the same turbine located at a location with a wind speed of 14 mph (6 meters per second).

Advantages of placing wind turbines offshore
Low audio noise
During its operation, the turbines produce an annoying sound that causes problems for people who live in the vicinity of the wind station, and some farmers are affected by the fact that their livestock is affected by the noise emanating from the blades of the wind turbine.
For this reason, you find that placing turbines in the sea, away from residential communities and populated areas, is the best and best solution in all cases.
It does not pose a threat to the life of migratory birds
Turbines located on land may cause birds to collide with their moving blades throughout the day, and the problem was solved by establishing wind stations far from bird migration areas, as birds rarely fly over the oceans.
There are many other features such as:
- The strength and speed of the offshore wind flow from land.
- The energy extracted from the wind is proportional to the cube of the wind speed, so a slight increase in the offshore wind speed increases the percentage of electrical energy productivity.
- Exploitation of the sea space.
Disadvantages of placing wind turbines offshore
There is only one drawback to building wind turbines in the seas, which is the initial cost, as the cost of the energy generated from these turbines can be about two to three and a half times higher than those on land.
In this regard, wind turbines in the sea are still under development and cost reduction, noting that the high cost is related to installation and maintenance work conditions, which require the use of special ships to be installed in sea water.
We hope that you are satisfied with the advantages of offshore wind turbines being demonstrated.
 If you have any questions, please contact us freely and we will be happy to serve you.
If you have any questions, please contact us freely and we will be happy to serve you.
We are pleased to have you visit our pages on social networking sites, where we publish exclusive offers on our website.
Our Facebook page here .
Our Twitter account here .














Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.