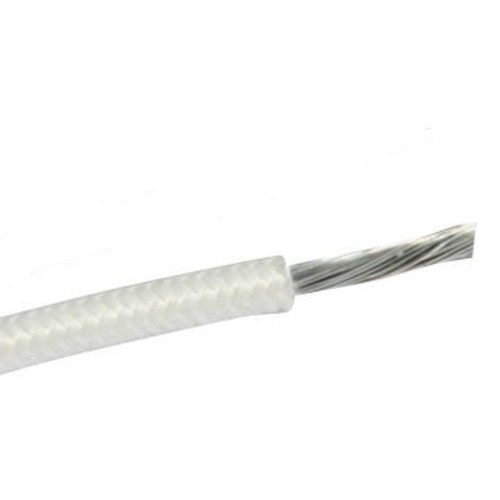
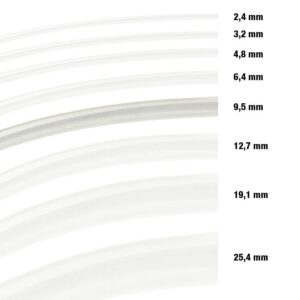
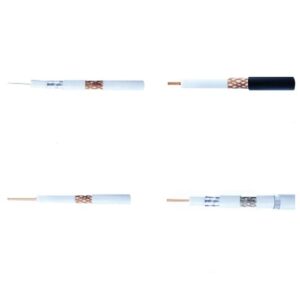
Fiberglass Cable Elcab Tinned Copper White
Price range: 2.343,00 EGP through 19.910,00 EGP
-
Fiberglass Cable Elcab Tinned Copper White
- Product or component type: power cord
- Colors: white
- Material: plastic
- AC at 50 / 60 Hz
- IP protection grade: IP20
- Age: long life